Information About Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs
Many companies conduct most of their business online and any loss of service can affect the profitability of the company. Internet service providers (ISPs) and even internal IT departments now offer a defined level of service--a service level agreement--to provide their customers with a degree of predictability.
The latest performance requirements for business-critical applications, voice over IP (VoIP) networks, audio and visual conferencing, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are creating internal pressures on converged IP networks to become optimized for performance levels. Network administrators are increasingly required to support service level agreements that support application solutions. IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) allow you to manage IP service levels for IP applications and services.
 Note |
IPSLA do not support rollback. The rollback is related to IPSLA configuration via CLI. |
Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs provides the following improvements over a traditional service level agreement:
- End-to-end measurements—The ability to measure performance from one end of the network to the other allows a broader reach and more accurate representation of the end-user experience.
- Sophistication--Statistics such as delay, jitter, packet sequence, Layer 3 connectivity, and path and download time that are broken down into bidirectional and round-trip numbers provide more data than just the bandwidth of a Layer 2 link.
- Ease of deployment--Leveraging the existing Cisco devices in a large network makes Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs easier and cheaper to implement than the physical probes often required with traditional service level agreements.
- Application-aware monitoring--Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs can simulate and measure performance statistics generated by applications running over Layer 3 through Layer 7. Traditional service level agreements can only measure Layer 2 performance.
- Pervasiveness--Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs support exists in Cisco networking devices that range from low-end to high-end switches. This wide range of deployment gives Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs more flexibility over traditional service level agreements.
The following figure shows how Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs have taken the traditional concept of Layer 2 service level agreements and applied a broader scope to support end-to-end performance measurement, including support of applications.
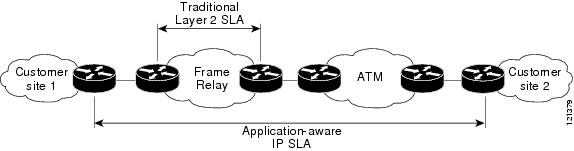
Using Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs, you can measure, provide, and verify service level agreements. You can also analyze and troubleshoot network performance for IP services and applications. Depending on the specific Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs operation, statistics of delay, packet loss, jitter, packet sequence, connectivity, path, server response time, and download time can be monitored within the Cisco device and stored in both CLI and SNMP MIBs. The packets have configurable IP and application layer options such as a source and destination IP address, User Datagram Protocol (UDP)/TCP port numbers, a type of service (ToS) byte (including Differentiated Services Code Point [DSCP] and IP prefix bits), a Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing/forwarding instance (VRF), and a URL web address.
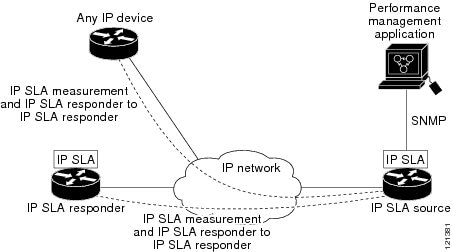
Because Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs are accessible using SNMP, it also can be used by performance monitoring applications such as CiscoWorks Internetwork Performance Monitor (IPM) and other third-party, Cisco partner performance management products.
SNMP notifications based on the data gathered by a Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs operation allow the switch to receive alerts when performance drops below a specified level and when problems are corrected. Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs use the Cisco RTTMON MIB for interaction between external Network Management System (NMS) applications and the Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs operations running on the Cisco devices. For a complete description of the object variables referenced by the Cisco NX-OS IP SLAs feature, see the text of the CISCO-RTTMON-MIB.my file, available from the Cisco MIB website.
 Feedback
Feedback