Cisco Nexus 6000 Series NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 6.x
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- July 30, 2013
Chapter: Using PowerOn Auto Provisioning
Using PowerOn Auto Provisioning
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information About PowerOn Auto Provisioning
- Configuration_File_Selection_Methods
- Guidelines and Limitations for POAP
- Setting Up the Network Environment To Use POAP
- Configuring a Switch Using POAP
- Verifying the Device Configuration
Information About PowerOn Auto Provisioning
PowerOn Auto Provisioning (POAP) automates the process of upgrading software images and installing configuration files on Cisco Nexus switches that are being deployed in the network for the first time.
When a Cisco Nexus Series switch with the POAP feature boots and does not find the startup configuration, the switch enters POAP mode and checks for a USB device containing the configuration script file. If it finds one, it checks that device to see if it also contains the software image files and the switch configuration file.
If the switch does not find a USB device, or if the USB device does not contain the needed image files or switch configuration file, the switch also locates a DHCP server and bootstraps itself with its interface IP address, gateway, and DNS server IP addresses. The switch then obtains the IP address of a TFTP server or the URL of an HTTP server from which it downloads the necessary configuration files.
 Note | The DHCP information is used only during the POAP process if any configuration files are unavailable on the USB device. |
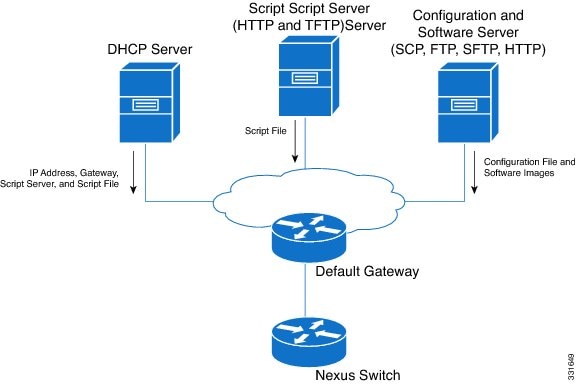
Network Requirements for POAP
POAP requires the following network infrastructure:
-
A DHCP server to bootstrap the interface IP address, gateway address, DNS server, and log server
-
A TFTP or HTTP server containing the configuration script used to automate the software image installation and configuration process
-
One or more servers containing the desired software images and configuration files
POAP Configuration Script
The reference script supplied by Cisco supports the following functionality:
Downloads the software image (system and kickstart images) if the files do not already exist on the switch. The software image is installed on the switch and is used at the next reboot.
Schedules the downloaded configuration to be applied at the next switch reboot.
Stores the configuration as the startup-configuration.
We provide sample configuration scripts that were developed using the Python programming language and Tool Command Language (Tcl). You can customize one of these scripts to meet the requirements of your network environment.
For information about customizing this script using Python, see the Cisco NX-OS Python API Reference Guide for your platform.
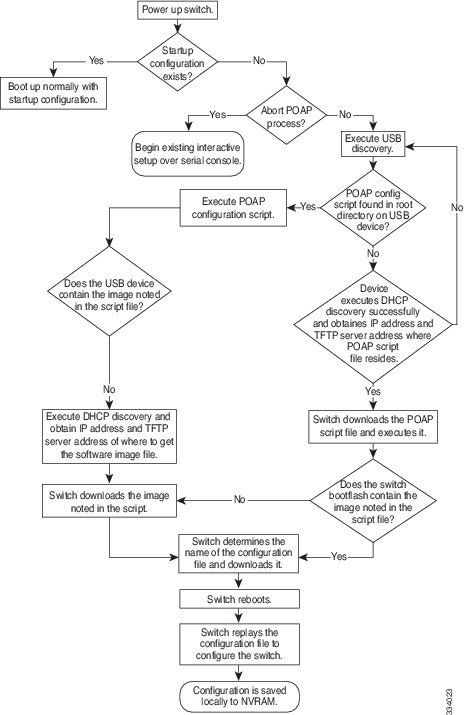
POAP Process
The POAP process has the following phases:
Within these phases, other process and decision points occur. The following illustration shows a flow diagram of the POAP process.
- Power-Up Phase
- USB Discovery Phase
- DHCP Discovery Phase
- Script Execution Phase
- Post-Installation Reload Phase
Power-Up Phase
When you power-up a switch for the first time, it loads the software image installed at manufacturing and tries to find a configuration file to apply after the switch boots. When no configuration file is found, POAP mode starts.
During startup, a prompt appears asking if you want to abort POAP and continue with normal setup. You can choose to exit or continue with POAP.
 Note | No user intervention is required for POAP to continue. The prompt that asks if you want to abort POAP remains available until the POAP process is complete. |
If you exit POAP mode, you enter the normal interactive setup script. If you continue in POAP mode, all the front-panel interfaces are set up in Layer 2 mode, which ensures that the device does not participate in any Layer 2 forwarding.
USB Discovery Phase
When POAP starts, the process searches the root directory of all accessible USB devices for the POAP configuration script file (either the Python script file, poap_script.py, or the Tcl script file, poap_script.tcl), configuration files, and system and kickstart images.
If the configuration script file is found on a USB device, POAP begins running the configuration script. If the configuration script file is not found on the USB device, POAP executes DHCP discovery. (When failures occur, the POAP process alternates between USB discovery and DHCP discovery, until POAP succeeds or you manually abort the POAP process.)
If the software image and switch configuration files specified in the configuration script are present, POAP uses those files to install the software and configure the switch. If the software image and switch configuration files are not on the USB device, POAP does some cleanup and starts DHCP phase from the beginning.
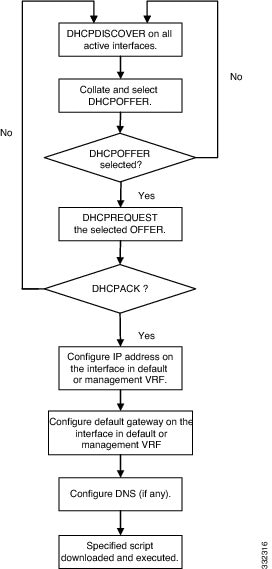
DHCP Discovery Phase
The switch sends out DHCP discover messages on all of the active interfaces (including the mgmt interface) soliciting DHCP offers from the DHCP server or servers. The DHCP client on the Cisco Nexus switch uses the switch serial number or its MAC address in the client-identifier option to identify itself to the DHCP server. The DHCP server can use this identifier to send information, such as the IP address and script file name, back to the DHCP client.
POAP requires a minimum DHCP lease period of 3600 seconds (1 hour). POAP checks the DHCP lease period. If the DHCP lease period is set to less than 3600 seconds (1 hour), POAP does not complete DHCP negotiation.
Option 66 ( TFTP server name) or Option 150 (TFTP server address)—The DHCP server relays the TFTP server name or TFTP server address to the DHCP client. The DHCP client uses this information to contact the TFTP server to obtain the script file.
IP address
Default gateway
Option 67 (Bootfile name)—The DHCP server relays the bootfile name to the DHCP client. The bootfile name includes the complete path to the bootfile on the TFTP server. The DHCP client uses this information to download the script file.
When multiple DHCP offers that meet the requirement are received, an offer is randomly chosen. The device completes the DHCP negotiation (request and acknowledgment) with the selected DHCP server, and the DHCP server assigns an IP address to the switch. If there is a failure in any of the subsequent steps in the POAP process, the IP address is released back to the DHCP server.
If no DHCP offers meet the requirements, the switch does not complete the DHCP negotiation (request and acknowledgment) and an IP address is not assigned. The POAP process is reinitiated until it succeeds or you manually abort the POAP process.
Script Execution Phase
Once the device has bootstrapped itself using the information in the DHCP acknowledgement, the switch downloads the script file from the TFTP server or the HTTP server.
The switch runs the configuration script, which downloads and installs the software image and downloads a switch-specific configuration file.
However, the configuration file is not applied to the switch at this point, because the software image currently running on the switch might not support all of the commands in the configuration file. After the switch reboots, it begins running the new software image, if one was installed. At that point, the configuration is applied to the switch.
 Note | If the switch loses connectivity, the script stops, and the switch reloads its original software images and bootup variables. |
Post-Installation Reload Phase
The switch restarts and applies (replays) the configuration on the upgraded software image. Afterward, the switch copies the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Configuration_File_Selection_Methods
Serial Number-Based Configuration File Selection
The switch can download a configuration file based on the switch's serial number. Name the configuration file with the serial number of the switch. For example, if a switch has serial number FOC1621R00R, the configuration file name is conf_FOC1621R00R.cfg.
Hostname-Based Configuration File Selection
When the switch solicits the DHCP server for its IP address and the configuration script filename, the DHCP server offers the switch hostname as well. Then, the switch downloads the configuration file for the specified hostname.
To download a configuration file based on the hostname of the switch, you must configure the following:
On the DHCP server, add the option host-name hostname command to the DHCP configuration file (dhcpd.conf). For example, add option host-name nexus-switch-1.
- In the configuration script, enable hostname support by modifying the configuration script to include the poap_config_file_mode = poap_hostname. When the switch runs the configuration script, the switch downloads the file that is named, conf_hostname.cfg, that includes the hostname retrieved from the DHCP server.
MAC-Based Configuration File Selection
The switch can use the MAC address of the mgmt 0 interface or of a single Layer 3 interface on the front panel to select the configuration file to be downloaded.
To use the MAC address to identify the configuration file to download, you need to modify the configuration script to include the poap_config_file_mode = poap_mac statement. When the switch runs the configuration script, the switch downloads the file that is named conf_mac-address.cfg, where the mac-addressis the MAC address of the switch. For example, using the MAC address of the management interface, 00:22:AA:BB:CC, the name of the configuration file that the switch downloads is conf_001122AABBCC.cfg.
Location-Based Configuration File Selection
The switch can download a configuration file based on the switch's location. POAP uses the show cdp neighbor interface command to derive the configuration file name. To download a configuration file based on the location of the switch, you must indicate poap_config_file_mode = poap_location in the POAP configuration script.
For example, Ethernet interface 1/1 on the Nexus 6000 Series switch is connected th Ethernet interface 1/2 on a Nexus 7000 Series switch. The configuration file name should be conf_N7k_eth1/2.cfg
Guidelines and Limitations for POAP
-
The Cisco Nexus switch software image must support POAP for this feature to function.
-
POAP does not support provisioning of the switch after it has been configured and is operational. Only auto-provisioning of a switch with no startup configuration is supported.
-
If you use POAP to bootstrap a Cisco Nexus device that is a part of a vPC pair using static port-channels on the VPC links, the Cisco Nexus device activates all of its links upon POAP startup. The dually connected device at the end of the VPC links might start sending some or all of its traffic to the port-channel member links connected to the Cisco Nexus device, and the traffic would be lost.
To work around this issue, you can configure LACP on the vPC links so that the links do not incorrectly start forwarding traffic to the Cisco Nexus device that is being bootstrapped using POAP.
-
If you use POAP to bootstrap a Cisco Nexus device that is connected downstream to a Cisco Nexus Series 7000 device through a LACP port-channel, the Cisco Nexus 7000 Series device defaults to suspend its member port if it cannot bundle it as a part of a port-channel. To work around this issue, configure the Cisco Nexus 7000 Series device to not suspend its member ports using the no lacp suspend-individual command from interface configuration mode.
-
Important POAP updates are logged in the syslog and are available from the serial console.
-
Critical POAP errors are logged to the bootflash. The filename format is date-time_poap_PID_[init,1,2].log, where date-time is in the YYYYMMDD_hhmmss format and PID is the process ID.
-
Script logs are saved in the bootflash directory. The filename format is date-time_poap_PID_script.log, where date-time is in the YYYYMMDD_hhmmss format and PID is the process ID.
-
If fabric extender or expansion module interfaces are configured in the configuration file that is used in the POAP process, you must use the Module Pre-Provisioning feature to provision these modules. For information about the Module Pre-Provisioning feature, see the Cisco Nexus System Management Configuration guide for your device.
-
During POAP, the Cisco Nexus devices boot up in Layer 2 mode by default. Therefore, uplink connectivity through the front panel ports must be in Layer 2 mode.
-
DHCP for NX-OS will be successful, if the DHCP response is set to IP address 255.255.255.255. Since not all the DHCP server including IOS DHCP server sends the DHCP responses to 255.255.255.255, NX-OS is unable to get an IP address as a result POAP does not succeed.
Setting Up the Network Environment To Use POAP
1. Modify the basic configuration script provided by Cisco or create your own script. For information, see the Python Scripting and API Configuration Guide.
2. (Optional) Put the POAP configuration script and any other desired software image and switch configuration files on a USB device accessible to the switch.
3. Deploy a DHCP server and configure it with the interface, gateway, and TFTP server IP addresses and a bootfile with the path and name of the configuration script file. (This information is provided to the switch when it first boots.)
4. Deploy a TFTP or HTTP server to host the configuration script.
5. Deploy one or more servers to host the software images and configuration files.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a Switch Using POAP
Make sure that the network environment is set up to use POAP. For more information, see the Setting Up the Network Environment To Use POAP section immediately preceeding this section.
1. Install the switch in the network.
2. Power on the switch.
3. (Optional) If you want to exit POAP mode and enter the normal interactive setup script, enter y (yes).
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 | Install the switch in the network. |
| Step 2 | Power on the
switch.
If no configuration file is found, the switch boots in POAP mode and displays a prompt that asks if you want to abort POAP and continue with a normal setup. No entry is required to continue to boot in POAP mode. |
| Step 3 | (Optional) If
you want to exit POAP mode and enter the normal interactive setup script, enter
y (yes).
The switch boots, and the POAP process begins. For more information, see the POAP Process section. |
What to Do Next
Verify the configuration.
Verifying the Device Configuration
To verify the configuration after bootstrapping the device using POAP, use one of the following commands:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
show running-config |
Displays the running configuration. |
|
show startup-config |
Displays the startup configuration. |
For detailed information about the fields in the output from these commands, see the Cisco Nexus command reference for your device.
 Feedback
Feedback