Administration Guide for Cisco TelePresence Software Release IX 8 and Later
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- May 11, 2017
Chapter: 802.1X Authentication
802.1X Authentication
IEEE 802.1X Authentication Overview
This section describes how to monitor and troubleshoot 802.1X authentication in the Cisco TelePresence System. 802.1X is an IEEE standard for port-based network access control. It offers the capability to permit or deny network connectivity, control Virtual LAN (VLAN) access, and apply traffic policy, based on user or machine identity.
802.1X permits or denies device access to the network by using authentication. Ethernet switch ports can be enabled dynamically based on the identity of the device that connects to it. Devices which are not authenticated cannot gain access to the network.
802.1X Authentication Components
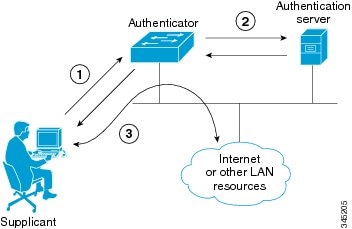
802.1X authentication involves the following three network devices:
- A supplicant : a client device (such as a laptop or endpoint) that attempts to access a LAN/Wireless LAN (WLAN), or the software that runs on this device and that provides credentials to the authenticator.
- An authenticator : a network device (such as an Ethernet switch or wireless access point) that acts as an access point to a protected network. For 802.1X authentication, the supplicant provides network credentials, such as username, password, digital security certificate, or a combination of these, to the authenticator. The authenticator then forwards the credentials to the authentication server for verification.
- An authentication server : a server (such as Cisco Secure Access Control Server) that guards the protected network. For 802.1X authentication, the authentication server receives the supplicant’s network credentials from the authenticator and verifies the supplicant’s identity. Then the supplicant is able to access the resources located on the network.
Figure 8-1 Diagram of 802.1X Authentication Process
Authenticating Your IX System
Your Cisco TelePresence IX system is equipped to function as an 802.1X-compliant supplicant. 802.1X authentication is enabled by default.

Note![]() Cisco recommends that you configure your switch port (or authenticator) for multi-domain mode.
Cisco recommends that you configure your switch port (or authenticator) for multi-domain mode.
Checking IX 802.1X Authentication Status
To check 802.1X authentication status in the Cisco TelePresence System, use either of the following options:
- View the IX main display screen during system bootup (see Checking 802.1X Authentication Status on the Main Display Screen)
- Enter the CLI command show dot1x status (see Checking 802.1X Authentication Status with a CLI Command)
Checking 802.1X Authentication Status on the Main Display Screen
To check the 802.1X authentication status on the Cisco TelePresence IX system main display screen, complete the following steps:
Step 1![]() Power off the Cisco TelePresence IX system.
Power off the Cisco TelePresence IX system.
Step 2![]() Power on the Cisco TelePresence IX system.
Power on the Cisco TelePresence IX system.
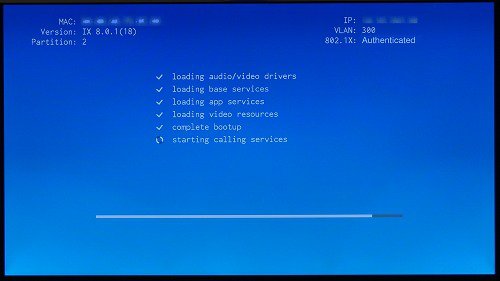
Step 3![]() View the bottom right of the main display screen. In a three-screen system, view the bottom-right of the center screen. Text will display to indicate whether 802.1X is authenticated, not authenticated, or not required on your system.
View the bottom right of the main display screen. In a three-screen system, view the bottom-right of the center screen. Text will display to indicate whether 802.1X is authenticated, not authenticated, or not required on your system.
This text, as viewed on the Cisco TelePresence System main display screen, indicates the success or failure of 802.1X authentication on that system. If the status line reads “Not Required,” 802.1X authentication is not required for that system.
Figure 8-2 Screenshot of Cisco TelePresence System Boot-Up Screen
See Table 8-1 for a summary of 802.1X authentication status displays for enabled and non-enabled networks.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|

Note![]() The 802.1X authentication status can only be viewed on your Cisco TelePresence System primary screen, not on a secondary screen (for example, a presentation screen, or in a three-screen system, the left or right screen). If the 802.1X authentication status does not show on the primary screen, follow the steps below listed under the “Checking 802.1X Authentication Status with a CLI Command” section
The 802.1X authentication status can only be viewed on your Cisco TelePresence System primary screen, not on a secondary screen (for example, a presentation screen, or in a three-screen system, the left or right screen). If the 802.1X authentication status does not show on the primary screen, follow the steps below listed under the “Checking 802.1X Authentication Status with a CLI Command” section
Checking 802.1X Authentication Status with a CLI Command
To check the 802.1X authentication status with a CLI command, complete the following steps:
Step 2![]() Input the following command: show dot1x status
Input the following command: show dot1x status
Step 3![]() View resulting text. Text will display indicating whether 802.1X is authenticated, not authenticated, or not required on your system.
View resulting text. Text will display indicating whether 802.1X is authenticated, not authenticated, or not required on your system.
Troubleshooting 802.1X Authentication Issues
When 802.1X does not authenticate properly, review the following sections:
Troubleshooting Issues in 802.1X Authentication
Table 8-2 summarizes some issues that may appear during 802.1X authentication, as well as potential resolutions.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Cisco Secure ACS authentication server rejects security certificate from the Cisco TelePresence System supplicant. |
The security certificate is invalid, expired, or not issued by CAPF. |
Install a valid, non-expired security certificate using the CAPF. See Viewing the Security Certificate. |
Errors may be present in the system’s most recent log files. |
Use the file list log dot1x command in the CLI to check logs for error or failure messages. |
|
Cisco TelePresence System displays “802.1X: Not Required” on its boot-up screen. |
Check the 802.1X authentication status on the Ethernet switch by logging into the switch and using the CLI command show authentication sessions interface { FastEthernet | GigabitEthernet } { Interface Number }. If the Ethernet switch is not 802.1X-enabled, enable it. Please refer to Identity-Based Networking Services: IP Telephony in IEEE 802.1X-Enabled Networks Deployment and Configuration Guide for instructions. |
|
Cisco Secure ACS authentication server rejects security certificate from the Cisco TelePresence System supplicant. |
Configure Cisco Secure ACS (and all backend network configurations) to support 802.1X. Please refer to Identity-Based Networking Services: IP Telephony in IEEE 802.1X-Enabled Networks Deployment and Configuration Guide for instructions. |
|
Cisco TelePresence System attempts authentication with the MIC instead of the LSC. |
The LSC has not been exported from CAPF and imported into Cisco Secure ACS. |
Check that the LSC is exported from CAPF and imported into Cisco Secure ACS. See Installing the LSC. |
After moving to a different CAPF and Unified CM, Cisco TelePresence System fails 802.1X authentication. |
The LSC no longer supports 802.1X authentication, since it was installed from the previous CAPF and Unified CM. Moving the Cisco TelePresence System to a different CAPF and Unified CM requires reinstalling the LSC and upgrading the system. |
Reinstall the LSC from Cisco Unified CM and upgrade the Cisco TelePresence System. See Installing the LSC. |
Viewing the Security Certificate
You may need to examine the security certificate (MIC or LSC) in order to verify that the certificates are valid, not expired, and issued by the CAPF. For more information on security certificates, see Examining the Security Certificate in Your IX System.
You can use the CLI or a third-party tool to view the MIC or LSC.
Viewing the Security Certificate from the CLI
To show the MIC or LSC from the CLI, complete the following steps:
Step 2![]() Enter the following command: show cert { mic | lsc }. You must enter either mic or lsc, not both.
Enter the following command: show cert { mic | lsc }. You must enter either mic or lsc, not both.
Step 3![]() View the certificate that displays within the CLI. Verify that the certificate is valid, not expired, and issued by the CAPF.
View the certificate that displays within the CLI. Verify that the certificate is valid, not expired, and issued by the CAPF.
Subject: C=US, O=organization, OU=department, CN=SEPXXXXXXXXXXXX
If you enter show cert lsc on a system where the LSC is not installed, the command line will read as follows:
If the security certificate is expired, invalid, or issued by a different source, install a new certificate using the CAPF.
Viewing the Security Certificate from a Third-Party Tool
You can also view the MIC or LSC using a third-party tool. Consult the documentation provided with the tool for instructions.
 Feedback
Feedback