- Preface
-
- Configuring the Cisco Application Control Engine
- Configuring the Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch
- Configuring the Cisco Router with IVR
- Configuring Cisco Unified Communications Manager
- Configuring Cisco TelePresence Manager
- Configuring Cisco Session Border Controllers
- Configuring Cisco TelePresence MSE 8000 Series
- Configuring Internet Group Management Protocol for Multicast Support
- Glossary
Installation and Administration Guide for the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System Release 1.0
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- June 30, 2011
Chapter: Preparing for Installation
- Preinstallation Checklist
- Recommendations for Rack Mounting the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System and Other Solution Components
- Power Recommendations for High Availability of the Database Servers
- Cabling Requirements
- VLAN Requirements
- Gathering Required Information Before Installation
- Setting Up the IMM
Preparing for Installation
The following sections describe the activities that you must follow before installing the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System software:
•![]() Power Recommendations for High Availability of the Database Servers
Power Recommendations for High Availability of the Database Servers
•![]() Gathering Required Information Before Installation
Gathering Required Information Before Installation
Preinstallation Checklist
|
|
|
|---|---|
Rack mount the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System and solution components. See the "Recommendations for Rack Mounting the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System and Other Solution Components" section. |
|
Check that the power cords for your servers and monitors are securely attached and plugged in to working power sources. Cisco recommends that you use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) or dual power sources, especially for the database servers. See the "Power Recommendations for High Availability of the Database Servers" section. |
|
Check that the servers are properly cabled. See the "Cabling Requirements" section. |
|
Check that you can access the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers (database, administration, and call engine) by using a local console. |
|
Check that you have one of the following browsers for configuring and using the integrated management module (IMM): • • |
|
Verify that your Cisco TelePresence Exchange System installation DVD has the latest software version. If you are not sure, or if you do not have the DVD, download the latest software from the following URL, and burn the disk image onto a DVD: http://www.cisco.com/go/ctx-download. |
|
Verify that you have all the required information before you begin the installation. See the "Gathering Required Information Before Installation" section. |
|
If you plan to enable the domain name system (DNS) client on each Cisco TelePresence Exchange System server, enter each hostname and IP address into the DNS servers, including the virtual hostname and virtual IP (VIP) address that are shared by the database servers. |
|
Specifically for the database servers, if you use separate VLANs for the system management network (IMM) and data network (Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 2), make sure that packets can be routed between the separate VLANs. |
|
Verify that each VLAN that will have a Cisco TelePresence Exchange System server can connect to the NTP servers. |
|
Set up the IMM for each database server and, optionally, each call engine and administration server. See the "Setting Up the IMM" section. |
Recommendations for Rack Mounting the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System and Other Solution Components

Note ![]() Leave a space of one-third of a rack unit (RU) between each unit to provide proper ventilation.
Leave a space of one-third of a rack unit (RU) between each unit to provide proper ventilation.
Use the following list to determine the rack position of each solution component, where item 1 is at the top of the rack:
1. ![]() Cisco router with interactive voice response (IVR)—two systems
Cisco router with interactive voice response (IVR)—two systems
2. ![]() Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE)—two systems
Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE)—two systems
3. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server
Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server
4. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Manager
Cisco TelePresence Manager
5. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch
Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch
6. ![]() Keyboard-video-mouse (KVM) switch for console access to all systems
Keyboard-video-mouse (KVM) switch for console access to all systems
7. ![]() Power distribution unit (PDU)—two units for redundancy
Power distribution unit (PDU)—two units for redundancy
8. ![]() Cisco Catalyst Switch—two systems
Cisco Catalyst Switch—two systems
9. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Exchange System database servers—two servers
Cisco TelePresence Exchange System database servers—two servers
10. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Exchange System administration servers—two servers
Cisco TelePresence Exchange System administration servers—two servers
11. ![]() Cisco TelePresence Exchange System call engine servers—two servers
Cisco TelePresence Exchange System call engine servers—two servers

Note ![]() The Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco Session Border Controller are also part of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System solution, but Cisco expects that those components are already installed and in use in the network and therefore does not provide rack-mounting recommendations.
The Cisco Unified Communications Manager and Cisco Session Border Controller are also part of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System solution, but Cisco expects that those components are already installed and in use in the network and therefore does not provide rack-mounting recommendations.
Power Recommendations for High Availability of the Database Servers
In order for the high availability (HA) implementation to work properly for the database servers, each database server must be able to reach the integrated management module (IMM) of the peer database server. If the IMM of the primary database server is unreachable by the secondary database server, and the primary database server fails, the secondary database server cannot take over the primary role. In this situation, all calls to or from the system fail, and meetings cannot be scheduled or modified. To recover from this situation, see the "Recovering from a Failed Primary Database Server" section on page 33-1.
Because power loss causes the server and its IMM to fail, make sure that both power cords are securely attached to each database server. Also, Cisco recommends that you take at least one of the following actions to prevent power loss to the database servers:
•![]() Connect each power cord to an independent power supply, so that each database server has dual power sources.
Connect each power cord to an independent power supply, so that each database server has dual power sources.
•![]() Use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to prevent power loss to each database server.
Use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to prevent power loss to each database server.
The IMM of the peer database server may also become unreachable due to network issues. Therefore, ensure reliable network connectivity between the database servers by connecting the cables as specified in the "Cabling Requirements for the Database Servers" section.
Cabling Requirements
•![]() Cabling Requirements for the Database Servers
Cabling Requirements for the Database Servers
•![]() Cabling Requirements for the Administration and Call Engine Servers
Cabling Requirements for the Administration and Call Engine Servers
Cabling Requirements for the Database Servers
To provide active/standby redundancy for the database servers, you must connect the primary and secondary database servers as shown in Figure 4-1.

Note ![]() You can use straight-through or crossover cables for these connections.
You can use straight-through or crossover cables for these connections.
Figure 4-1 Required Cabling Between the Database Servers
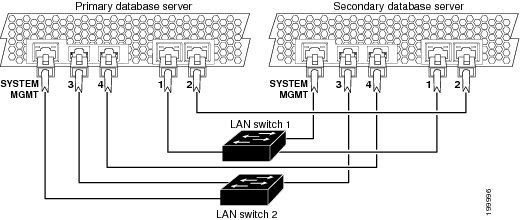
When the servers are cabled as shown in Figure 4-1, the system remains connected if any one component or cable fails. Specifically:
•![]() The IMM interfaces are connected to separate switches.
The IMM interfaces are connected to separate switches.
•![]() The NICs on each server are connected to separate switches.
The NICs on each server are connected to separate switches.
In each server, Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 1 are on one NIC, while Ethernet 3 and Ethernet 4 are on a second NIC.
•![]() On each database server, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System software automatically implements NIC teaming to bond the following interfaces together:
On each database server, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System software automatically implements NIC teaming to bond the following interfaces together:
–![]() Ethernet 0 with Ethernet 2.
Ethernet 0 with Ethernet 2.
–![]() Ethernet 1 with Ethernet 3.
Ethernet 1 with Ethernet 3.
•![]() Each NIC has a heartbeat connection to the redundant server.
Each NIC has a heartbeat connection to the redundant server.
Cabling Requirements for the Administration and Call Engine Servers
To provide switch and network redundancy for the administration servers and call engine servers, you must connect the servers as shown in Figure 4-2.

Note ![]() You can use straight-through or crossover cables for these connections.
You can use straight-through or crossover cables for these connections.
Figure 4-2 Required Cabling Between Administration Servers and Between Call Engine Servers
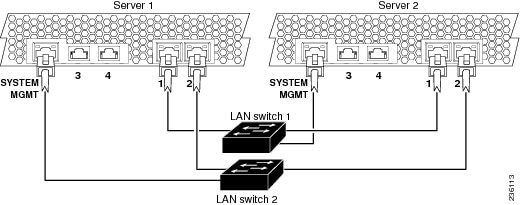
On each administration server and call engine server, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System software bonds Ethernet 0 with Ethernet 1. When the servers are cabled as shown in Figure 4-2, the bonded interface is connected to both LAN switches.
Cisco recommends that you connect the IMM interfaces to separate LAN switches.
VLAN Requirements
Apply the following requirements and recommendations as you assign IP addresses to the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System:
•![]() The following requirements apply to the data network interfaces of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System:
The following requirements apply to the data network interfaces of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System:
–![]() Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 2 of both database servers must be on the same VLAN.
Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 2 of both database servers must be on the same VLAN.
–![]() Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 1 of both administration servers and both call engine servers must be on the same VLAN.
Ethernet 0 and Ethernet 1 of both administration servers and both call engine servers must be on the same VLAN.
–![]() You may use the same VLAN for the data network interfaces of all nodes in the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System server cluster.
You may use the same VLAN for the data network interfaces of all nodes in the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System server cluster.
•![]() The data VLAN of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System call engine servers must be separate from the data VLANs that are used by the following solution components:
The data VLAN of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System call engine servers must be separate from the data VLANs that are used by the following solution components:
–![]() Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
–![]() Cisco Session Border Controller
Cisco Session Border Controller
–![]() Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch
Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch
–![]() Cisco Router with Integrated Voice Response (IVR)
Cisco Router with Integrated Voice Response (IVR)
•![]() Cisco recommends that you use a separate system management VLAN for the integrated management module (IMM) interfaces on the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers.
Cisco recommends that you use a separate system management VLAN for the integrated management module (IMM) interfaces on the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers.

Note ![]() Make sure that packets can be routed between all of the VLANs that you implement for the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System solution.
Make sure that packets can be routed between all of the VLANs that you implement for the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System solution.
Gathering Required Information Before Installation
Complete the worksheets in Appendix A, "Installation Worksheets," as you collect the following information. Before you proceed, however, read the "VLAN Requirements" section.
•![]() Unique hostnames:
Unique hostnames:
–![]() One hostname for each of the database, call engine, and administration servers.
One hostname for each of the database, call engine, and administration servers.
–![]() One virtual hostname to be shared by the two database servers.
One virtual hostname to be shared by the two database servers.
•![]() Unique IP addresses and their subnet masks:
Unique IP addresses and their subnet masks:
–![]() One IP address for each of the database, call engine, and administration servers.
One IP address for each of the database, call engine, and administration servers.
–![]() One virtual IP (VIP) address to be shared by the two database servers. The database VIP is the only address that the network recognizes for the database servers, only one of which is active at any given time.
One virtual IP (VIP) address to be shared by the two database servers. The database VIP is the only address that the network recognizes for the database servers, only one of which is active at any given time.
–![]() One IP address for each integrated management module (IMM) interface.
One IP address for each integrated management module (IMM) interface.
The two database servers are the only servers that require configured IMM interfaces, but you may want to configure the IMM interfaces on the call engine and administration servers to enable remote control of those servers.
•![]() IP address of the default gateway for each server and IMM interface.
IP address of the default gateway for each server and IMM interface.
•![]() Administrator usernames and passwords:
Administrator usernames and passwords:
–![]() For accessing the CLI of each database, administration, and call engine server. To simplify management, Cisco recommends that you use the same username and password on all Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers.
For accessing the CLI of each database, administration, and call engine server. To simplify management, Cisco recommends that you use the same username and password on all Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers.
–![]() For accessing each IMM interface. The two database servers are the only servers that require configured IMM interfaces, but you may want to configure the IMM interfaces on the call engine and administration servers to enable remote control of the servers.
For accessing each IMM interface. The two database servers are the only servers that require configured IMM interfaces, but you may want to configure the IMM interfaces on the call engine and administration servers to enable remote control of the servers.
•![]() A security password.
A security password.
The database server uses this password to authenticate data requests from the administration and call engine servers. Therefore, you must define the same security password for the database, administration, and call engine servers.

Note ![]() After you configure the security password on a server, you cannot change it without reinstalling the server.
After you configure the security password on a server, you cannot change it without reinstalling the server.
•![]() (Optional) Domain Name System (DNS) information:
(Optional) Domain Name System (DNS) information:
–![]() IP address of a primary DNS server.
IP address of a primary DNS server.
–![]() (Optional) IP address of a secondary DNS server.
(Optional) IP address of a secondary DNS server.
–![]() Domain name.
Domain name.
•![]() IP addresses, hostnames, or pool names for external Network Time Protocol (NTP) clocking sources. Cisco recommends that you use at least three external NTP clocking sources.
IP addresses, hostnames, or pool names for external Network Time Protocol (NTP) clocking sources. Cisco recommends that you use at least three external NTP clocking sources.
You must configure the same NTP entries on the database, call engine, and administration servers.
•![]() For the SIP load balancer, which is the Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE):
For the SIP load balancer, which is the Cisco Application Control Engine (ACE):
–![]() VIP address.
VIP address.
–![]() Port number—Cisco recommends that you use the default port 5060.
Port number—Cisco recommends that you use the default port 5060.
•![]() For generating locally significant certificates (LSC) for each database, call engine, and administration server:
For generating locally significant certificates (LSC) for each database, call engine, and administration server:
–![]() Organization—typically your company name.
Organization—typically your company name.
–![]() Unit—typically your business unit and department.
Unit—typically your business unit and department.
–![]() Location—typically the building, floor, and rack in which the server is installed.
Location—typically the building, floor, and rack in which the server is installed.
–![]() State and Country—where the server is located.
State and Country—where the server is located.
Use the following guidelines to determine each entry for generating LSCs:
–![]() Refer to your company guidelines for format and entry requirements.
Refer to your company guidelines for format and entry requirements.
–![]() Supported characters include alphanumeric, space, and the following special characters: .,-_:;{}()[]#.
Supported characters include alphanumeric, space, and the following special characters: .,-_:;{}()[]#.
–![]() Each field supports up to 255 characters.
Each field supports up to 255 characters.
Setting Up the IMM
You must set up the IMM on the database servers before you install the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System software. The IMM is required to implement active/standby redundancy for the two database servers.
You may also choose to set up the IMM on the administration and call engine servers to enable you to control those servers remotely; this remote access is available whenever the server is plugged in to a working power source, even if the server is turned off.
To set up the IMM, complete the following tasks:
•![]() Setting Up the IMM Network Connection
Setting Up the IMM Network Connection
Setting Up the IMM Network Connection
Before You Begin
Find your completed Appendix A, "Installation Worksheets."
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Attach a console to the console port of the server.
Attach a console to the console port of the server.
The console port is located on the front of the server.
Step 2 ![]() Turn the server on by pressing the power button that is located on the front of the server.
Turn the server on by pressing the power button that is located on the front of the server.
After approximately one minute, an IBM System x screen is displayed on the console.
Step 3 ![]() Watch for the F1 <setup> option to appear at the bottom of the IBM System x screen. This may take another minute or two.
Watch for the F1 <setup> option to appear at the bottom of the IBM System x screen. This may take another minute or two.
Step 4 ![]() Press the F1 key as soon as the option appears.
Press the F1 key as soon as the option appears.
If the option disappears before you press F1, then turn the server off and on, and try again.

Tip ![]() At any time in the following steps, if you accidentally end up in the wrong screen or select the wrong field, press the Esc key to back out of that screen or field selection.
At any time in the following steps, if you accidentally end up in the wrong screen or select the wrong field, press the Esc key to back out of that screen or field selection.
Step 5 ![]() In the System Configuration and Boot Management screen, select System Settings.
In the System Configuration and Boot Management screen, select System Settings.
Step 6 ![]() In the System Settings screen, select Integrated Management Module.
In the System Settings screen, select Integrated Management Module.
Step 7 ![]() In the Integrated Management Module screen, select Network Configuration.
In the Integrated Management Module screen, select Network Configuration.
Step 8 ![]() In the Network Configuration screen, select the DHCP Control field value.
In the Network Configuration screen, select the DHCP Control field value.
Step 9 ![]() In the DHCP Control field, select the Static IP option.
In the DHCP Control field, select the Static IP option.
Step 10 ![]() Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway IP address for the IMM interface.
Enter the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway IP address for the IMM interface.
Step 11 ![]() Select Save Network Settings.
Select Save Network Settings.
Step 12 ![]() Press the Enter or Return key to continue.
Press the Enter or Return key to continue.
Step 13 ![]() Press the Esc key repeatedly to exit each setup screen.
Press the Esc key repeatedly to exit each setup screen.
Step 14 ![]() When prompted, press the Y key to exit the setup utility.
When prompted, press the Y key to exit the setup utility.
The server reboots.
Step 15 ![]() Repeat this procedure for the redundant server.
Repeat this procedure for the redundant server.
What to Do Next
Proceed to the "Creating an IMM User Account" section.
Creating an IMM User Account
Before You Begin
•![]() Complete the procedure in the "Setting Up the IMM Network Connection" section.
Complete the procedure in the "Setting Up the IMM Network Connection" section.
•![]() Complete this task by using one of the following web browsers:
Complete this task by using one of the following web browsers:
–![]() Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 or later with the latest Service Pack
Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 or later with the latest Service Pack
–![]() Mozilla Firefox version 1.5 or later
Mozilla Firefox version 1.5 or later
•![]() Make sure that the browser allows popup windows from the IMM.
Make sure that the browser allows popup windows from the IMM.
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Point a web browser to the IP address of the IMM interface.
Point a web browser to the IP address of the IMM interface.
Step 2 ![]() Log in to the IMM web interface with following default username and password:
Log in to the IMM web interface with following default username and password:
username: USERID
password: PASSW0RD (Enter a zero instead of the letter O.)
Step 3 ![]() (Optional) Set the inactive session timeout value.
(Optional) Set the inactive session timeout value.
Step 4 ![]() Click Continue.
Click Continue.
Step 5 ![]() In the left navigation area, select System > IMM Control > Login Profiles.
In the left navigation area, select System > IMM Control > Login Profiles.
Step 6 ![]() In the Login Profiles area, click Add User.
In the Login Profiles area, click Add User.
Step 7 ![]() In the Login ID field, enter the username.
In the Login ID field, enter the username.
The username must have between 4 and 16 characters, and may include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, periods, and underscores.
Step 8 ![]() In the Password and Confirm password fields, enter a password that contains a minimum of five characters, one of which must be a nonalphabetic character. You cannot use a null or empty password.
In the Password and Confirm password fields, enter a password that contains a minimum of five characters, one of which must be a nonalphabetic character. You cannot use a null or empty password.
Step 9 ![]() Select the Supervisor authority level, which provides unlimited access.
Select the Supervisor authority level, which provides unlimited access.
Step 10 ![]() Click Save.
Click Save.
Step 11 ![]() (Optional) To prevent unauthorized access, change the password for the default IMM user account by completing these steps:
(Optional) To prevent unauthorized access, change the password for the default IMM user account by completing these steps:
a. ![]() In the Login Profiles area, click the USERID Login ID.
In the Login Profiles area, click the USERID Login ID.
b. ![]() Enter a new password into the Password and Confirm password fields.
Enter a new password into the Password and Confirm password fields.
c. ![]() Click Save.
Click Save.
What to Do Next
Proceed to the "Enabling SSH for the IMM" section.
Enabling SSH for the IMM
The secure shell (SSH) provides secure access to the command-line interface (CLI) and the serial redirect features of the IMM. An SSH user is authenticated by exchanging the username and password, which are sent after the encryption channel is established. The username and password can be one of the 12 username and password pairs that the server stores locally, or they can be stored on a lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) server. Public key authentication is not supported.
Before You Begin
•![]() Complete the procedure in the "Creating an IMM User Account" section.
Complete the procedure in the "Creating an IMM User Account" section.
•![]() Complete this task by using one of the following web browsers:
Complete this task by using one of the following web browsers:
–![]() Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 or later with the latest Service Pack
Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6.0 or later with the latest Service Pack
–![]() Mozilla Firefox version 1.5 or later
Mozilla Firefox version 1.5 or later
•![]() Make sure that the browser allows popup windows from the IMM.
Make sure that the browser allows popup windows from the IMM.
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() In the IMM web interface, choose System > IMM Control > Security.
In the IMM web interface, choose System > IMM Control > Security.
Step 2 ![]() Scroll down to the SSH Server Key Management area.
Scroll down to the SSH Server Key Management area.
Step 3 ![]() Click Generate SSH Server Private Key.
Click Generate SSH Server Private Key.
An SSH server key is used to authenticate the identity of the SSH server to the client.
Step 4 ![]() Wait for the progress bar to indicate completion.
Wait for the progress bar to indicate completion.
Step 5 ![]() In the SSH Server field, select Enabled.
In the SSH Server field, select Enabled.
Step 6 ![]() Click Save.
Click Save.
Step 7 ![]() In the left navigation area, select System > IMM Control > Restart IMM.
In the left navigation area, select System > IMM Control > Restart IMM.
Step 8 ![]() Click Restart.
Click Restart.
Step 9 ![]() Click OK to confirm the restart.
Click OK to confirm the restart.
 Feedback
Feedback