- New and Changed Information
- Preface
- Overview
- Tools
- Installation
- Licenses
- Upgrade
- High Availability
- VSM and VEM Modules
- Ports
- Port Profiles
- Port Channels and Trunking
- Layer 2 Switching
- VLAN
- Private VLAN
- NetFlow
- ACL
- Quality of Service
- SPAN
- Multicast IGMP
- DHCP, DAI, and IPSG
- Virtual Service Domain
- System
- Network Segmentation Manager
- VXLANs
- Ethanalyzer
- Before Contacting Technical Support
- Index
Cisco Nexus 1000V Troubleshooting Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.1)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- January 31, 2012
Chapter: Layer 2 Switching
Layer 2 Switching
This chapter describes how to identify and resolve problems that relate to Layer 2 switching.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•![]() Information About Layer 2 Ethernet Switching
Information About Layer 2 Ethernet Switching
•![]() Troubleshooting Microsoft NLB Unicast Mode
Troubleshooting Microsoft NLB Unicast Mode
Information About Layer 2 Ethernet Switching
Nexus1000V provides a distributed, layer 2 virtual switch that extends across many virtualized hosts.
It consists of two components:
•![]() Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM), which is also known as the Control Plane (CP), acts as the Supervisor and contains the Cisco CLI, configuration, and high-level features.
Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM), which is also known as the Control Plane (CP), acts as the Supervisor and contains the Cisco CLI, configuration, and high-level features.
•![]() Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM), which is also known as the Data Plane (DP), acts as a line card and runs in each virtualized server to handle packet forwarding and other localized functions.
Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM), which is also known as the Data Plane (DP), acts as a line card and runs in each virtualized server to handle packet forwarding and other localized functions.
Port Model
This section describes the following port perspectives:
Viewing Ports from the VEM
The Nexus1000V differentiates between virtual and physical ports on each of the VEMs. Figure 11-1 shows how ports on the Nexus1000V switch are bound to physical and virtual VMware ports within a VEM.
Figure 11-1 VEM View of Ports
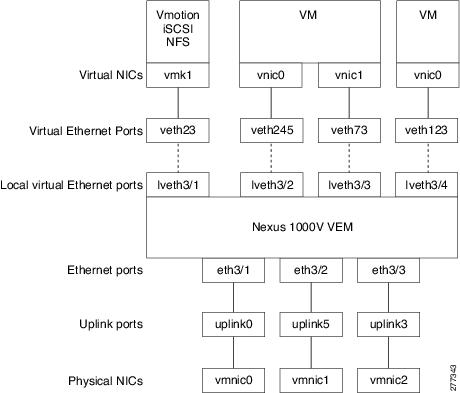
On the virtual side of the switch, there are three layers of ports that are mapped together:
•![]() Virtual NICs: There are three types of Virtual NICs in VMware. The virtual NIC (vnic) is part of the VM, and represents the physical port of the host which is plugged into the switch. The virtual kernel NIC (vmknic) is used by the hypervisor for management, VMotion, iSCSI, NFS and other network access needed by the kernel. This interface would carry the IP address of the hypervisor itself, and is also bound to a virtual Ethernet port. The vswif (not shown) appears only in COS-based systems, and is used as the VMware management port. Each of these types maps to a veth port within Nexus1000V.
Virtual NICs: There are three types of Virtual NICs in VMware. The virtual NIC (vnic) is part of the VM, and represents the physical port of the host which is plugged into the switch. The virtual kernel NIC (vmknic) is used by the hypervisor for management, VMotion, iSCSI, NFS and other network access needed by the kernel. This interface would carry the IP address of the hypervisor itself, and is also bound to a virtual Ethernet port. The vswif (not shown) appears only in COS-based systems, and is used as the VMware management port. Each of these types maps to a veth port within Nexus1000V.
•![]() Virtual Ethernet Ports (VEth): A VEth port is a port on the Cisco Nexus 1000V Distributed Virtual Switch. Cisco Nexus 1000V has a flat space of VEth ports 0..N. The virtual cable plugs into these VEth ports that are moved to the host running the VM.
Virtual Ethernet Ports (VEth): A VEth port is a port on the Cisco Nexus 1000V Distributed Virtual Switch. Cisco Nexus 1000V has a flat space of VEth ports 0..N. The virtual cable plugs into these VEth ports that are moved to the host running the VM.
VEth ports are assigned to port groups.
•![]() Local Virtual Ethernet Ports (lveth): Each host has a number of local VEth ports. These ports are dynamically selected for VEth ports that are needed on the host.
Local Virtual Ethernet Ports (lveth): Each host has a number of local VEth ports. These ports are dynamically selected for VEth ports that are needed on the host.
These local ports do not move, and are addressable by the module-port number method.
On the physical side of the switch, from bottom to top:
•![]() Each physical NIC in VMware is represented by an interface called a vmnic. The vmnic number is allocated during VMware installation, or when a new physical NIC is installed, and remains the same for the life of the host.
Each physical NIC in VMware is represented by an interface called a vmnic. The vmnic number is allocated during VMware installation, or when a new physical NIC is installed, and remains the same for the life of the host.
•![]() Each uplink port on the host represents a physical interface. It acts a lot like an lveth port, but because physical ports do not move between hosts, the mapping is 1:1 between an uplink port and a vmnic.
Each uplink port on the host represents a physical interface. It acts a lot like an lveth port, but because physical ports do not move between hosts, the mapping is 1:1 between an uplink port and a vmnic.
•![]() Each physical port added to Nexus1000V switch appears as a physical Ethernet port, just as it would on a hardware-based switch.
Each physical port added to Nexus1000V switch appears as a physical Ethernet port, just as it would on a hardware-based switch.
The uplink port concept is handled entirely by VMware, and is used to associate port configuration with vmnics. There is no fixed relationship between the uplink # and vmnic #, and these can be different on different hosts, and can change throughout the life of the host. On the VSM, the Ethernet interface number, such as ethernet 2/4, is derived from the vmnic number, not the uplink number.
Viewing Ports from the VSM
Figure 11-2 shows the VSM view ports.
Figure 11-2 VSM View of Ports
Port Types
The following types of ports are available:
•![]() Veths (Virtual Ethernet Interfaces) can be associated with any one of the following:
Veths (Virtual Ethernet Interfaces) can be associated with any one of the following:
–![]() VNICs of a Virtual Machine on the ESX Host.
VNICs of a Virtual Machine on the ESX Host.
–![]() VMKNICs of the ESX Host
VMKNICs of the ESX Host
–![]() VSWIFs of an ESX COS Host.
VSWIFs of an ESX COS Host.
•![]() Eths (Physical Ethernet Interfaces) - correspond to the Physical NICs on the ESX Host.
Eths (Physical Ethernet Interfaces) - correspond to the Physical NICs on the ESX Host.
•![]() Po (Port Channel Interfaces) - The physical NICs of an ESX Host can be bundled into a logical interface. This logical bundle is referred to as a port channel interface.
Po (Port Channel Interfaces) - The physical NICs of an ESX Host can be bundled into a logical interface. This logical bundle is referred to as a port channel interface.
For more information about Layer 2 switching, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 4.2(1)SV1(5.1).
Layer 2 Switching Problems
This section describes how to troubleshoot Layer 2 problems and lists troubleshooting commands. This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Verifying a Connection Between VEM Ports
Verifying a Connection Between VEM Ports
•![]() Verifying a Connection Between VEMs
Verifying a Connection Between VEMs
•![]() Isolating Traffic Interruptions
Isolating Traffic Interruptions
Verifying a Connection Between VEM Ports
To verify a connection between two veth ports on a VEM, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() On the VSM, enter the show vlan command to view the state of the VLANs associated with the port. If the VLAN associated with a port is not active, then the port may be down. In this case, you must create the VLAN and activate it.
On the VSM, enter the show vlan command to view the state of the VLANs associated with the port. If the VLAN associated with a port is not active, then the port may be down. In this case, you must create the VLAN and activate it.
Step 2 ![]() To see the state of the port on the VSM, enter a show interface brief command.
To see the state of the port on the VSM, enter a show interface brief command.
Step 3 ![]() Enter the module vem module-number execute vemcmd show port command to display the ports that are present on the VEM, their local interface indices, VLAN, type (physical or virtual), CBL state, port mode, and port name.
Enter the module vem module-number execute vemcmd show port command to display the ports that are present on the VEM, their local interface indices, VLAN, type (physical or virtual), CBL state, port mode, and port name.
The key things to look for in the output are:
•![]() State of the port.
State of the port.
•![]() CBL.
CBL.
•![]() Mode.
Mode.
•![]() Attached device name.
Attached device name.
•![]() The LTL of the port you are trying to troubleshoot. It will help you identify the interface quickly in other VEM commands where the interface name is not displayed.
The LTL of the port you are trying to troubleshoot. It will help you identify the interface quickly in other VEM commands where the interface name is not displayed.
•![]() Make sure the state of the port is up. If not, verify the configuration of the port on the VSM.
Make sure the state of the port is up. If not, verify the configuration of the port on the VSM.
Step 4 ![]() To view the VLANs and their port lists on a particular VEM, use the module vem module-number execute vemcmd show bd command:
To view the VLANs and their port lists on a particular VEM, use the module vem module-number execute vemcmd show bd command:
n1000V# module vem 5 execute vemcmd show bd
If you are trying to verify that a port belongs to a particular VLAN, make suer you see the port name or LTL in the port list of that VLAN.
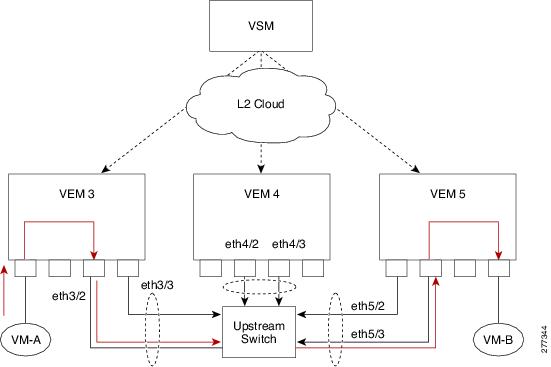
Verifying a Connection Between VEMs
To verify a connection between veth ports on two separate VEMs, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Issue the show vlan command to check if the VLAN associated with the port is created on the VSM.
Issue the show vlan command to check if the VLAN associated with the port is created on the VSM.
Step 2 ![]() Issue the show interface brief command to check if the ports are up in the VSM.
Issue the show interface brief command to check if the ports are up in the VSM.
Step 3 ![]() On the VEM, issue the module vem 3 execute vemcmd show port command to check if the CBL state of the two ports is set to the value of 1 for forwarding (active).
On the VEM, issue the module vem 3 execute vemcmd show port command to check if the CBL state of the two ports is set to the value of 1 for forwarding (active).
Step 4 ![]() On the VEM, issue the module vem 3 execute vemcmd show bd command to check if the two veth ports are listed in the flood list of the VLAN to which they are trying to communicate.
On the VEM, issue the module vem 3 execute vemcmd show bd command to check if the two veth ports are listed in the flood list of the VLAN to which they are trying to communicate.
Step 5 ![]() Verify that the uplink switch to which the VEMs are connected is carrying the VLAN to which the ports belong.
Verify that the uplink switch to which the VEMs are connected is carrying the VLAN to which the ports belong.
Step 6 ![]() Find out the port on the upstream switch to which the pnic (that is supposed to be carrying the VLAN) on the VEM is connected to.
Find out the port on the upstream switch to which the pnic (that is supposed to be carrying the VLAN) on the VEM is connected to.
n1000v# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans-Bridge, B - Source-Route-Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater,
V - VoIP-Phone, D - Remotely-Managed-Device,
s - Supports-STP-Dispute
Device ID Local Intrfce Hldtme Capability Platform Port ID
swordfish-6k-2 Eth5/2 168 R S I WS-C6506-E Gig1/38
The PNIC (Eth 5/2) is connected to swordfish-6k-2 on port Gig1/38.
Step 7 ![]() Log in to the upstream switch and make sure the port is configured to allow the VLAN you are looking for.
Log in to the upstream switch and make sure the port is configured to allow the VLAN you are looking for.
n1000v#show running-config interface gigabitEthernet 1/38
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 161 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/38
description Srvr-100:vmnic1
switchport
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,60-69,231-233
switchport mode trunk
end
As this output shows, VLANs 1,60-69, 231-233 are allowed on the port. If a particular VLAN is not in the allowed VLAN list, make sure to add it to the allowed VLAN list of the port.
Isolating Traffic Interruptions
Use the following steps to isolate the cause for no traffic passing across VMs on different VEMs.
Step 1 ![]() In output of the show port-profile name command, verify the following information:
In output of the show port-profile name command, verify the following information:
•![]() The control and packet VLANs that you configured are present (in the example, these are 3002 and 3003)
The control and packet VLANs that you configured are present (in the example, these are 3002 and 3003)
•![]() If the physical NIC in your configuration carries the VLAN for VM, then that VLAN is also present in the allowed VLAN list.
If the physical NIC in your configuration carries the VLAN for VM, then that VLAN is also present in the allowed VLAN list.
n1000v#show port-profile name alluplink
port-profile alluplink
description:
status: enabled
system vlans: 3002,3003
port-group: alluplink
config attributes:
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,80,3002,610,620,630-650
no shutdown
evaluated config attributes:
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,80,3002,3003,610,620,630-650
no shutdown
assigned interfaces:
Ethernet2/2
Step 2 ![]() Inside the VM, use the following command to verify that the Ethernet interface is up.
Inside the VM, use the following command to verify that the Ethernet interface is up.
ifconfig -a
If not, consider deleting that NIC from the VM, and adding another NIC.
Step 3 ![]() Using any sniffer tool, verify that ARP requests and responses are received on the VM interface.
Using any sniffer tool, verify that ARP requests and responses are received on the VM interface.
Step 4 ![]() On the upstream switch, use the following commands to look for the association between the IP and MAC address:
On the upstream switch, use the following commands to look for the association between the IP and MAC address:
debug arp
show arp
Example:
n1000v_CAT6K# debug arp
ARP packet debugging is on
11w4d: RARP: Rcvd RARP req for 0050.56b7.3031
11w4d: RARP: Rcvd RARP req for 0050.56b7.3031
11w4d: RARP: Rcvd RARP req for 0050.56b7.4d35
11w4d: RARP: Rcvd RARP req for 0050.56b7.52f4
11w4d: IP ARP: rcvd req src 10.78.1.123 0050.564f.3586, dst 10.78.1.24 Vlan3002
11w4d: RARP: Rcvd RARP req for 0050.56b7.3031
n1000v_CAT6K#
Example:
n1000v_CAT6K# sh arp
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 10.78.1.72 - 001a.6464.2008 ARPA
Internet 7.114.1.100 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan140
Internet 41.0.0.1 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan410
Internet 7.61.5.1 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan1161
Internet 10.78.1.5 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan3002
Internet 7.70.1.1 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan700
Internet 7.70.3.1 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan703
Internet 7.70.4.1 - 0011.bcac.6c00 ARPA Vlan704
Internet 10.78.1.1 0 0011.bc7c.9c0a ARPA Vlan3002
Internet 10.78.1.15 0 0050.56b7.52f4 ARPA Vlan3002
Internet 10.78.1.123 0 0050.564f.3586 ARPA Vlan3002
Step 5 ![]() You have completed this procedure.
You have completed this procedure.
Verifying Layer 2 Switching
Use the following commands to display and verify the Layer 2 MAC address configuration.
|
|
|
|---|---|
show mac address-table |
Displays the MAC address table to verify all MAC addresses on all VEMs controlled by the VSM. See Example 11-1 |
show mac address-table module module-number |
Displays all the MAC addresses on the specified VEM. |
show mac address-table static HHHH.WWWW.HHHH |
Displays the MAC address table static entries. See Example 11-2 |
show mac address-table address HHHH.WWWW.HHHH |
Displays the interface on which the MAC address specified is learned or configured. • • |
show mac address-table static | inc veth |
Displays the static MAC address of vEthernet interfaces in case a VEM physical port learns a dynamic MAC and the packet source is in another VEM on the same VSM. See Example 11-3 |
show running-config vlan <vlan-id> |
Displays VLAN information in the running configuration. |
show vlan [all-ports | brief | id <vlan-id> | name <name> | dot1q tag native] |
Displays VLAN information as specified. See Example 11-4. |
show vlan summary |
Displays a summary of VLAN information. |
show interface brief |
Displays a table of interface states. |
module vem module-number execute vemcmd show port |
On the VEM, displays the port state on a particular VEM. This command can only be used from the VEM. See Example 11-6. |
module vem module-number execute vemcmd show bd command |
For the specified VEM, displays its VLANs and their port lists. See Example 11-7. |
module vem module-number execute vemcmd show trunk |
For the specified VEM, displays the VLAN state on a trunk port. • • See Example 11-8. |
module vem module-number execute vemcmd show l2 vlan-id |
For the specified VEM, displays the VLAN forwarding table for a specified VLAN. See Example 11-9. |
show interface interface_id mac |
Displays the MAC addresses and the burn-in MAC address for an interface. |
Example 11-1 show mac address-table

Note ![]() The Cisco Nexus 1000VMAC address table does not display multicast MAC addresses.
The Cisco Nexus 1000VMAC address table does not display multicast MAC addresses.

Tip ![]() Module indicates the VEM on which this MAC is seen.
Module indicates the VEM on which this MAC is seen.
N1KV Internal Port refers to an internal port created on the VEM. This port is used for control and management of the VEM and is not used for forwarding packets.
n1000v# show mac address-table
VLAN MAC Address Type Age Port Module
---------+-----------------+-------+---------+------------------------------+---------
1 0002.3d11.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d21.5500 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d21.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d31.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d41.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d61.5500 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d61.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
1 0002.3d81.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
3 12ab.47dd.ff89 static 0 Eth3/3 3
342 0002.3d41.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
342 0050.568d.5a3f dynamic 0 Eth3/3 3
343 0002.3d21.5502 static 0 N1KV Internal Port 3
343 0050.568d.2aa0 dynamic 9 Eth3/3 3
Total MAC Addresses: 13
n1000v#
Example 11-2 show mac address-table address

Tip ![]() This command shows all interfaces on which a MAC is learned dynamically.
This command shows all interfaces on which a MAC is learned dynamically.
In this example, the same MAC appears on Eth3/3 and Eth4/3.
n1000v# show mac address-table address 0050.568d.5a3f
VLAN MAC Address Type Age Port Module
---------+-----------------+-------+---------+------------------------------+---------
342 0050.568d.5a3f dynamic 0 Eth3/3 3
342 0050.568d.5a3f dynamic 0 Eth4/3 4 Total MAC Addresses: 1
n1000v#
Example 11-3 show mac address-table static | inc veth
n1000v# show mac address-table static | inc veth
460 0050.5678.ed16 static 0 Veth2 3
460 0050.567b.1864 static 0 Veth1 4
n1000v#
Example 11-4 show vlan

Tip ![]() This command shows the state of each VLAN created on the VSM.
This command shows the state of each VLAN created on the VSM.
n1000v# show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Eth3/3, Eth3/4, Eth4/2, Eth4/3
110 VLAN0110 active
111 VLAN0111 active
112 VLAN0112 active
113 VLAN0113 active
114 VLAN0114 active
115 VLAN0115 active
116 VLAN0116 active
117 VLAN0117 active
118 VLAN0118 active
119 VLAN0119 active
800 VLAN0800 active
801 VLAN0801 active
802 VLAN0802 active
803 VLAN0803 active
804 VLAN0804 active
805 VLAN0805 active
806 VLAN0806 active
807 VLAN0807 active
808 VLAN0808 active
809 VLAN0809 active
810 VLAN0810 active
811 VLAN0811 active
812 VLAN0812 active
813 VLAN0813 active
814 VLAN0814 active
815 VLAN0815 active
816 VLAN0816 active
817 VLAN0817 active
818 VLAN0818 active
819 VLAN0819 active
820 VLAN0820 active
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
Remote SPAN VLANs
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- --------------- -------------------------------------------
Example 11-5 show interface brief
n1000v# show int brief
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Port VRF Status IP Address Speed MTU
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
mgmt0 -- up 172.23.232.143 1000 1500
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ethernet VLAN Type Mode Status Reason Speed Port
Interface Ch #
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eth3/4 1 eth trunk up none 1000(D) --
Eth4/2 1 eth trunk up none 1000(D) --
Eth4/3 1 eth trunk up none 1000(D) --
Example 11-6 module vem module-number execute vemcmd show port

Tip ![]() Look for the state of the port.
Look for the state of the port.
~ # module vem 3 execute vemcmd show port
LTL IfIndex Vlan Bndl SG_ID Pinned_SGID Type Admin State CBL Mode Name
8 0 3969 0 2 2 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l20
9 0 3969 0 2 2 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l21
10 0 115 0 2 0 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l22
11 0 3968 0 2 2 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l23
12 0 116 0 2 0 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l24
13 0 1 0 2 2 VIRT UP UP 0 Access l25
14 0 3967 0 2 2 VIRT UP UP 1 Access l26
16 1a030100 1 T 0 0 2 PHYS UP UP 1 Trunk vmnic1
17 1a030200 1 T 0 2 2 PHYS UP UP 1 Trunk vmnic2
Example 11-7 module vem module-number execute vemcmd show bd

Tip ![]() If a port belongs to a particular VLAN, the port name or LTL should be in the port list for the VLAN.
If a port belongs to a particular VLAN, the port name or LTL should be in the port list for the VLAN.
~ # module vem 5 execute vemcmd show bd
Number of valid BDS: 8 BD 1, vdc 1, vlan 1, 2 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1 17 vmnic2
BD 100, vdc 1, vlan 100, 0 ports Portlist: BD 110, vdc 1, vlan 110, 1 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1
BD 111, vdc 1, vlan 111, 1 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1
BD 112, vdc 1, vlan 112, 1 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1
BD 113, vdc 1, vlan 113, 1 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1
BD 114, vdc 1, vlan 114, 1 ports Portlist: 16 vmnic1
BD 115, vdc 1, vlan 115, 2 ports Portlist: 10 l22 16 vmnic1
Example 11-8 module vem module-number execute vemcmd show trunk

Tip ![]() If a VLAN is active on a port, then its CBL state should be 1.
If a VLAN is active on a port, then its CBL state should be 1.
If a VLAN is blocked, then its CBL state is 0.
~ # module vem 5 execute vemcmd show trunk
Trunk port 16 native_vlan 1 CBL 1
vlan(1) cbl 1, vlan(110) cbl 1, vlan(111) cbl 1, vlan(112) cbl 1, vlan(113) cbl 1, vlan(114) cbl 1,vlan(115) cbl 1, vlan(116) cbl 1, vlan(117) cbl 1, vlan(118) cbl 1, vlan(119) cbl 1,
Trunk port 17 native_vlan 1 CBL 0
vlan(1) cbl 1, vlan(117) cbl 1,
~ #
Example 11-9 module vem module-number execute vemcmd show l2
Bridge domain 115 brtmax 1024, brtcnt 2, timeout 300 Dynamic MAC 00:50:56:bb:49:d9 LTL 16 timeout 0 Dynamic MAC 00:02:3d:42:e3:03 LTL 10 timeout 0
Troubleshooting Microsoft NLB Unicast Mode
Microsoft Network Load Balancing (MS-NLB) is a clustering technology offered by Microsoft as part of the Windows server operating systems. Clustering enables a group of independent servers to be managed as a single system for higher availability, easier manageability, and greater scalability.
For more information about Microsoft Network Load Balancing. See this URL:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb742455.aspx

Note ![]() Access to third-party websites identified in this document is provided solely as a courtesy to customers and others. Cisco Systems, Inc. and its affiliates are not in any way responsible or liable for the functioning of any third-party website, or the download, performance, quality, functioning or support of any software program or other item accessed through the website, or any damages, repairs, corrections or costs arising out of any use of the website or any software program or other item accessed through the website. Cisco's End User License Agreement does not apply to the terms and conditions of use of a third-party website or any software program or other item accessed through the website.
Access to third-party websites identified in this document is provided solely as a courtesy to customers and others. Cisco Systems, Inc. and its affiliates are not in any way responsible or liable for the functioning of any third-party website, or the download, performance, quality, functioning or support of any software program or other item accessed through the website, or any damages, repairs, corrections or costs arising out of any use of the website or any software program or other item accessed through the website. Cisco's End User License Agreement does not apply to the terms and conditions of use of a third-party website or any software program or other item accessed through the website.
Limitations and Restrictions
A syslog is generated if one of the following configurations exists when you try to disable automatic static MAC learning for MS-NLB because they do not support this feature:
•![]() PVLAN port
PVLAN port
•![]() Ports configured with unknown unicast flood blocking (UUFB)
Ports configured with unknown unicast flood blocking (UUFB)
•![]() Ports configured with switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Ports configured with switchport port-security mac-address sticky
Disabling Automatic Static MAC Learning on vEthernet
You must disable automatic static MAC learning before you can successfully configure NLB on vEthernet (vEth).
In interface configuration mode use the following commands:
switch(config)# int veth 1
switch(config-if)# no mac auto-static-learn
In port profile configuration mode use the following commands:
switch(config)# port-profile type vethernet ms-nlb
switch(config-port-prof)# no mac auto-static-learn
Checking Status on a VSM
If the NLB unicast mode configuration does not function, check the status of the Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM).
Confirm that no mac auto-static-learn is listed in the vEth and/or port profile configurations.
In interface configuration mode use the following command to generate the VSM status:
switch(config-if)# show running-config int veth1
interface Vethernet1
inherit port-profile vm59
description Fedora117, Network Adapter 2
no mac auto-static-learn
vmware dvport 32 dvswitch uuid "ea 5c 3b 50 cd 00 9f 55-41 a3 2d 61 84 9e 0e c4"
In port profile configuration mode use the following command to generate the VSM status:
switch(config-if)# show running-config port-profile ms-nlb
port-profile type vethernet ms-nlb
vmware port-group
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 59
no mac auto-static-learn
no shutdown
state enabled
Checking Status on a VEM
If the NLB unicast mode configuration does not function, check the status of the Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM). Check the following:
•![]() Confirm that MS-NLB veths are disabled.
Confirm that MS-NLB veths are disabled.
•![]() Confirm that MS-NLB shared-MAC (starting with 02:BF) is not listed in the layer 2 (L2) MAC table
Confirm that MS-NLB shared-MAC (starting with 02:BF) is not listed in the layer 2 (L2) MAC table
Use the following command to generate the VEM status:
~ # vemcmd show port auto-smac-learning
LTL VSM Port Auto Static MAC Learning
49 Veth4 DISABLED
50 Veth5 DISABLED
51 Veth6 DISABLED
Use the following command to generate the L2 MAC table for VLAN59:
~ # vemcmd show l2 59
Bridge domain 15 brtmax 4096, brtcnt 6, timeout 300
VLAN 59, swbd 59, ""
Flags: P - PVLAN S - Secure D - Drop
Type MAC Address LTL timeout Flags PVLAN
Dynamic 00:15:5d:b4:d7:02 305 4
Dynamic 00:15:5d:b4:d7:04 305 25
Dynamic 00:50:56:b3:00:96 51 4
Dynamic 00:50:56:b3:00:94 305 5
Dynamic 00:0b:45:b6:e4:00 305 5
Dynamic 00:00:5e:00:01:0a 51 0
Configuring MS NLB for Multiple VM NICs in the Same Subnet
When MS NLB VMs have more than one port on the same subnet, a request is flooded, which causes both ports to receive it. The server cannot manage this situation.
To workaround this situation, enable Unknown Unicast Flood Blocking (UUFB).
Enabling UUFB
To enable UUFB, enter these configuration commands, one on each line. At the end, enter Cntl + Z.
n1000v# configure terminal
n1000v (config)# uufb enable
n1000v (config)#
This configuration conceals the requests from the non-NLB ports and allows the system to function as it is expected.
Disabling UUFB for VMs that use Dynamic MAC Addresses
Issues might occur for VMs that use dynamic MAC addresses, other than those assigned to VMware. For ports hosting these types of VMs, disable UUFB. Enter the following commands:
n1000v(config)# int veth3
n1000v(config-if)# switchport uufb disable
n1000v(config-if)#
 Feedback
Feedback