Public Internet
Direct SIP Trunk (Over the Top)
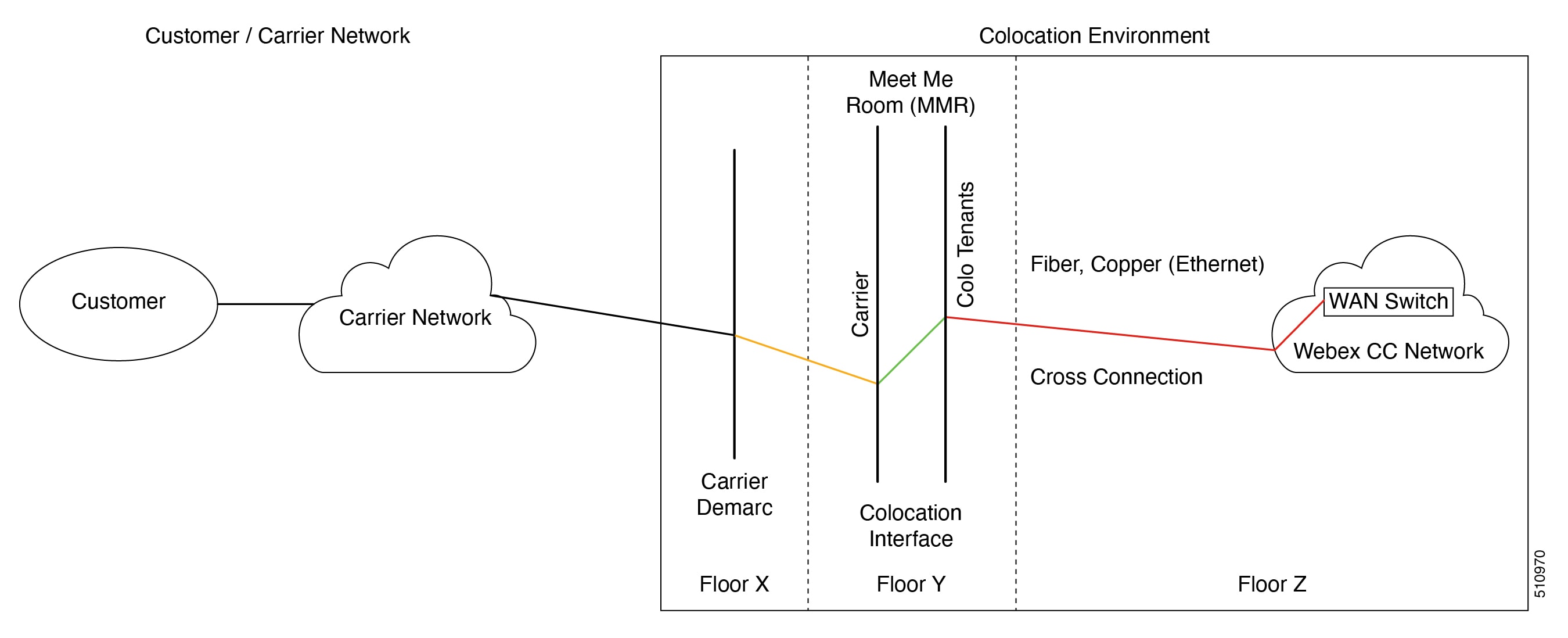
The customer’s CUBE or SBC should be placed on a public IP. This is our recommended standard deployment model.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
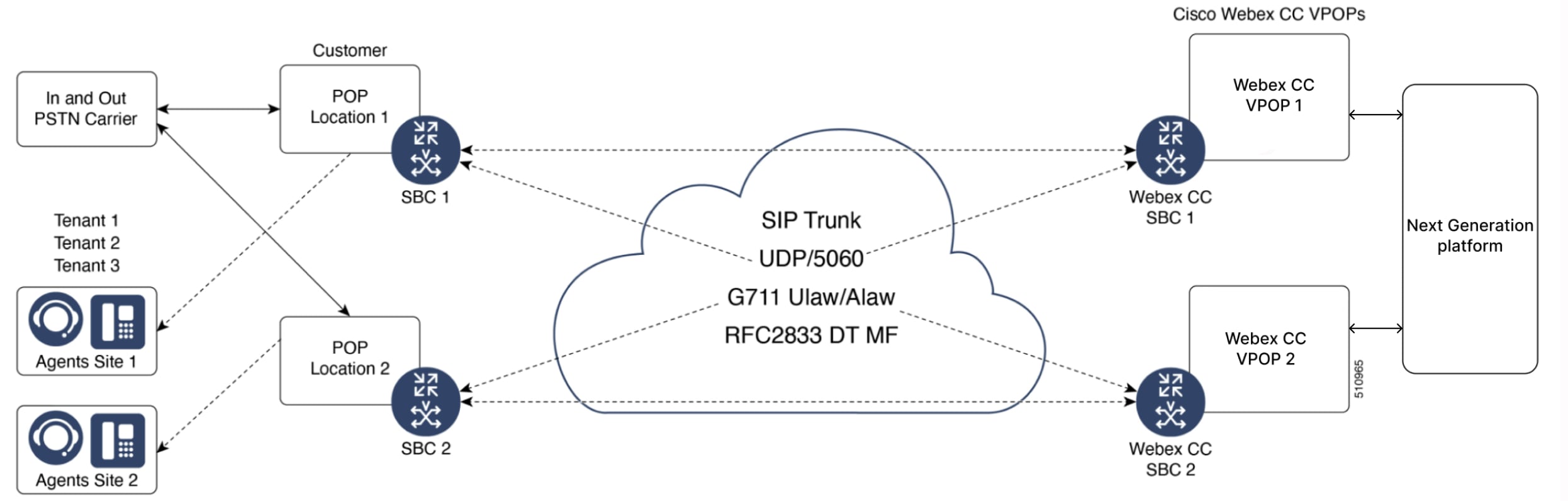
As this is the most simplistic approach, it is also the least flexible. The benefits of a simplified topology are ease of management and troubleshooting. Network diagrams are completed by the customer and submitted to the Voice team, and dial-peers are created. Placing the CUBE in a DMZ alleviates the complexities of dealing with NAT. The CUBE itself is a firewall, and most medium/large providers place their CUBE in a public IP and use its security capabilities.
VPNs
A VPN is another type of connection that uses public internet. VPNs are often needed when a customer requires a secure connection for SIP and RTP. A VPN might also be required if the customer cannot place the CUBE in a public IP space. A provisioning meeting with Voice Engineering is required for VPN connections.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Voice Ports
-
RTP: 8000 - 48199
-
SIP: UDP 5060
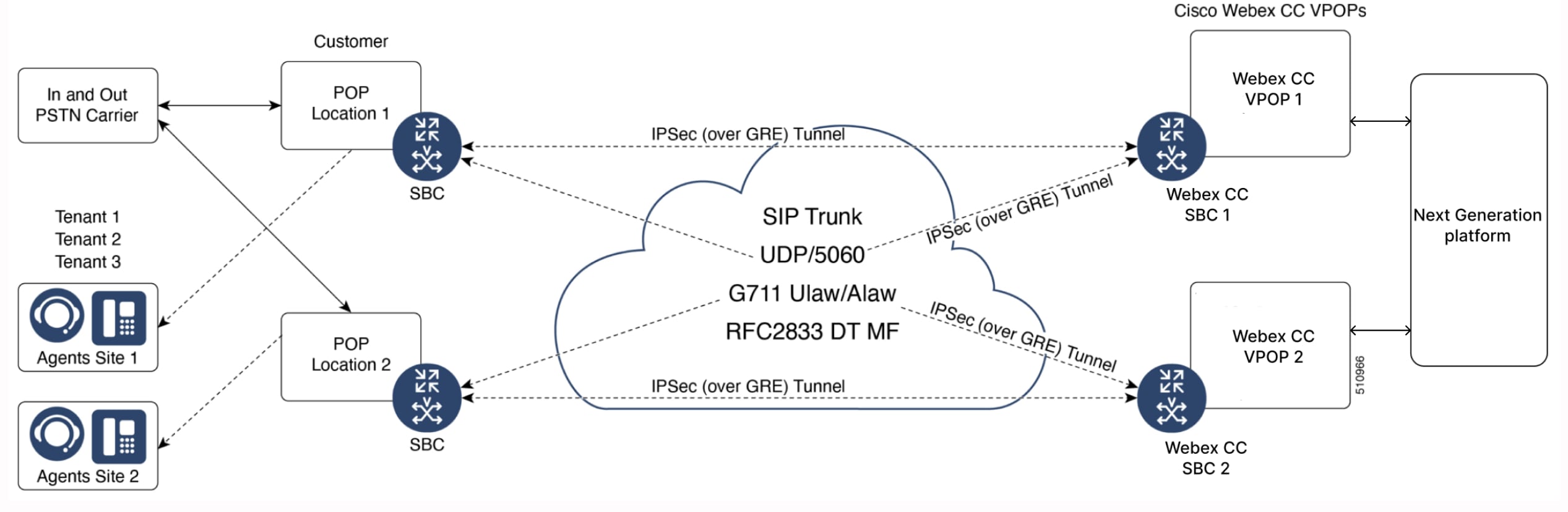
IPSec VPN or IPSec over GRE
The following options are available for VPN Connectivity:
-
SBC to SBC connectivity
-
GW to GW connectivity
Webex Contact Center (IPSec or IPSec over GRE tunnel and Webex Contact Center S2S Connectivity) to use UDP/5060 instead of TCP/5060
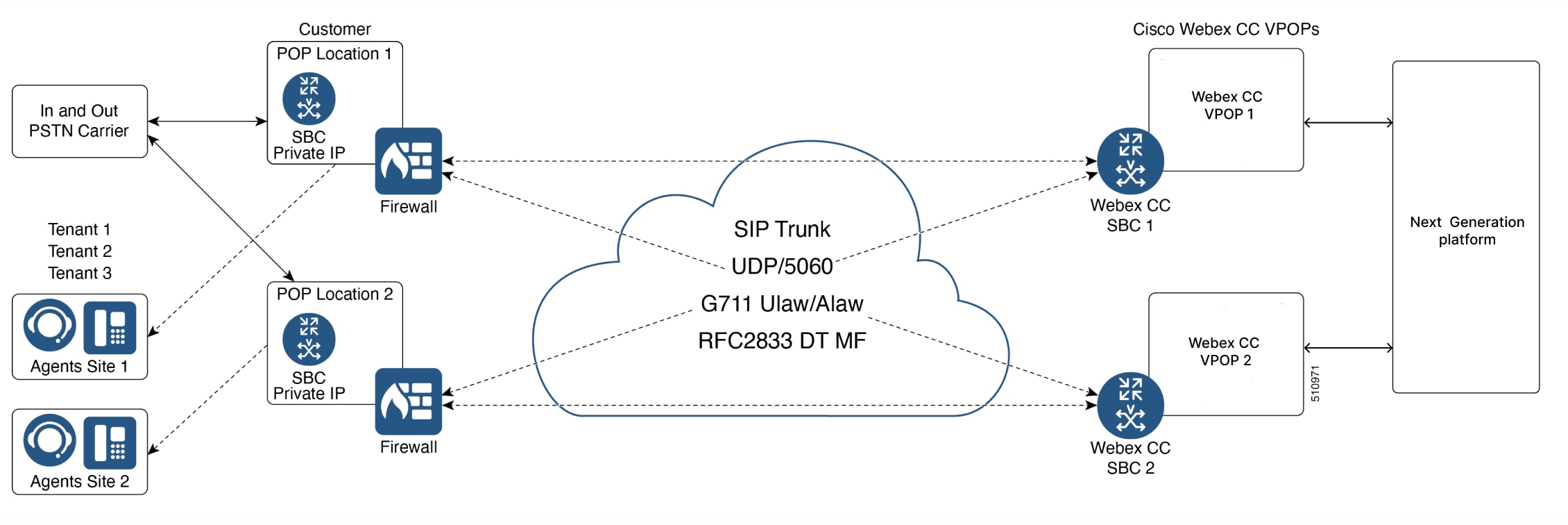
An IPSec VPN or IPSec over GRE is a good option for a secure SIP Trunk when the CUBE is on a public IP. This is an SBC to SBC connection (Figure 2) with VPN tunnels. Private IP address schemes must also be considered to avoid any overlap between customers. For GRE connections, IP subnets are 10.x.248.x and 10.x.249.x.
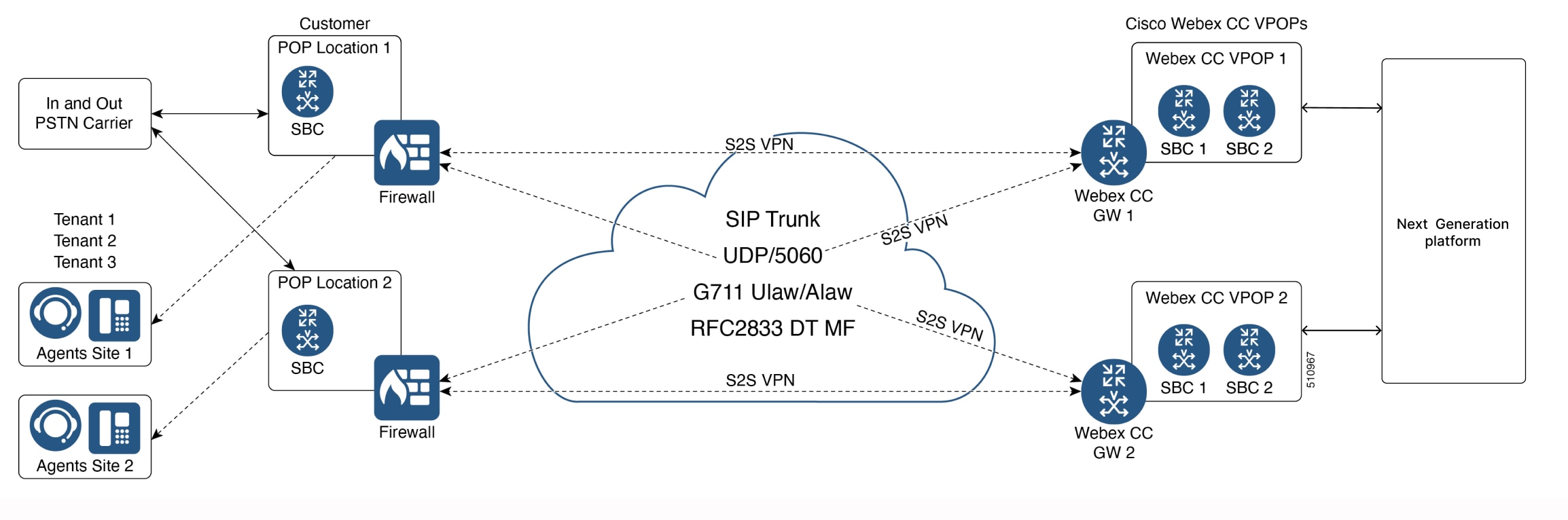
Site-to-Site (S2S)
A S2S connection can be deployed if the customer needs a secure connection or cannot place the CUBE in a public IP. This is a gateway to gateway connection. There are no subnets specifically designated for S2S VPN connections as routing is based on interesting traffic without the involvement of a logical interface.
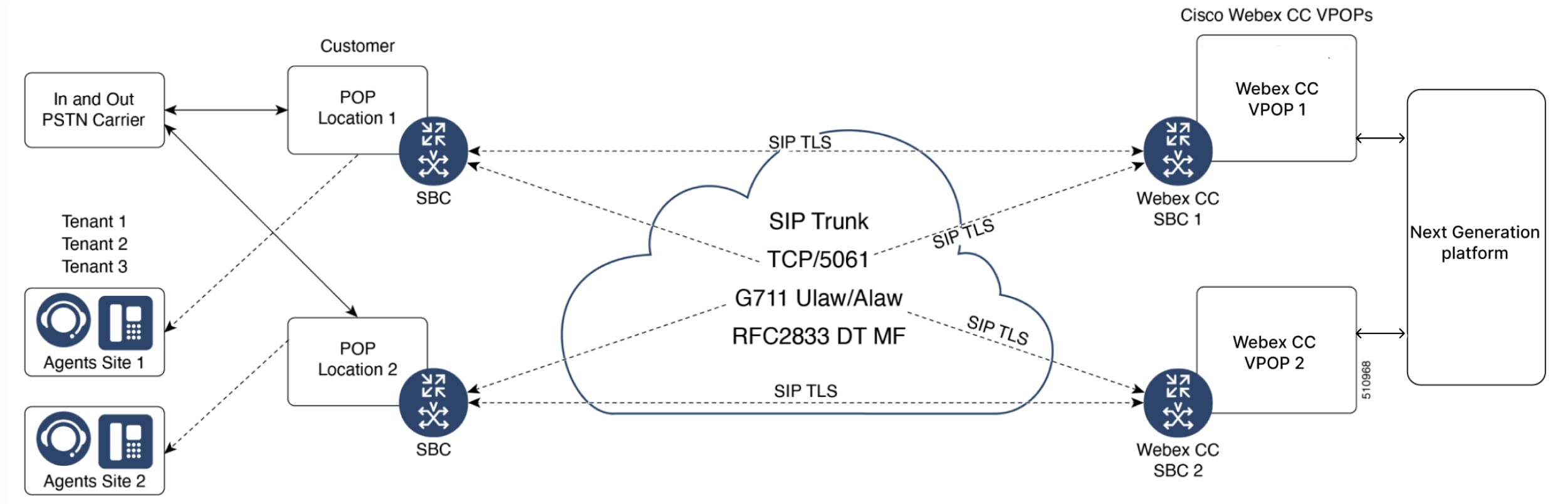
SIP TLS and SRTP
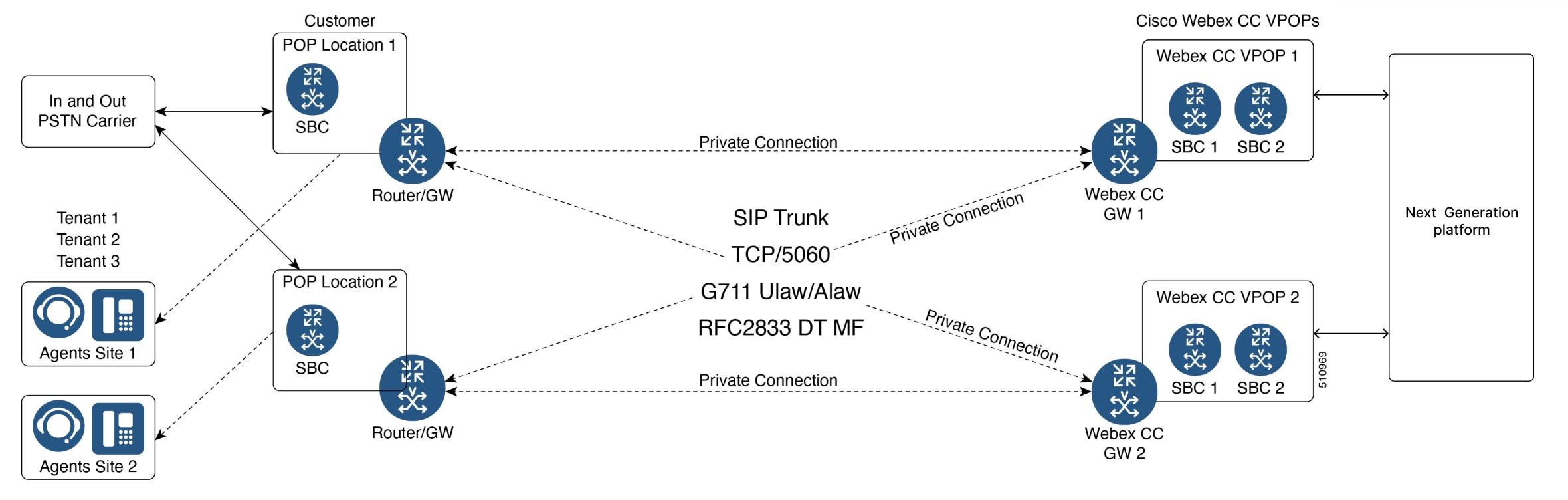
Using SRTP/SIP TLS is another option when the CUBE is on a public IP address. However, there is a performance hit for using SRTP/SIP TLS. A CUBE device can handle one-third of the SIP sessions if you have secured the calls using either TLS or SRTP. This is a SBC to SBC connection.
In order to establish a SIP TLS connection, it is necessary to exchange certificates. The following options are available:
-
Self-signed certificates are generated and exchanged between the customer and Webex Contact Center.
-
Public CA – the following steps need to be completed to support Public CA:
-
Customer needs to share the root certificate which will be loaded into the Webex Contact Center SBC.
-
Customer needs to update the DNS to include the IPs of the Webex Contact Center SBCs.
-

 Feedback
Feedback