Pasos para recrear la imagen del controlador APIC a través del servidor HTTP
Opciones de descarga
-
ePub (1.2 MB)
Visualice en diferentes aplicaciones en iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader o Windows Phone -
Mobi (Kindle) (698.5 KB)
Visualice en dispositivo Kindle o aplicación Kindle en múltiples dispositivos
Lenguaje no discriminatorio
El conjunto de documentos para este producto aspira al uso de un lenguaje no discriminatorio. A los fines de esta documentación, "no discriminatorio" se refiere al lenguaje que no implica discriminación por motivos de edad, discapacidad, género, identidad de raza, identidad étnica, orientación sexual, nivel socioeconómico e interseccionalidad. Puede haber excepciones en la documentación debido al lenguaje que se encuentra ya en las interfaces de usuario del software del producto, el lenguaje utilizado en función de la documentación de la RFP o el lenguaje utilizado por un producto de terceros al que se hace referencia. Obtenga más información sobre cómo Cisco utiliza el lenguaje inclusivo.
Acerca de esta traducción
Cisco ha traducido este documento combinando la traducción automática y los recursos humanos a fin de ofrecer a nuestros usuarios en todo el mundo contenido en su propio idioma. Tenga en cuenta que incluso la mejor traducción automática podría no ser tan precisa como la proporcionada por un traductor profesional. Cisco Systems, Inc. no asume ninguna responsabilidad por la precisión de estas traducciones y recomienda remitirse siempre al documento original escrito en inglés (insertar vínculo URL).
Introducción
Este documento describe cómo recrear imágenes del Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) con la ayuda del servidor HTTP.
Prerequisites
Requirements
- Cisco Integrated Management Controller (CIMC) debe configurarse con una dirección IP OOB.
- Compruebe las notas de la versión de APIC y confirme con qué imagen de software de APIC necesita volver a crear la imagen.
- Obtenga la imagen del software en software.cisco.com.
- Confirme que la suma de comprobación MD5 de la imagen coincida con la publicada en Cisco.com.
- Cargue la imagen APIC en el servidor HTTP.
Componentes Utilizados
Este documento no tiene restricciones específicas en cuanto a versiones de software y de hardware.
La información que contiene este documento se creó a partir de los dispositivos en un ambiente de laboratorio específico. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si tiene una red en vivo, asegúrese de entender el posible impacto de cualquier comando.
Antecedentes
En caso de que se produzca un fallo en un clúster APIC o una migración de hardware de L2/M2 a L4/M4, los dispositivos APIC individuales pueden necesitar una recreación de imágenes para restaurar la funcionalidad. Este procedimiento describe un enfoque simplificado para recrear imágenes de APIC uno por uno mediante un servidor HTTP que facilita una recuperación más rápida del clúster con las mínimas interrupciones.
Repita el proceso de forma secuencial para cada dispositivo APIC que necesite recreación de imágenes. Una vez que se hayan recreado todas las APIC, restaure la configuración del clúster según sea necesario y realice pruebas exhaustivas para validar la funcionalidad.
Este conciso procedimiento permite una recuperación eficaz de APIC, lo que permite a los administradores solucionar rápidamente las averías de los clústeres y restaurar las operaciones de red de forma eficaz.
Solución
Para volver a crear una imagen del APIC mediante un servidor HTTP, es necesario realizar los pasos siguientes.
Paso 1.Descargue el firmware del sitio web de Cisco.
Abra software.cisco.com/download.
Paso 2. Introduzca APIC y seleccione aquí la versión adecuada para ACI; en este caso, se selecciona 4.2(7F).
Por ejemplo:
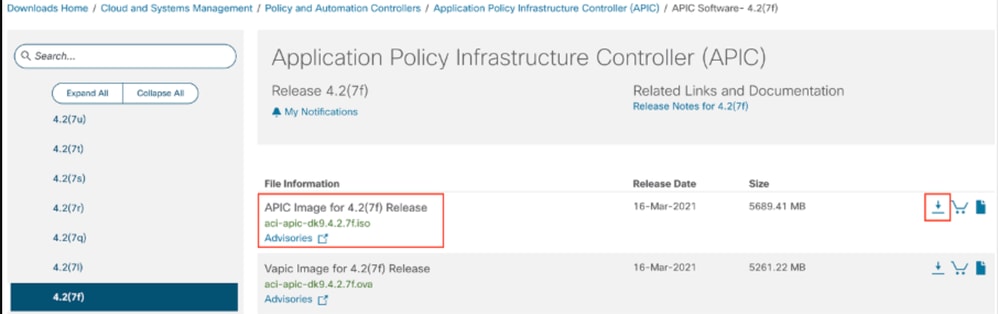
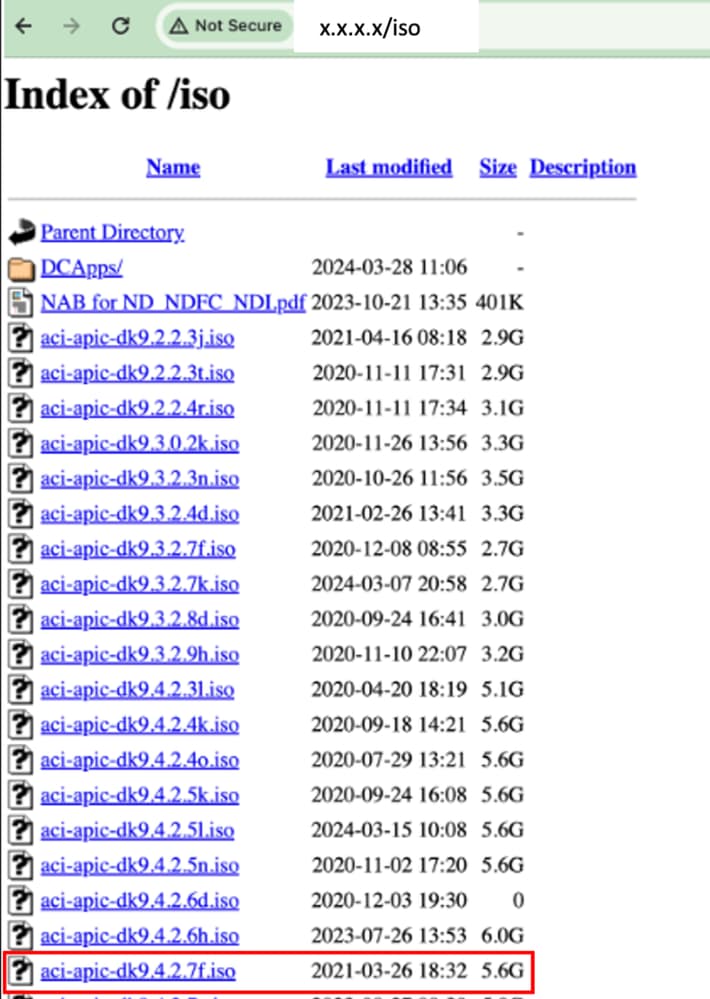
Paso 3. Copie la imagen ISO del software APIC en el servidor HTTP.
Ejemplo: http://x.x.x.x/iso/
Paso 4. SSH/Consola a Cisco Integrated Management Controller.
-
Desde una ventana de terminal, inicie sesión en la consola CIMC.
# ssh admin@cimc_ip
Donde cimc_ip es la dirección IP de CIMC. Por ejemplo:
# ssh admin@x.x.x.x
admin@x.x.x.x's password:
system#
-
Cambie el alcance a medio virtual:
system# scope vmedia
system /vmedia #
-
Asigne la imagen .iso al servidor HTTP.
system /vmedia # map-www volume_name http://http_server_ip_and_path iso_file_name
Where:
- volume_name es el nombre del volumen.
- http_server_ip_and_path es la dirección IP del servidor HTTP y la ruta de acceso a la ubicación del archivo .iso.
- iso_filename es el nombre del archivo .iso.

Nota: Hay espacio entre http_server_ip_and_path y iso_filename.
Por ejemplo:
system /vmedia # map-www apic http://x.x.x.x/iso/ aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso
Server username: admin
Server password:
Confirm password:

Nota: /* Si no se requiere autenticación aquí, simplemente pulse Enter (Intro).
-
Compruebe el estado de asignación:
system /vmedia # show mappings detail
El Map-Status debe aparecer como OK.
Por ejemplo:
system /vmedia # show mappings detail
Volume apic:
Map-Status: OK
Drive-Type: CD
Remote-Share: http://x.x.x.x/iso/
Remote-File: aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso
Mount-Type: www
Mount-Options: noauto,username=admin,password=********3
system /vmedia #
-
Conéctese a SOL para supervisar el proceso de instalación:
system /vmedia # connect host
CISCO Serial Over LAN:
Press Ctrl+x to Exit the session
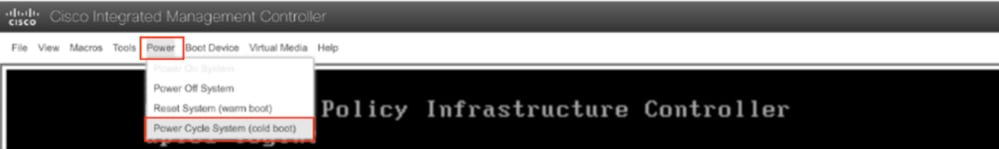
Paso 5. Apague y encienda la consola KVM de la GUI de CIMC.
Elija Power > Power Cycle System (arranque en frío) para apagar y encender el controlador
Desde la consola SOL: Observe la pantalla durante el proceso de arranque y prepárese para presionar F6 en el momento apropiado para ingresar al menú de selección de arranque.
Por ejemplo:
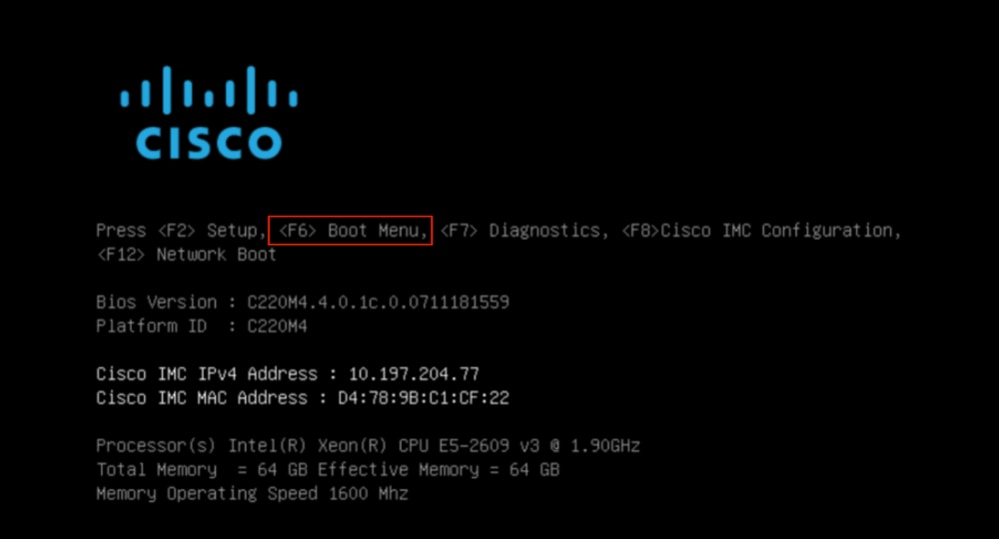
Después de pulsar el botón F6

Nota: Si pierde la oportunidad y no pudo presionar F6 en el momento apropiado, regrese al paso 5 para apagar y encender el controlador y repita el proceso hasta que pueda presionar F6 para ingresar al menú de selección de inicio.
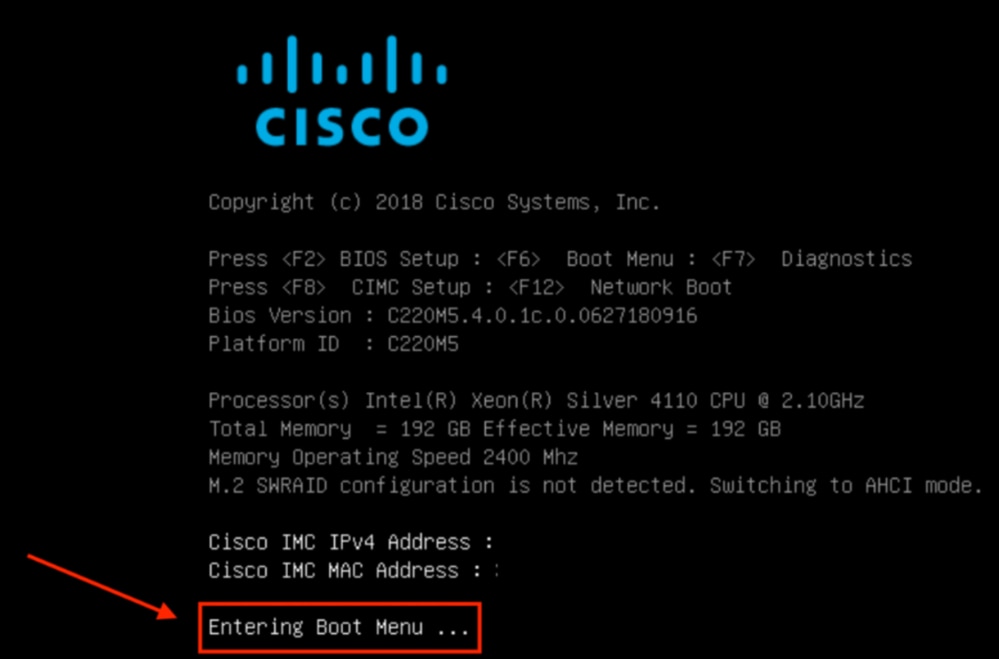
También puede tener que introducir la contraseña del BIOS. La contraseña predeterminada es password.
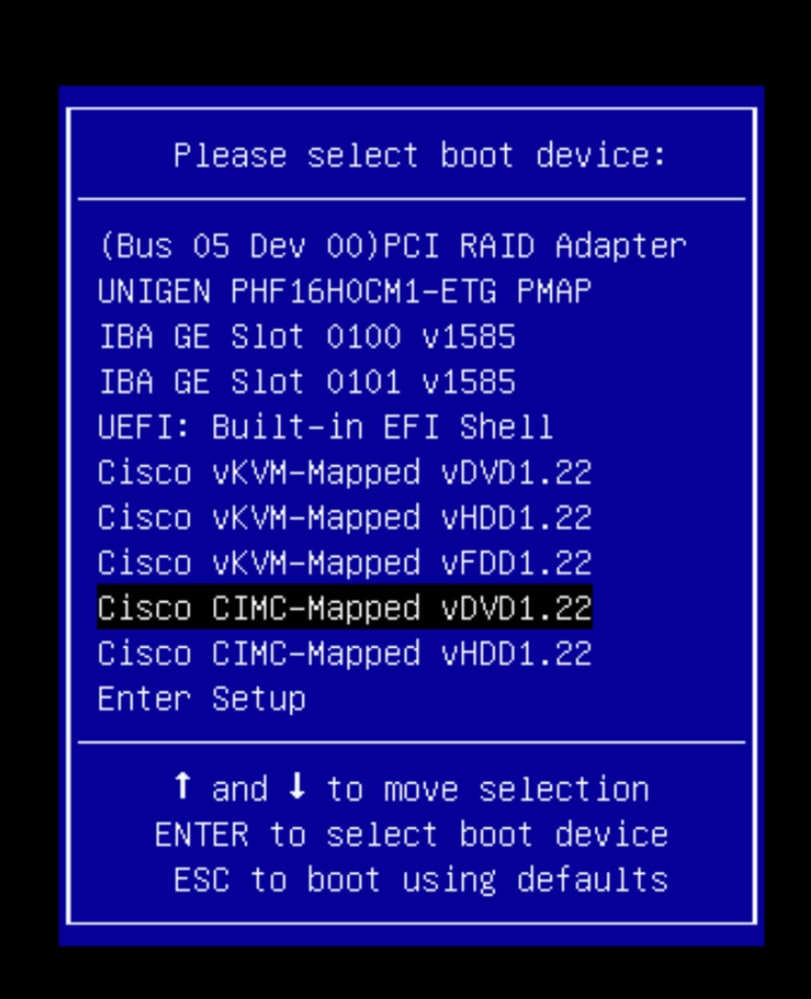
En el menú de selección de arranque, seleccione la opción vDVD1.22 asignada a Cisco CIMC como dispositivo de arranque único.
Paso 6. Vuelva a CLI de CIMC y supervise el resultado de Connect Host.
Supervise la CLI de CIMC cuando aparezca el mensaje Para acelerar la instalación, ingrese iso url en los próximos diez minutos y luego ingrese http server URL with APIC image.
++ grep /run/install/repo
++ cut -f 1 -d ' '
++ tr -d '[:digit:]'
+ usbdevice=/dev/sr
+ mkdir /mnt/usbdata
+ mount /dev/sr2 /mnt/usbdata
mount: special device /dev/sr2 does not exist
+ true
+ '[' -f /mnt/usbdata/ifabric.iso ']'
+ mountpoint -q /mnt/usbdata
+ true
+ echo 'INFO: found second partition on install media but did not find ifabric.iso. '
INFO: found second partition on install media but did not find ifabric.iso.
+ echo 'Continuing on to ISO URL prompt.'
Continuing on to ISO URL prompt.
+ '[' 0 -eq 0 ']'
+ read_iso_url
+ true,,
+ echo 'To speed up the install, enter iso url in next ten minutes: ' << Enter the http server URL with apic image >>
To speed up the install, enter iso url in next ten minutes:
+ read -t 600 -p '? ' url
?
http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso 5:program-log << Enter the http server details >>
[anaconda] 1:main* 2:shell 3:log 4:storage-lo> Switch tab: Alt+Tab | Help: F1

Nota: No hay espacio entre http_server_ip_and_path y iso_filename.
Paso 7. Después de ingresar la URL HTTP, el proceso de inicio continuará.

Nota: Si elige la opción estática, se le pedirá que introduzca el nombre de la interfaz, la dirección IP de gestión y la puerta de enlace.
+ '[' 0 -eq 0 ']'
+ read_iso_url
+ true
+ echo 'To speed up the install, enter iso url in next ten minutes: '
To speed up the install, enter iso url in next ten minutes:
+ read -t 600 -p '? ' url
?
[ahttp://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso 5:program-log
++ awk -F '/|:' '{print $4}'
+ urlip=x.x.x.x
+ '[' -z http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso ']'
+ '[' -z x.x.x.x ']'
+ break
+ '[' -n http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso ']'
+ set +e
+ configured=0
+ '[' 0 -eq 0 ']'
+ echo 'Configuring network interface'
Configuring network interface
+ echo 'type static, dhcp, bash for a shell to configure networking, or url to re-enter the url: '
>>
<< Type static and configure the APIC OOB IP address with it’s gateway>>
type static, dhcp, bash for a shell to configure networking, or url to re-enter the url:
+ read -p '? ' ntype
? static. << Enter the static to configure the networking >>
[anaconda] 1:main* 2:shell 3:log 4:storage-lo> Switch tab: Alt+Tab | Help: F1

Nota: Después de escribir la estática, aparecerá una lista en la interfaz CIMC, seleccione la interfaz correcta. si seleccionó la interfaz incorrecta, la pérdida de paquetes será del 100% y luego después de tres intentos fallidos de ping , se le pedirá nuevamente que seleccione la interfaz correcta hasta que la pérdida de paquetes sea 0 si no es consciente de la interfaz, seleccione la interfaz all uno por uno.
Por ejemplo:
+ case $ntype in
+ configure_static
+ echo 'Available interfaces'
Available interfaces
+ ls -l /sys/class/net
total 0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 May 3 07:08 enp11s0 -> ../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.0/0000:06:00.0/0000:07:01.0/0000:09:00.0/0000:0a:00.0/0000:0b:00.0/net/enp11s0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 May 3 07:08 enp12s0 -> ../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:03.0/0000:06:00.0/0000:07:01.0/0000:09:00.0/0000:0a:01.0/0000:0c:00.0/net/enp12s0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 May 3 07:08 enp1s0f0 -> ../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0/net/enp1s0f0
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 May 3 07:08 enp1s0f1 -> ../../devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.1/net/enp1s0f1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 May 3 07:08 lo -> ../../devices/virtual/net/lo
+ read -p 'Interface to configure: ' interface
Interface to configure: enp1s0f0 << select the correct interface >>
[anaconda] 1:main* 2:shell 3:log 4:storage-lo>
Paso 8. Comprobación correcta de la interfaz.
Después de ingresar a la interfaz, intentará hacer ping al servidor http y si la interfaz seleccionada es correcta, la pérdida de paquetes debe ser 0% y comenzar a recuperar la imagen del servidor http.
Por ejemplo: Después de ingresar a la interfaz correcta con pérdida de paquetes al 0%.
+ read -p 'Interface to configure: ' interface
Interface to configure: enp1s0f0
+ read -p 'address: ' addr
address: x.x.x.x/24
+ read -p 'gateway: ' gw
gateway: x.x.x.x
+ ip addr add x.x.x.x/24 dev enp1s0f0
+ ip link set enp1s0f0 up
+ ip route add default via x.x.x.x
++ seq 1 2
+ for count in '$(seq 1 2)'
+ ping -c 1 x.x.x.x
PING x.x.x.x (x.x.x.x) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from x.x.x.x: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=55.0 ms
--- x.x.x.x ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 55.056/55.056/55.056/0.000 ms
+ configured=1
+ break
+ '[' 1 -eq 0 ']'
+ echo 'Fetching http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso'
Fetching http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso >> started fetching the apic image from HTTP server
+ wget -o /dev/null -O /tmp/cdrom.iso http://x.x.x.x/iso/aci-apic-dk9.4.2.7f.iso
Si seleccionó la interfaz incorrecta, la pérdida de paquetes será del 100% y luego de tres intentos fallidos de ping, se le pedirá nuevamente que seleccione la interfaz correcta.
Por ejemplo: Después de ingresar a la interfaz incorrecta con pérdida de paquetes al 100%.
+ read -p 'Interface to configure: ' interface
Interface to configure: enp11s0
+ read -p 'address: ' addr
address: x.x.x.x/24
+ read -p 'gateway: ' gw
gateway: x.x.x.x
+ ip addr add x.x.x.x/24 dev enp11s0
+ ip link set enp11s0 up
+ ip route add default via x.x.x.x
++ seq 1 2
+ for count in '$(seq 1 2)'
+ ping -c 1 x.x.x.x
PING x.x.x.x (x.x.x.x) 56(84) bytes of data.
From x.x.x.x icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
--- x.x.x.x ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 0ms
+ sleep 20
+ for count in '$(seq 1 2)'
+ ping -c 1 x.x.x.x
PING x.x.x.x (x.x.x.x) 56(84) bytes of data.
From x.x.x.x icmp_seq=1 Destination Host Unreachable
--- x.x.x.x ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 0ms
+ sleep 20
+ '[' 0 -eq 0 ']'
+ echo 'Configuring network interface'
Configuring network interface
+ echo 'type static, dhcp, bash for a shell to configure networking, or url to re-enter the url: ' <>
type static, dhcp, bash for a shell to configure networking, or url to re-enter the url:
+ read -p '? ' ntype
?
Mantenga Monitor en la CLI de CIMC y espere aproximadamente 40-50 min , obtendrá la siguiente salida en la cli.
[anaconda] 1:main* 2:shell 3:log 4:storage-lo> Switch tab: Alt+Tab | Help: F1
[ OK ] Started Show Plymouth Power Off Screen.
[ OK ] Stopped Availability of block devices.
Stopping Logout off all iSCSI sessions on shutdown...
Stopping LVM2 metadata daemon...
[ OK ] Stopped LVM2 metadata daemon.
[ OK ] Stopped Logout off all iSCSI sessions on shutdown.
[ OK ] Stopped target Network.
[ OK ] Stopped Remount Root and Kernel File Systems.
Stopping Remount Root and Kernel File Systems...
[ OK ] Started Restore /run/initramfs.
[ OK ] Reached target Shutdown.
dracut Warning: Killing all remaining processes
Powering off.
reboot: Power down
Paso 9. Salir de SOL después de apagarse
Espere hasta que vea el mensaje de apagado en la consola SOL, luego salga de SOL presionando Ctrl y x (Ctrl+x) e inicie sesión en CIMC nuevamente y cambie el alcance nuevamente.
(i) Change the scope to virtual media again:
system# scope vmedia
system /vmedia #
(ii) Unmap the .iso image that you mapped in 2.c:
system /vmedia # unmap volume_name
At the Save mapping prompt, enter yes if you want to save the mapping or no if you do not want to save the mapping. For example:
system /vmedia # unmap apic
Save mapping? Enther 'yes' or 'no' to confirm (CTRL-C to cancel) → yes
system /vmedia #
(iii) Connect back to SOL again:
system /vmedia # connect host
Paso 10. Configuración inicial
Desde la consola KVM: Elija Power > Power on System para encender el controlador y el Lunch KVM , solicitará la configuración inicial de APIC.
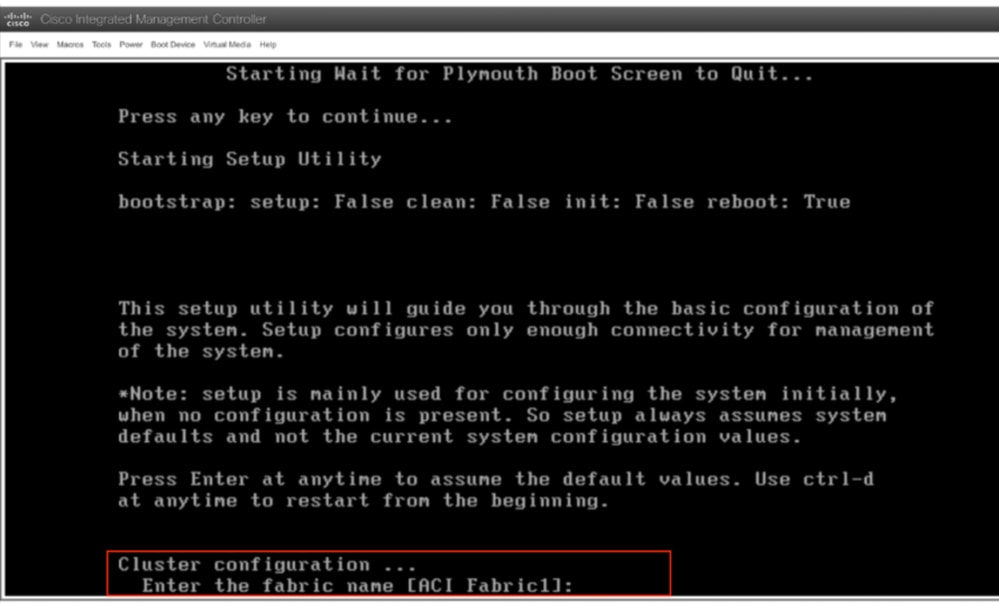

Precaución: Este método se aplica exclusivamente al direccionamiento fuera de banda (OOB) de IPv4 APIC (servidor HTTP). Tenga en cuenta que la compatibilidad con IPv6 no está disponible en este momento.
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
03-Jun-2024
|
Versión inicial |
Con la colaboración de ingenieros de Cisco
- Shivam TripathiTAC
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios