Configuración un túnel GRE a través de un cable
Contenido
Introducción
Este documento contiene las descripciones, las configuraciones y las verificaciones para el Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) en un entorno de cable. GRE es un protocolo de tunelización desarrollado por Cisco que encapsula una amplia variedad de tipos de paquetes de protocolo dentro de los túneles IP.
Antes de que usted comience
Convenciones
Para más información sobre los convenios del documento, vea los convenios de los consejos técnicos de Cisco.
prerrequisitos
No hay requisitos previos específicos para este documento.
Componentes Utilizados
La información que contiene este documento se basa en las versiones de software y hardware indicadas a continuación.
-
Módem cable uBR924 que funciona con el Software Release 12.1(5)T4 de Cisco IOS®
Nota: Aunque sea posible configurar los túneles GRE en otras Plataformas del módem cable de Cisco, por ejemplo en el uBR904 usando diversas versiones del Cisco IOS, el soporte oficial para esta característica está en el Cisco IOS 12.1(5)T4 para uBR920 y del Cisco IOS 12.1(3) para uBR910.
| Plataforma del módem cable | Versión de software del IOS de Cisco |
|---|---|
| uBR920 | 12.1(5)T4 |
| uBR910 | A partir de la 12.1(3) y más adelante |
Para funcionar con esta configuración, usted necesita tener Conectividad IP entre el dos Cable módems.
La Información presentada en este documento fue creada de los dispositivos en un entorno específico del laboratorio. Todos los dispositivos que se utilizan en este documento se pusieron en funcionamiento con una configuración verificada (predeterminada). Si la red está funcionando, asegúrese de haber comprendido el impacto que puede tener un comando antes de ejecutarlo.
Teoría previa
El Tunelización proporciona a una manera de encapsular los paquetes de un protocolo externo dentro de un Transport Protocol. El Tunelización se ejecuta como interfaz virtual para proporcionar a una interfaz simple para la configuración. La interfaz del túnel no se ata al pasajero específico o los protocolos de transporte, sin embargo, es una arquitectura que se diseña para proporcionar los servicios necesarios ejecutar cualquier esquema estándar de la encapsulación Point-to-Point. Los túneles son links de punto a punto, y usted debe configurar un túnel diferente para cada link.
GRE establece un link Point-to-Point virtual al Routers de Cisco en las puntas remotas sobre una red interna IP. Conectando los redes secundarios multiprotocol en un entorno de estructura básica de un solo protocolo, el Tunelización IP usando GRE permite la expansión de la red a través de un entorno de estructura básica de un solo protocolo. Un Sistema de terminación del cablemódem (CMTS) es cualquier Data-over-Cable Service Interface Specifications (DOCSIS) - de cabecera compatible con telegrafíe al router, tal como el uBR7246 de Cisco, uBR7223, o uBR7246VXR.
Configurar
En esta sección encontrará la información para configurar las funciones descritas en este documento.
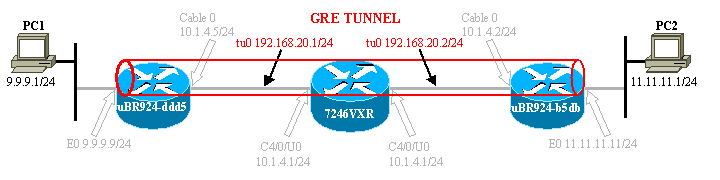
Diagrama de la red
Este documento utiliza la instalación de red que se muestra en el siguiente diagrama.
Esta disposición crea un túnel entre el dos Cable módems uBR924-ddd5 y uBR924-b5db. El ejemplo debajo de las aplicaciones dos uBR924s y un uBR7246VXR. Para esta disposición, los nombres del Cable módems son ubr924-ddd5 y ubr924-b5db, y utilizan la versión 12.1(5)T4 del Cisco IOS. Las interfaces del túnel son creadas dinámicamente en el modo de configuración global publicando el comando interface tunnel 0.
Nota: Siempre y cuando haya conectividad de la IP entre los dos cablemódems, no es necesario que los cablemódems uBR900 estén conectados al mismo uBR7200 CMTS o a la misma red del proveedor de servicio.
Configuraciones
Este documento usa las configuraciones detalladas a continuación.
Nota: El texto intrépido refiere a los Comandos relacionados GRE. Los comentarios están en el azul y refieren a la línea arriba.
| ubr924-ddd5 |
|---|
version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr924-ddd5 ! logging rate-limit console 10 except errors ! clock timezone - -80 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! call rsvp-sync ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! interface Tunnel0 !--- Tunnel interface 0. ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 !--- IP address of the GRE tunnel interface 0. tunnel source Ethernet0 !--- IP source of the tunnel. It is best to make this an !--- interface with a public, routable IP address so that !--- it is reachable from the other endpoint of the tunnel. tunnel destination 11.11.11.11 !--- IP destination of the tunnel. Make sure this is !--- reachable via the ping command !--- Otherwise, the tunnel will not be created properly. ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 9.9.9.9 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 !--- Send RIP version 2 packets. ip rip receive version 2 !--- Receive RIP version 2 packets. ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 !--- Send RIP version 2 packets. ip rip receive version 2 !--- Receive RIP version 2 packets. cable-modem downstream saved channel 525000000 40 1 cable-modem mac-timer t2 40000 no cable-modem compliant bridge ! router rip version 2 passive-interface Tunnel0 !--- This command is used to avoid recursive routing. network 10.0.0.0 network 9.0.0.0 no auto-summary ! ip default-gateway 10.1.4.1 ip classless no ip http server no ip http cable-monitor ! snmp-server packetsize 4096 snmp-server manager ! voice-port 0 input gain -2 ! voice-port 1 input gain -2 ! ! line con 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 login ! end ubr924-ddd5# |
| ubr924-b5db |
|---|
version 12.1 no service single-slot-reload-enable no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! hostname ubr924-b5db ! logging rate-limit console 10 except errors enable password ww ! clock timezone - -80 ip subnet-zero no ip finger ! mgcp call rsvp-sync ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! interface Tunnel0 !--- Tunnel interface 0 ip address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0 !--- IP address of the gre tunnel interface 0 tunnel source Ethernet0 !--- IP source of the tunnel. It is best to make this an !--- interface with a public, routable IP address so that !--- it is reachable from the other endpoint of the tunnel. tunnel destination 9.9.9.9 !--- IP destination of the tunnel. Make sure this is !--- reachable via the ping command !--- Otherwise, the tunnel will not be created properly. ! interface Ethernet0 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.0 ip rip send version 2 !--- Send RIP version 2 packets. ip rip receive version 2 !--- Receive RIP version 2 packets. ! no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache ! interface cable-modem0 ip rip send version 2 !--- Send RIP version 2 packets. ip rip receive version 2 !--- Receive RIP version 2 packets. no ip route-cache no ip mroute-cache no cable-modem compliant bridge ! router rip version 2 passive-interface Tunnel0 !--- This command is used to avoid recursive routing. network 10.0.0.0 network 11.0.0.0 no auto-summary ! ip default-gateway 10.1.4.1 ip classless no ip http server no ip http cable-monitor ! snmp-server packetsize 4096 snmp-server manager ! voice-port 0 input gain -2 ! voice-port 1 input gain -2 ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 transport input none line vty 0 4 password ww login ! end ubr924-b5db# |
Verificación
En esta sección encontrará información que puede utilizar para confirmar que su configuración esté funcionando correctamente.
La herramienta intérprete de la salida apoyan a los ciertos comandos show, que permite que usted vea un análisis de la salida del comando show.
Verifique que la configuración CMTS (7246VXR) esté correcta, y que el Cable módems está en línea. La configuración del CMTS se muestra abajo.
7246VXR#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 4579 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 13:22:17 PDT Mon Feb 26 2001
! NVRAM config last updated at 13:22:46 PDT Mon Feb 26 2001
!
version 12.1
no service single-slot-reload-enable
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime
service timestamps log datetime localtime
no service password-encryption
service linenumber
service udp-small-servers max-servers no-limit
!
hostname 7246VXR
!
logging buffered 1000000 debugging
logging rate-limit console 10 except errors
enable password cable
!
cable qos profile 8
cable qos profile 10
cable qos profile 10 grant-size 1500
cable qos profile 12 guaranteed-upstream 100000
no cable qos permission create
no cable qos permission update
cable qos permission modems
cable time-server
clock timezone PDT -8
clock summer-time PDT recurring
clock calendar-valid
ip subnet-zero
no ip finger
!
interface Ethernet2/0
ip address 172.16.30.4 255.255.255.192
no ip mroute-cache
half-duplex
!
interface Cable4/0
ip address 172.16.29.1 255.255.255.224 secondary
ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0
no keepalive
cable downstream rate-limit token-bucket shaping
cable downstream annex B
cable downstream modulation 64qam
cable downstream interleave-depth 32
cable downstream frequency 555000000
cable upstream 0 frequency 40000000
cable upstream 0 power-level 0
no cable upstream 0 shutdown
cable upstream 1 shutdown
cable upstream 2 shutdown
cable upstream 3 shutdown
cable upstream 4 shutdown
cable upstream 5 shutdown
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
cable helper-address 172.16.30.2
!
interface Cable5/0
ip address 172.16.29.225 255.255.255.224 secondary
ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0
load-interval 30
no keepalive
cable downstream rate-limit token-bucket shaping
cable downstream annex B
cable downstream modulation 64qam
cable downstream interleave-depth 32
cable downstream frequency 620000000
cable upstream 0 frequency 25008000
cable upstream 0 power-level 0
no cable upstream 0 shutdown
no cable upstream 1 shutdown
cable dhcp-giaddr policy
!
router eigrp 202
redistribute connected
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
network 172.16.0.0
no auto-summary
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
!
router rip
version 2
redistribute connected
redistribute static
network 10.0.0.0
network 172.16.0.0
no auto-summary
!
ip default-gateway 172.16.30.1
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.30.1
ip route 172.16.30.0 255.255.255.0 Ethernet2/0
ip http server
ip http authentication local
!
access-list 188 permit tcp any any eq www log
access-list 188 permit ip any any
route-map docsis permit 10
!
snmp-server engineID local 00000009020000E01ED77E40
snmp-server community public RO
snmp-server community private RW
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport input none
line aux 0
speed 19200
line vty 0 4
session-timeout 60
exec-timeout 0 0
!
ntp clock-period 17179973
end
7246VXR#show cable modem
Interface Prim Online Timing Rec QoS CPE IP address MAC address
Sid State Offset Power
Cable4/0/U0 69 online 2812 0.25 5 0 10.1.4.3 0002.1685.b5db
Cable4/0/U0 70 online 2288 0.00 5 0 10.1.4.6 0010.7bed.9b23
Cable4/0/U0 71 online 2289 0.50 5 0 10.1.4.2 0010.7bed.9b45
Cable4/0/U0 72 online 2812 0.00 5 0 10.1.4.4 0002.fdfa.0a63
Cable4/0/U0 73 online 2812 -0.75 5 0 10.1.4.5 0004.2752.ddd5
Cable4/0/U0 74 online 2813 0.25 5 0 10.1.4.7 0001.64ff.e47d
Si el estado en línea del Cable módems no muestra en línea, refiera al documento en línea que no viene del Cable módems del uBR del troubleshooting.
7246VXR#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 192.168.7.253 YES NVRAM up down
Ethernet2/0 172.16.30.4 YES manual up up
Ethernet2/1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Ethernet2/2 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Ethernet2/3 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
Cable3/0 10.1.3.1 YES manual up up
Cable4/0 10.1.4.1 YES manual up up
Cable5/0 10.1.5.1 YES manual up up
7246VXR#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.30.1 to network 0.0.0.0
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 3 masks
C 172.16.29.224/27 is directly connected, Cable5/0
C 172.16.29.0/27 is directly connected, Cable4/0
S 172.16.30.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet2/0
C 172.16.30.0/26 is directly connected, Ethernet2/0
9.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 9.9.9.0 [120/1] via 10.1.4.5, 00:00:09, Cable4/0
R 192.168.20.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.4.5, 00:00:09, Cable4/0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, Cable3/0
R 10.5.5.0/24 [120/1] via 10.1.4.4, 00:00:01, Cable4/0
R 10.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 172.16.30.10, 00:00:24, Ethernet2/0
C 10.1.5.0/24 is directly connected, Cable5/0
C 10.1.4.0/24 is directly connected, Cable4/0
11.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
R 11.11.11.0 [120/1] via 10.1.4.3, 00:00:15, Cable4/0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected
Del Cable módems eche a un lado, verifique la versión sh de ambos dispositivos, como se muestra abajo.
ubr924-ddd5#sh ver Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 920 Software (UBR920-K1V4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(5)T4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) TAC Support: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/ibld/view.pl?i=support Copyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 02-Feb-01 10:55 by ccai Image text-base: 0x800100A0, data-base: 0x806DB770 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.0(6r)T3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ROM: 920 Software (UBR920-K1V4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(5)T4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ubr924-ddd5 uptime is 2 hours, 1 minute System returned to ROM by reload at 12:45:25 - Fri Feb 23 2001 System restarted at 12:46:07 - Fri Feb 23 2001 System image file is "flash:ubr920-k1v4y556i-mz.121-5.T4" cisco uBR920 CM (MPC850) processor (revision 4.d) with 15872K/1024K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FAA0444Q14Z Bridging software. 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 1 Cable Modem network interface(s) 3968K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) 1536K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write) Configuration register is 0x2102 ubr924-b5db#show ver Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) 920 Software (UBR920-K1V4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(5)T4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) TAC Support: http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/ibld/view.pl?i=support Copyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 02-Feb-01 10:55 by ccai Image text-base: 0x800100A0, data-base: 0x806DB770 ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.0(6r)T3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ROM: 920 Software (UBR920-K1V4Y556I-M), Version 12.1(5)T4, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) ubr924-b5db uptime is 1 hour, 53 minutes System returned to ROM by reload at 12:55:34 - Fri Feb 23 2001 System restarted at 12:56:15 - Fri Feb 23 2001 System image file is "flash:ubr920-k1v4y556i-mz.121-5.T4" cisco uBR920 CM (MPC850) processor (revision 3.e) with 15872K/1024K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FAA0422Q04F Bridging software. 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 1 Cable Modem network interface(s) 3968K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write) 1536K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write) Configuration register is 0x2102
El túnel mostrará up/up, mientras existan las condiciones siguientes:
-
Se configura con los IP Addresses válidos.
-
Hay una ruta en la tabla de encaminamiento a la dirección IP del destino del túnel, y no la dirección IP asignada al extremo lejano del túnel.
Esto debe ser verdad sin importar si usted puede hacer ping el direccionamiento de destino. Una Static ruta incorrecta o un default route que señala en la dirección incorrecta traerá para arriba el túnel, sin embargo, el túnel no funcionará.
El primer paso para verificar que los trabajos del túnel sean verificar que el túnel está para arriba. Publique los comandos show ip interface brief y show interface tunnel 0 en ambo Cable módems. A continuación, se incluye un resultado de ejemplo del comando
ubr924-ddd5#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 9.9.9.9 YES manual up up
Tunnel0 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up
cable-modem0 10.1.4.5 YES unset up up
ubr924-ddd5#show interface tunnel 0
Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
Internet address is 192.168.20.1/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 9 Kbit, DLY 500000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Tunnel source 9.9.9.9 (Ethernet0), destination 11.11.11.11
Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IP, key disabled, sequencing disabled
Checksumming of packets disabled
Last input 00:15:25, output 00:14:27, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/0, 2 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
146 packets input, 21024 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
172 packets output, 57392 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
ubr924-b5db#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 11.11.11.11 YES manual up up
Tunnel0 192.168.20.2 YES manual up up
cable-modem0 10.1.4.3 YES NVRAM up up
ubr924-b5db#show interface tunnel 0
Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Tunnel
Internet address is 192.168.20.2/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 9 Kbit, DLY 500000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Tunnel source 11.11.11.11 (Ethernet0), destination 9.9.9.9
Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IP, key disabled, sequencing disabled
Checksumming of packets disabled
Last input 00:16:42, output 00:17:40, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/0, 5 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
118 packets input, 19144 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
164 packets output, 49624 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Verifique que los trabajos del túnel sean hacer ping la dirección IP del destino del túnel. Esto verificará la Conectividad IP solamente, no el funcionamiento real del túnel.
From ubr924-ddd5 we ping 11.11.11.11 ubr924-ddd5#ping 11.11.11.11 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 11.11.11.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/14/17 ms ubr924-ddd5#
Ping de ubr924-b5db el direccionamiento de destino 9.9.9.9.
ubr924-b5db#ping 9.9.9.9 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 9.9.9.9, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/14/16 ms ubr924-b5db#
Para verificar que el túnel funcione, publique el comando show ip route x x x x, donde está la dirección IP x.x.x.x asignada al extremo lejano del túnel. En este caso, sería el direccionamiento del loop-detrás del router lejano. Si la única ruta mostrada está a la interfaz del túnel, un ping a ese direccionamiento probará que el túnel funciona.
Si hay un esquema de dirección IP que hace publicidad de las rutas a la parte posterior del segmento del túnel a través de la red, habría más de una ruta al extremo lejano de la interfaz del túnel. Si ése es el caso, es muy difícil verificar que el túnel está funcionando. Típicamente en esta situación, usted no quiere las rutas duplicados a la red de túneles. Las medidas se deben tomar para prevenir el anuncio de las rutas por un protocolo de la encaminamiento a través de la red. Si el túnel se está utilizando para transportar el tráfico de un diverso protocolo del IP, el mismo método de la verificación básica se aplica.
From ubr924-ddd5 we get
ubr924-ddd5#show ip route 192.168.20.2
Routing entry for 192.168.20.0/24
Known via "connected", distance 0, metric 0 (connected, via interface)
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via Tunnel0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
From ubr924-b5db we get
ubr924-b5db#show ip route 192.168.20.1
Routing entry for 192.168.20.0/24
Known via "connected", distance 0, metric 0 (connected, via interface)
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via Tunnel0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
Para verificar que el PC1 pueda tener acceso al PC2 y vice versa, realice los pings extendidos en el Cable módems, y también hace ping de las PC.
Realice un ping extendido en ubr924-b5db de su interfaz de los Ethernetes (11.11.11.11) al interfaz de los Ethernetes ubr924-ddd5 (9.9.9.9).
ubr924-b5db#ping ip Target IP address: 9.9.9.9 !--- ubr924-ddd5 Ethernet's IP address. Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 11.11.11.11 !--- ubr924-b5db Ethernet's IP address. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 9.9.9.9, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/16/28 ms ubr924-b5db#
Realice el contrario para probar la otra Conectividad del lado.
ubr924-ddd5#ping ip Target IP address: 11.11.11.11 !--- ubr924-b5db Ethernet's IP address. Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands [n]: y Source address or interface: 9.9.9.9 !--- ubr924-ddd5 Ethernet's IP address. Type of service [0]: Set DF bit in IP header? [no]: Validate reply data? [no]: Data pattern [0xABCD]: Loose, Strict, Record, Timestamp, Verbose[none]: Sweep range of sizes [n]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 11.11.11.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/14/16 ms ubr924-ddd5#
La Prueba final es hacer ping del PC1 al PC2, y del PC2 al PC1.
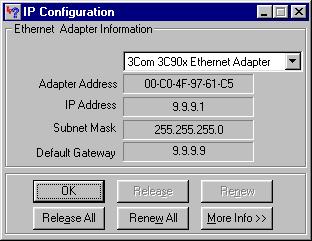
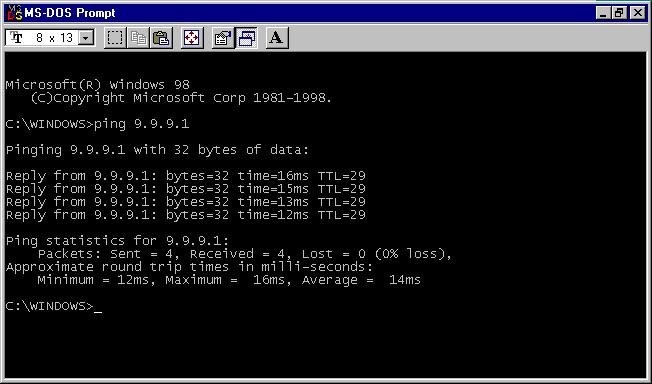
PC1 tiene una dirección IP 9.9.9.1.
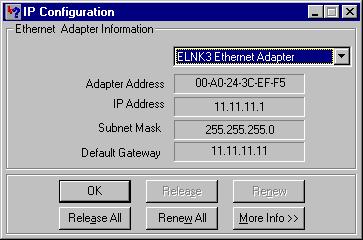
La dirección IP de PC2 es 11.11.11.1.
Ping de PC1 a PC2.
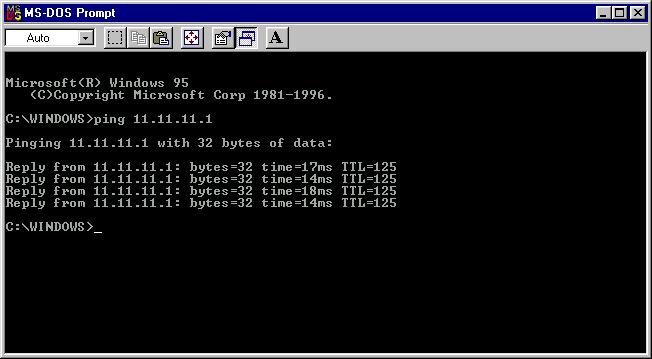
Comando ping desde PC2 a PC1.
Troubleshooting
Actualmente, no hay información específica de troubleshooting disponible para esta configuración.
Información Relacionada
Historial de revisiones
| Revisión | Fecha de publicación | Comentarios |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
04-Oct-2005
|
Versión inicial |
Contacte a Cisco
- Abrir un caso de soporte

- (Requiere un Cisco Service Contract)
 Comentarios
Comentarios