Information About IGMP Snooping
 Note |
We recommend that you do not disable IGMP snooping on the switch. If you disable IGMP snooping, you may see reduced multicast performance because of excessive false flooding within the switch. |
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping software examines Layer 2 IP multicast traffic within a VLAN to discover the ports where interested receivers reside. Using the port information, IGMP snooping can reduce bandwidth consumption in a multi-access LAN environment to avoid flooding the entire VLAN. The IGMP snooping feature tracks which ports are attached to multicast-capable routers to help the routers forward IGMP membership reports. The IGMP snooping software responds to topology change notifications. By default, IGMP snooping is enabled on the switch.
The following figure shows an IGMP snooping switch that sits between the host and the IGMP router. The IGMP snooping switch snoops the IGMP membership reports and Leave messages and forwards them only when necessary to the connected IGMP routers.
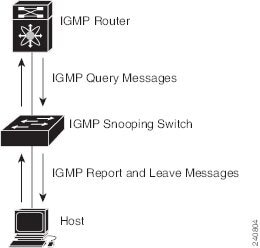
The IGMP snooping software operates upon IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 control plane packets where Layer 3 control plane packets are intercepted and influence the Layer 2 forwarding behavior.
For more information about IGMP, see .
The Cisco NX-OS IGMP snooping software has the following proprietary features:
-
Source filtering that allows forwarding of multicast packets based on destination and source IP.
-
Multicast forwarding based on IP address rather than MAC address.
-
Optimized multicast flooding (OMF) that forwards unknown traffic to routers only and performs no data driven state creation.
For more information about IGMP snooping, see RFC 4541.
This section includes the following topics:
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2
Both IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 support membership report suppression, which means that if two hosts on the same subnet want to receive multicast data for the same group, then the host that receives a member report from the other host suppresses sending its report. Membership report suppression occurs for hosts that share a port.
If no more than one host is attached to each VLAN switch port, then you can configure the fast leave feature in IGMPv2. The fast leave feature does not send last member query messages to hosts. As soon as the software receives an IGMP leave message, the software stops forwarding multicast data to that port.
IGMPv1 does not provide an explicit IGMP leave message, so the software must rely on the membership message timeout to indicate that no hosts remain that want to receive multicast data for a particular group.
 Note |
The software ignores the configuration of the last member query interval when you enable the fast leave feature because it does not check for remaining hosts. |
IGMPv3
The IGMPv3 snooping implementation on Cisco NX-OS supports full IGMPv3 snooping, which provides constrained flooding based on the (S, G) information in the IGMPv3 reports. This source-based filtering enables the switch to constrain multicast traffic to a set of ports based on the source that sends traffic to the multicast group.
By default, the software tracks hosts on each VLAN port. The explicit tracking feature provides a fast leave mechanism. Because every IGMPv3 host sends membership reports, report suppression limits the amount of traffic that the switch sends to other multicast-capable routers. When report suppression is enabled, and no IGMPv1 or IGMPv2 hosts requested the same group, the software provides proxy reporting. The proxy feature builds the group state from membership reports from the downstream hosts and generates membership reports in response to queries from upstream queriers.
Even though the IGMPv3 membership reports provide a full accounting of group members on a LAN segment, when the last host leaves, the software sends a membership query. You can configure the parameter last member query interval. If no host responds before the timeout, the software removes the group state.
IGMP Snooping Querier
When PIM is not enabled on an interface because the multicast traffic does not need to be routed, you must configure an IGMP snooping querier to send membership queries. You define the querier in a VLAN that contains multicast sources and receivers but no other active querier.
When an IGMP snooping querier is enabled, it sends out periodic IGMP queries that trigger IGMP report messages from hosts that want to receive IP multicast traffic. IGMP snooping listens to these IGMP reports to establish appropriate forwarding.
Currently, you can configure the same SVI IP address for the switch querier and the IGMP snooping querier. Both queriers will then be active at the same time, and both queriers will send general queries to the VLAN periodically. To prevent this from happening, ensure that you use different IP addresses for the IGMP snooping querier and the switch querier.
IGMP Snooping Filter
Cisco NX-OS Release 6.0(2)A4(1) supports filtering of IGMP packets at the snooping layer. You can filter out IGMP snooping reports at the interface level. This filtering is based on a prefix-list or a route-map policy. The router compares a group to the prefix-list or route-map policy defined and performs the specified action. Thus, only groups that match the prefix-list or route-map that you specify will be filtered to the IGMP snooping reports.
 Feedback
Feedback