Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series Installation Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform 6
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- December 16, 2015
Chapter: Installing and Configuring the VXLAN Gateway
- Information About the VXLAN Gateway Deployment
- Guidelines and Limitations for Cisco Nexus 1000V VXLAN Gateway
- Steps to Install and Configure VXLAN Gateway
- Configuring Port Profiles on the VSM
- Installing VXLAN Gateway
Installing and Configuring the VXLAN Gateway
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information About the VXLAN Gateway Deployment
- Guidelines and Limitations for Cisco Nexus 1000V VXLAN Gateway
- Steps to Install and Configure VXLAN Gateway
- Configuring Port Profiles on the VSM
- Installing VXLAN Gateway
- Configuring the VXLAN Gateway Data and Management Interfaces Using the OpenStack CLI
- Configuring High Availability
- Verifying the VXLAN Gateway Configuration
- Managing the VXLAN-to-VLAN Mappings on the VXLAN Gateway
Information About the VXLAN Gateway Deployment
The Virtual Extensible Local Area Network (VXLAN) Gateway has the following deployment requirements:
-
To configure the VXLAN Gateway, you must install the Advanced Edition license on the Cisco Nexus 1000V switch.
-
vCPU and memory requirements:
-
Network requirements:
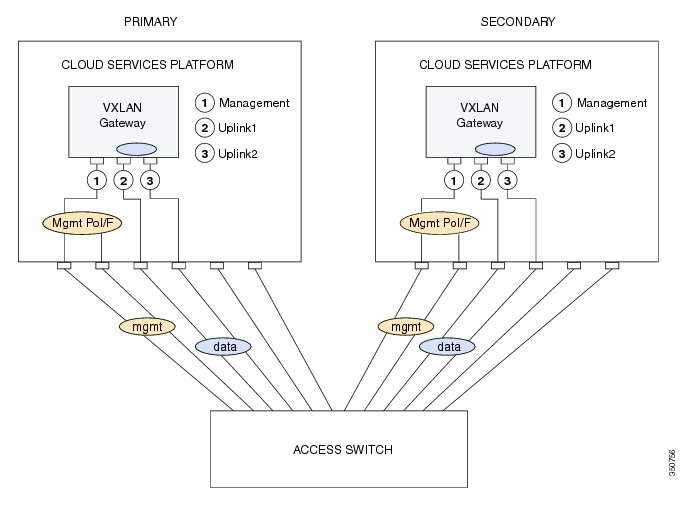
This figure shows the VXLAN Gateway deployment.
Guidelines and Limitations for Cisco Nexus 1000V VXLAN Gateway
VXLAN Gateways have the following configuration guidelines and limitations:
-
You must configure the VSM to use the Layer 3 control. We strongly recommend that VSM Layer 3 control is through mgmt 0. For more information about Layer 3 control, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V System Management Configuration Guide.
-
A single VSM can manage a maximum of eight VXLAN Gateway high availability (HA) clusters.
- You must configure the HA mode of the VXLAN Gateway as standalone or primary/secondary so that when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is either active or standby and the VXLAN-to-VLAN mappings are either active or pending. If you do not configure an HA role for the VXLAN Gateway, when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is unknown, and VXLAN-to-VLAN traffic is not processed.
-
The VXLAN Gateway virtual machine (VM) uses two vCPUs; one vCPU for management traffic and one vCPU for the data interface.
Steps to Install and Configure VXLAN Gateway
There are several key steps to install and configure a VXLAN Gateway.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Create two port profiles on the switch (VSM): one for the uplinks on the gateway and one for the VTEP interface. |
See Configuring a Port Profile for the Uplink on the VXLAN Gateway and Configuring a Port Profile for the VTEP on the VXLAN Gateway. |
| Step 2 | Deploy the VXLAN Gateway. |
Choose one of the following deployment models:
|
| Step 3 | Create the VXLAN Gateway data and management interfaces. |
Choose one of the following methods: |
| Step 4 | Configure high availability on the VSMs. You must configure the HA mode of the VXLAN Gateway as standalone or primary/secondary so that when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is either active or standby and the VXLAN-to-VLAN mappings are either active or pending. If you do not configure an HA role for the VXLAN Gateway, when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is unknown, and VXLAN-to-VLAN traffic is not processed. | |
| Step 5 | Set up the VXLAN-to-VLAN mappings on the VXLAN Gateway. |
See Managing the VXLAN-to-VLAN Mappings on the VXLAN Gateway. |
| Step 6 | Verify the VXLAN Gateway installation and configuration. | (Optional) |
Configuring Port Profiles on the VSM
You must create port profiles on the VSM before you can install and configure the VXLAN Gateway.
- Configuring a Port Profile for the Uplink on the VXLAN Gateway
- Configuring a Port Profile for the VTEP on the VXLAN Gateway
Configuring a Port Profile for the Uplink on the VXLAN Gateway
Before installing the VXLAN Gateway, you must create two port profiles on the switch (VSM), one for the uplinks on the gateway and one for the VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint (VTEP) interface.
-
Ensure that the VSM is configured in the Advanced mode by entering the svs switch edition advanced configuration command to enable Advanced mode.
-
Ensure that the VXLAN feature is enabled on the VSM by entering the feature segmentation configuration command to enable VXLANs on the VSM.
-
Ensure that the VXLAN Gateway is enabled on the VSM by entering the feature vxlan-gateway configuration command.
-
Ensure that the interfaces of the upstream switch are configured with a matching port channel and VLAN trunk configuration.
This example shows how to configure and display the gateway mappings:
vsm# configuration terminal vsm(config)# port-profile type ethernet gw-uplink vsm(config)# switchport mode trunk vsm(config)# switchport trunk allowed vlan 1545 vsm(config)# mtu 1550 vsm(config-port-prof)# service instance 1 vsm(config-port-prof)# encapsulation profile gw_mappings vsm(config-port-prof-srv)# encapsulation profile segment gw-segment vsm(config-port-prof-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 753 bridge-domain bd-753 vsm(config-port-prof-srv)# exit vsm(config-port-prof)# channel-group auto vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile
Configuring a Port Profile for the VTEP on the VXLAN Gateway
You can create a port profile that can be applied to the VTEP virtual interface on the VXLAN Gateway.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | vsm# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | vsm(config) # port-profile type vethernet port-profile name |
Configures a port profile for the VTEP on the VXLAN gateway.
| ||
| Step 3 | vsm(config-port-prof) # switchport mode access |
Designates that the interfaces are to be used as a trunking ports. A trunk port transmits untagged packets for the native VLAN and transmits encapsulated, tagged packets for all other VLANs. | ||
| Step 4 | vsm(config-port-prof) # switchport access vlan vlan-id-access |
Assigns an access VLAN ID to this port profile. The VLAN ID provided must be added to the allowed VLAN set of the uplink port profile. This VLAN should not be mapped to any VXLAN.
| ||
| Step 5 | vsm(config-port-prof ) # capability vxlan |
Configures the capability VXLAN feature on the specified virtual ethernet port and enables encapsulation and decapsulation of VXLAN packets. | ||
| Step 6 | vsm(config-port-prof) # transport ip address ip-address netmask network mask [gateway ip-address] |
| ||
| Step 7 | vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown |
Administratively enables all ports in the profile. | ||
| Step 8 | vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled |
Enables the port profile and applies its configuration to the assigned ports. | ||
| Step 9 | vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile |
Publishes the port profile. |
This example displays how to configure a VTEP on the VXLAN gateway:
vsm# configure terminal vsm(config)# port-profile type vethernet gw-vtep vsm(config-port-prof)# switchport mode access vsm(config-port-prof)# switchport access vlan 760 vsm(config-port-prof)# capability vxlan vsm(config-port-prof)# transport ip address 192.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.0.2.254 vsm(config-port-prof)# no shutdown vsm(config-port-prof)# state enabled vsm(config-port-prof)# publish port-profile
Installing VXLAN Gateway
Installing the VXLAN Gateway as a VM Using OpenStack
You install the VXLAN Gateway as a VM on compute hosts.
-
Ensure that the Cisco Yum repository has been added to the yum repository list. If it has not been added, see Setting Up the Cisco Yum Repository
-
Ensure that the host on which you create the VXLAN Gateway VM meets the networking requirements, as described in Minimum Networking Requirements.
-
Create the required port profiles in the VSM, as described in Configuring Port Profiles on the VSM.
-
If you are not using DHCP to configure IP addresses of the VTEPs, ensure that static IP addresses are configured on the VTEPs. See
| Step 1 | Source the
keystonerc_admin file.
/root/keystonerc_admin
If the keystonerc_admin file is not found, change the password and authorization URL of the openrc file, and source the openrc file instead. This example shows the OS_PASSWORD and OS_AUTH_URL parameters that you need to define in the openrc file. export OS_NO_CACHE=true export OS_TENANT_NAME=admin export OS_USERNAME=admin export OS_PASSWORD=<password> export OS_AUTH_URL=http://<IP>/v2.0/ export OS_AUTH_STRATEGY=keystone export OS_REGION_NAME=RegionOne export CINDER_ENDPOINT_TYPE=publicURL export GLANCE_ENDPOINT_TYPE=publicURL export KEYSTONE_ENDPOINT_TYPE=publicURL export NOVA_ENDPOINT_TYPE=publicURL export QUANTUM_ENDPOINT_TYPE=publicURL
|
| Step 2 | Download the
VXLAN Gateway image.
yum update
yum install nexus-1000v-vxgw
ls /opt/cisco/vxgw/
image_name
|
| Step 3 | Upload the image
to Glance.
glance image-create --name=IMG_NAME --is-public=true --property hw_vif_model=virtio --property hw_disk_bus=ide --property hw_cdrom_bus=ide --container-format=ovf --disk-format=qcow2 < /opt/cisco/vxgw/image_name |
Installing the VXLAN Gateway on a Cloud Services Platform
There are three basic steps to install the VXLAN Gateway on a Cloud Services Platform.
| Step 1 | Create and
deploy the VXLAN Gateway.
For details, see Creating and Deploying a VXLAN Gateway |
| Step 2 | Configure the
VXLAN Gateway.
For details, see Configuring the VXLAN Gateway Using the Setup Script |
| Step 3 | Modify and
customize the initial setup script.
For details, see Modifying the Initial Setup Script Parameters |
Creating and Deploying a VXLAN Gateway
You can create and deploy a VXLAN Gateway as a VSB on all Cisco Nexus Cloud Services Platforms.
You must be logged in to the Cisco Nexus Cloud Services Platform on which you want to install the VXLAN Gateway.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | CSP#
copy
scp://
server where
the VXGW image is located
source
path
iso image
of vxlan gw
bootflash:repository
>
|
Copies the VXLAN gateway image to the bootflash/repository on the CCPA Manager. |
| Step 2 | CSP# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | CSP(config) # virtual-service-blade name of the VXLAN GW VSB |
Creates a VXLAN Gateway VSB. |
| Step 4 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # virtual-service-blade-type new iso image of the vxlan gw |
Deploys the downloaded VXLAN Gateway. The image is always populated from the bootflash or repository and there is no need to specify the path. |
| Step 5 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface gw-uplink1 uplink Physical-Interface Cloud Services Platform |
Assigns a physical interface on the Cloud Services Platform to the gateway uplink. GigabitEthernet3 through GigabitEthernet6 are available in the flexible mode physical interfaces. You must configure the port channels using LACP on the upstream switches. |
| Step 6 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface gw-uplink1 mode passthrough |
Configures the gateway uplink as passthrough. The corresponding Gigabit Ethernet interface cannot be shared with other VSBs on the Cloud Services Platform. |
| Step 7 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface gw-uplink2 uplink Physical-Interface Cloud Services Platform |
Assigns a physical interface on the Cloud Services Platform to the gateway uplink. GigabitEthernet3 through GigabitEthernet6 are available in the flexible mode physical interfaces. You must configure the port channels using LACP on the upstream switches. |
| Step 8 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface gw-uplink2 mode passthrough |
Configures the gateway uplink as passthrough. The corresponding Gigabit Ethernet interface cannot be shared with other VSBs on the Cloud Services Platform. |
| Step 9 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface management vlan vlan id |
Allows the specified VLAN ID on the management uplink. The VLAN range is from 1 to 4096. |
| Step 10 | CSP(config-vsb-config) # interface management uplink interface |
Specifies the interface as either a physical interface of the Cloud Services Platform or a port channel interface previously created on the Cloud Services Platform. |
| Step 11 | Use one of the following commands to deploy a gateway: |
Use the enable command to install two VSBs, one on the primary Cloud Services Platform and another on the secondary cloud services platform. Use the enable primary command to deploy the gateway in standalone mode on the primary Cloud Services Platform. Use the enable secondary command to deploy the gateway in standalone mode on the secondary Cloud Services Platform. Initiates a setup script to configure the VXLAN gateway, IP address, subnet mask, gateway, hostname, and password for the VXLAN gateway VSB. You are also required to specify the details of the VSMs domain ID, IP address, primary and secondary MAC addresses on the control interface. For more information, see Setup Script to Configure the VXLAN Gateway. |
This example shows how to bring up a gateway as a VSB on a VSA pair:
CSP# configure terminal CSP(config)# virtual-service-blade VXLAN-GW CSP(config-vsb-config)# virtual-service-blade-type new vxgw.4.2.1.SV2.2.0.264.iso CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface gw-uplink1 uplink GigabitEthernet3 CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface gw-uplink2 uplink GigabitEthernet4 CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface gw-uplink1 mode passthrough CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface gw-uplink2 mode passthrough CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface management uplink GigabitEthernet1 CSP(config-vsb-config)# interface management vlan 751 CSP(config-vsb-config)# enable
Configuring the VXLAN Gateway Using the Setup Script
After you enter enable while installing a VXLAN Gateway as a VSB, the setup script to configure the VXLAN gateway is executed. The setup script configures the following parameters on the VXLAN gateway:
| Step 1 | On the command
prompt, enter the VSB image and press Enter.
Enter VSB image:x.x.x.x.x.x.x.iso: [vxgw.5.2.1.SK1.2.1.iso] | ||||
| Step 2 | Enter the VSM
domain ID. The range is from 1 to 1023.
Enter domain [1-1023]:405
| ||||
| Step 3 | Enter the
management IP version.
Management IP version [V4]:v4 | ||||
| Step 4 | Configure the
management IP address to interface mgmt 0 on the VXLAN Gateway that is deployed
on the primary Cloud Services Platform.
Enter management IP address of service module on primary: 192.168.1.104
| ||||
| Step 5 | Enter the
management subnet mask.
Enter management subnet mask of service module on primary: 255.255.255.0 | ||||
| Step 6 | Enter the
management default gateway.
Enter default gateway IP address of service module on primary: 192.168.1.1 | ||||
| Step 7 | Configure the
management IP address to interface mgmt 0 on the VXLAN gateway deployed on the
secondary Cloud Services Platform.
Enter management IP address of service module on secondary: 192.168.1.105
| ||||
| Step 8 | Enter the
management subnet mask.
Enter management subnet mask of service module on secondary: 255.255.255.0 | ||||
| Step 9 | Enter the
management interface default gateway.
Enter default gateway IP address of service module on secondary: 192.168.1.1 | ||||
| Step 10 | Enter the VXLAN
Gateway hostname.
Enter HostName: VXLAN-GW-DOCS | ||||
| Step 11 | Enter the login
credentials.
Enter the password for admin:Sfish123 | ||||
| Step 12 | Enter the IP
address of the VSM.
VSM L3 Ctrl IPv4 address:192.168.1.210 | ||||
| Step 13 | Enter the uplink
trunk port profile configured on the VSM.
Enter VSM uplink port-profile name: gw-uplink
| ||||
| Step 14 | Enter the VTEP
profile name.
Enter VTEP port-profile name: gw-vtep
|
This example shows how to bring up the VXLAN Gateway:
CSP(config-vsb-config)# enable Enter vsb image: [vxgw.4.2.1.SV2.2.0.264.iso] Enter the VSM domain id[1-4095]: 405 Enter Management IP version [V4]: [V4] Enter Management IP address of service module on primary: 192.168.1.104 Enter Management subnet mask of service module on primary: 255.255.255.0 Enter default gateway IP address of service module on primary: 192.168.1.1 Enter management IP address of service module on secondary: 192.168.1.105 Enter management subnet mask of service module on secondary: 255.255.255.0 Enter default gateway IP address of service module on secondary: 192.168.1.1 Enter HostName: VXLAN-GW-DOCS Enter the password for 'admin': Sfish123 VSM L3 Ctrl IPv4 address : 192.168.1.210 Enter VSM uplink port-profile name: gw-uplink Enter VTEP port-profile name: gw-vtep Note: VSB installation is in progress, please use show virtual-service-blade commands to check the installation status. CSP(config-vsb-config)#
Modifying the Initial Setup Script Parameters
After executing the setup script for the first time, if you need to modify any of the setup parameters, use the following commands on the VSM:
 Note | If an HA pair is installed, ensure that you apply the same changes individually on both gateway modules. |
 Note | Ensure the port profile that you update is first saved on the VSM. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | vsm(config)# service module update port-profile type ethernet name VXLAN Gateway Uplink port-profile name |
Modifies the VXLAN Gateway uplink port profile from the VSM. |
| Step 2 | vsm(config)# service module update port-profile type vethernet name VXLAN Gateway VTEP port-profile name |
Modifies the VXLAN Gateway VTEP port profile from the VSM. |
Configuring the VXLAN Gateway Data and Management Interfaces Using the OpenStack CLI
Steps to Configure the VXLAN Gateway Interfaces Using the OpenStack CLI
Create one or more port profiles in the VSM. For more information, see Configuring a Port Profile for the Uplink on the VXLAN Gateway and Configuring a Port Profile for the VTEP on the VXLAN Gateway.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | If you have not already done so, log in to the OpenStack CLI as a user with admin privileges. |
— |
| Step 2 | Create the VXLAN Gateway data interface. |
For details, see Creating the VXLAN Gateway Data Interface. |
| Step 3 | Create theVXLAN Gateway management interface. |
For details, see Creating a VXLAN Gateway Management Interface. |
| Step 4 | Boot the VXLAN Gateway VM. |
For details, see Booting a VXLAN Gateway VM. |
Creating the VXLAN Gateway Data Interface
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | neutron net-create
network_name
|
Creates a network using the network profile. | ||
| Step 2 | neutron subnet-create
network_name
cidr_blocks
--name
subnet_name
--disable-dhcp
|
Creates a subnet for the network profile.
| ||
| Step 3 |
neutron
cisco-policy-profile-list
|
Lists the policy profiles available in neutron. | ||
| Step 4 | neutron port-create
network_name
n1kv:profile
cisco_policy_profile_id
|
Creates a trunk port. For network_name, specify the name of the network that you created in Step 3. For cisco_policy_profile_id, specify the profile with the mode trunk from the list of available profiles obtained in Step 3.
|
Creating a VXLAN Gateway Management Interface
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | neutron net-create
network_name
|
Creates an access network. |
| Step 2 | neutron subnet-create
network_name
cidr_blocks
--name
subnet_name
|
Creates a subnet for the access network segment profile. |
| Step 3 | neutron cisco-policy-profile-list
|
Lists the policy profiles available in Neutron. |
| Step 4 | neutron port-create
network_name
n1kv:profile
cisco_policy_profile_id
|
Creates an access port. Use a Cisco policy profile ID from the list of available profiles listed in Step 5. |
Booting a VXLAN Gateway VM
You must manually launch a VM instance using the OpenStack CLI.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Launch the VXLAN Gateway VM. | nova boot
--image
image_id
--flavor
3
--nic
port-id=
trunk_port-id
--nic
port-id=
access_port-id
vxlan_gateway_name
| ||
| Step 2 | List the active servers. | nova list |
Configuring High Availability
VXLAN Gateway and High Availability
The operation of high availability (HA) involves the following terminology:
-
Cluster—A cluster is a pair of gateway modules that operate together as a single HA module. Each cluster is distinguished by a unique cluster ID. A gateway module that is deployed in a standalone mode of operation is assigned a dummy cluster ID of 0.
-
HA role—The gateway modules that make up an HA cluster are assigned separate roles. One is designated as primary and the other as secondary. This role decides which of the two modules goes to active state first and which stays in a standby state. These states persist until the active module fails. In the event of any failure in the active gateway module, the standby gateway module detects the failure and moves to the active state. This way, one of the two modules is always providing active service.
-
HA state— At any given time, only one gateway module from a given cluster is actively performing the gateway function. The other module stays in the standby state pending the failure of the active module. A gateway module can be in the active or standby state. In addition, there is a transient initial state called the Init state. In this state, a gateway is either waiting to be assigned a role or negotiating its state with its peer.
After a gateway module is installed and brought up, the VSM assigns a role to the gateway module and can result in one of the following transitions:
-
Unconfigured-Init to Standalone-Active
-
Unconfigured-Init to Primary-Active
-
Unconfigured-Init to Secondary-Standby
-
Standalone-Active to Primary-Active
-
Standalone-Active to Secondary-Active
For all other combinations, we recommend that you first fall back to the Unconfigured-Init mode by using the no service VXLAN Gateway module command and then proceed to the desired role or states.
 Note | Roles must be preassigned to module numbers in the VSM. When a VXLAN gateway is attached to the VSM on that module, it inherits the role and state that are assigned by the VSM. You must configure the HA mode of the VXLAN Gateway as standalone or primary/secondary so that when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is either active or standby and the VXLAN-to-VLAN mappings are either active or pending. If you do not configure an HA role for the VXLAN Gateway, when you bring up the VXLAN Gateway, the HA state is unknown, and VXLAN-to-VLAN traffic is not processed. |
Configuring the VXLAN Gateway HA Mode as Standalone
You can create a service module in a standalone mode. Perform these steps on the VSM.
Roles must be preassigned to module numbers in the VSM. When a VXLAN gateway is attached to the VSM on that module, it inherits the role and state that are assigned by the VSM.
| Command or Action | Purpose |
|---|
This example shows how to display the cluster ID mapping and the details about active, standby, and standalone service modules:
vsm(config)# show module service Mod Cluster-id Role HA Mode Status --- ---------- ----------- ---------- ------- 36 0 Standalone Standalone Active
Configuring the VXLAN Gateway as an HA Pair
You can create a service module as a HA pair. Perform these steps on the VSM.
You must create a second instance of the VXLAN Gateway VM.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | vsm(config)# service modNo1 role primary ha-cluster clusterNo |
Configures the service module in HA and adds a primary service module to a cluster. |
| Step 2 | vsm(config)# service modNo2 role secondary ha-cluster clusterNo |
Configures another service module as secondary in the same cluster. |
| Step 3 | vsm(config)# show module service-module |
Displays the service module number, cluster ID, role, HA mode, and status. |
This example shows how to display the cluster ID mapping and the details about active, standby, and standalone service modules:
vsm(config)# show module service Mod Cluster-id Role HA Mode Status --- ---------- ----------- ---------- ------- 9 1 Primary HA Active 10 1 Secondary HA Standby
To switch over between the active and standby VXLAN gateway, enter the following command on the VSM:
vsm# service ha-cluster <1-8> switchover
Verifying the VXLAN Gateway Configuration
To display the VXLAN gateway (GW) installation and configuration information, perform one of the following tasks on the VSM:
| Command | Purpose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
show running-config port-profile gw-uplink |
Displays the configuration of the port profile assigned to the VXLAN gateway uplinks. |
||
|
show running-config port-profile gw-vtep |
Displays the configuration of the port profile assigned to the VXLAN VTEP. |
||
|
show module |
Displays the VXLAN gateway service modules. |
||
|
show module service |
Verifies the role of the VXLAN gateway module and displays the cluster ID mapping and the details about active, standby, and standalone service modules. |
||
|
show vxlan gateway interface |
Displays if the VTEPs are configured properly. |
||
|
show interface vethernet 6 |
Displays if both the VTEP Virtual Ethernet interfaces are in up state. |
||
|
show port-channel summary |
Displays if the port channels are up for gateway service modules. |
||
|
show bridge-domain mappings |
Displays VXLAN gateway mappings. |
||
|
show switch edition |
Displays if the VSM is in Advanced mode. |
||
|
show feature |
Displays if the VXLAN gateway is enabled on the VSM. |
||
|
Displays the status of the VXLAN gateway VSB as it transitions from the VSB DEPLOY IN PROGRESS to VSB POWERED ON. |
||
|
show virtual-service-blade
|
Displays the VXLAN Gateway configuration. |
||
|
show encapsulation profile |
Displays the VLAN-to-VXLAN mappings for all encapsulation profiles or for the specified encapsulation profile. |
This example shows how to display the status of the VXLAN gateway VSB:
CSP# show virtual-service-blade summary ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Name HA-Role HA-Status Status Location ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VXLAN-GW PRIMARY ACTIVE VSB POWERED ON PRIMARY VXLAN-GW SECONDARY ACTIVE VSB POWERED ON SECONDARY
This example shows how to display the VXLAN gateway configuration:
CSP# show virtual-service-blade
virtual-service-blade VXLAN-GW
Description:
Slot id: 1
Host Name: VXLAN-GW-DOCS
Management IP: 192.168.1.104
VSB Type Name : vx-gw-1.5
Configured vCPU: 3
Operational vCPU: 3
Configured Ramsize: 2048
Operational Ramsize: 2048
Disksize: 3
Heartbeat: 154764
Legends: P - Passthrough
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interface Type MAC VLAN State Uplink-Int
Pri Sec Oper Adm
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
VsbEthernet1/1 gw-uplink1 0002.3d71.a303 up up Gi3(P) Gi3(P)
VsbEthernet1/2 management 0002.3d71.a302 751 up up Gi1 Gi1
VsbEthernet1/3 gw-uplink2 0002.3d71.a304 up up Gi4(P) Gi4(P)
internal NA NA NA up up
HA Role: Primary
HA Status: ACTIVE
Status: VSB POWERED ON
Location: PRIMARY
SW version:
HA Role: Secondary
HA Status: ACTIVE
Status: VSB POWERED ON
Location: SECONDARY
SW version:
VSB Info:
Domain ID : 405
This example shows how to display the port-profile configuration assigned to the VXLAN Gateway uplinks:
vsm# show running-config port-profile gw-uplink port-profile type ethernet gw-uplink switchport mode trunk switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,81,751-760 mtu 1550 channel-group auto mode active no shutdown state enabled
This example shows how to display the port-profile configuration assigned to the VXLAN VTEP:
vsm# show running-config port-profile gw-vtep port-profile type vethernet gw-vtep switchport mode access switchport access vlan 760 capability vxlan transport ip address 182.168.1.253 255.255.255.0 gateway 182.168.1.1 no shutdown state enabled
This example shows how to display the VXLAN Gateway service modules as soon as they are online:
vsm# show module Mod Ports Module-Type Model Status --- ----- -------------------------------- ------------------ ------------ 1 0 Virtual Supervisor Module Nexus1000V ha-standby 2 0 Virtual Supervisor Module Nexus1000V active * 11 332 Virtual Ethernet Module NA ok 18 332 Virtual Ethernet Module NA ok 20 13 Virtual Service Module VXLAN Gateway ok 21 13 Virtual Service Module VXLAN Gateway ok 22 13 Virtual Service Module VXLAN Gateway ok Mod Sw Hw --- ------------------ ------------------------------------------------ 1 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) 0.0 2 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) 0.0 11 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) Linux 3.2.0-23-generic 18 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) Linux 3.8.0-29-generic 20 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) Linux 2.6.27.10 21 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) Linux 2.6.27.10 22 5.2(1)SK1(2.1) Linux 2.6.27.10 Mod Server-IP Server-UUID Server-Name --- --------------- ------------------------------------ -------------------- 1 192.0.2.166 NA NA 2 192.0.2.166 NA NA 11 192.0.2.147 47DE0F4A-8072-0E4D-A218-84A2C058FF3C vxlan-gw-ubuntu 18 192.0.2.54 EE04B285-6BA6-5642-AC8E-EDB12D07811B vxlan-gw-ubuntu2 20 192.0.2.90 7a4f6171-3235-4fd2-9797-80149df55171 ab-vxgw-1110 21 192.0.2.53 48ad3898-401f-4377-8de1-dcfa22df78ec VxLanGW 22 192.0.2.55 5a996a7e-fa85-4630-89e5-18a3a3b413b8 VxLanGW * this terminal session
This example shows how to display the cluster ID mapping and the details about active, standby, and standalone service modules:
vsm# show module service Mod Cluster-id Role HA Mode Status --- ---------- ----------- ---------- ------- 9 1 Primary HA Active 10 1 Secondary HA Standby
This example shows how to display the module for virtual Ethernet interface binding:
vsm(config-if)# show vxlan gateway interface ----------------------------------------------------------------- Port IPAddress Netmask Gateway Mod Status Role ----------------------------------------------------------------- Veth6 192.0.2.253 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 9 up Active Veth22 192.0.2.253 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 10 up Standby
This example shows how to display whether both the VTEP virtual Ethernet interfaces are in up state:
vsm# show interface vethernet 6
Vethernet6 is up
Port description is VXLANGW VTEP, Network Adapter 1
Hardware: Virtual, address: 0002.3d71.a303 (bia 0002.3d71.a303)
Owner is VM "VXLANGW VTEP", adapter is Network Adapter 1
Active on module 9
Port-Profile is gw-vtep
Port mode is access
5 minute input rate 8 bits/second, 0 packets/second
5 minute output rate 0 bits/second, 0 packets/second
Rx
6 Input Packets 6 Unicast Packets
0 Multicast Packets 588 Broadcast Packets
468 Bytes
Tx
34321 Output Packets 34321 Unicast Packets
33609 Multicast Packets 24 Broadcast Packets 33633 Flood Packets
2193700 Bytes
0 Input Packet Drops 0 Output Packet Drops
vsm# show interface vethernet 22
Vethernet22 is up
Port description is VXLANGW VTEP, Network Adapter 1
Hardware: Virtual, address: 0002.3d71.a383 (bia 0002.3d71.a383)
Owner is VM "VXLANGW VTEP", adapter is Network Adapter 1
Active on module 10
Port-Profile is gw-vtep
Port mode is access
5 minute input rate 8 bits/second, 0 packets/second
5 minute output rate 0 bits/second, 0 packets/second
Rx
6 Input Packets 6 Unicast Packets
0 Multicast Packets 25 Broadcast Packets
468 Bytes
Tx
33742 Output Packets 33742 Unicast Packets
33609 Multicast Packets 133 Broadcast Packets 33742 Flood Packets
2158956 Bytes
0 Input Packet Drops 0 Output Packet Drops
This example shows how to display whether the port channels are up for VXLAN Gateway service modules:
vsm# show port-channel summary
Flags: D - Down P - Up in port-channel (members)
I - Individual H - Hot-standby (LACP only)
s - Suspended r - Module-removed
S - Switched R - Routed
U - Up (port-channel)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Group Port- Type Protocol Member Ports
Channel
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 Po1(SU) Eth NONE Eth3/3(P) Eth3/4(P) Eth3/5(P)
Eth3/6(P)
2 Po2(SU) Eth NONE Eth4/3(P) Eth4/4(P) Eth4/5(P)
Eth4/6(P)
3 Po3(SU) Eth NONE Eth5/3(P) Eth5/4(P) Eth5/5(P)
Eth5/6(P)
4 Po4(SU) Eth NONE Eth6/3(P) Eth6/4(P) Eth6/5(P)
Eth6/6(P)
5 Po5(SU) Eth NONE Eth7/3(P) Eth7/4(P) Eth7/5(P)
Eth7/6(P)
6 Po6(SU) Eth NONE Eth8/4(P)
7 Po7(SU) Eth LACP Eth9/1(P) Eth9/3(P)
8 Po8(SU) Eth LACP Eth10/1(P) Eth10/3(P)
This example shows how to display VXLAN Gateway mappings:
vsm# show bridge-domain mappings ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Interface Module Serv Inst Vlan BD-Name ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- port-channel7 9 753 753 bd-753 port-channel8 10 753 753 bd-753
This example shows how to display the IP address for module binding:
vsm(config-if)# show module service mgmt-int -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Mod Interface-Name IP-address Speed MTU -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4 Mgmt0 10.10.10.2 0 0 5 Mgmt0 10.10.10.3 0 0 Remember the management IP address user installs gateway with (in this example 10.10.10.2, which occupies module slot 4)
This example shows how to display whether the VSM is in Advanced mode:
vsm# show switch edition Switch Edition: Advanced Advanced Features Feature Name Feature State ----------------------------- vxlan-gateway enabled Licenses Available: 1020 Licenses In Use: 4 License Expiry Date: 13 Jun 2013
This example shows how to display whether the VXLAN Gateway is enabled on the VSM:
vsm# show feature Feature Name Instance State -------------------- -------- -------- cts 1 enabled dhcp-snooping 1 enabled http-server 1 enabled lacp 1 enabled netflow 1 disabled network-segmentation 1 enabled port-profile-roles 1 disabled private-vlan 1 disabled segmentation 1 enabled sshServer 1 enabled tacacs 1 disabled telnetServer 1 disabled vtracker 1 enabled vxlan-gateway 1 enabled
Perform one of the following tasks on the VXLAN Gateway. If your VSM is on Layer 3 through management and your gateway is also on the same management subnet, use the attach module service module number command to acces the gateway CLI. If your VSM is on Layer 3 through control, you can access the gateway CLI from any machine on that control subnet. This example shows the VSM which is on Layer 3 control.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
show redundancy config |
Displays the high availability status. |
This example shows how to display the HA status:
gw# show redundancy config
HA Manager Node Information:
Cluster Node Count: 2
Local Node:
state : Active
HA mode : High Availability
uuid : 56fa6753-4dc5-4a7d-ad07-cc817114f838
cluster_id : 1
node_priority : 2
node_type : VXLAN Gateway
ipaddr [mgmt] : 192.168.1.104
Peer Node 1:
state : Standby
uuid : 4cbd05df-b3e5-468a-9497-89aa3fae8153
node_type : VXLAN Gateway
ipaddr [mgmt] : 192.168.1.105
This example shows how to display the VLAN-to-VXLAN mappings for all encapsulation profiles:
gw# show encapsulation profile ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Vlan Bridge-domain ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2100 segment5050 2055 segment5031 2056 segment5032 2057 segment5033 2058 segment5034
Managing the VXLAN-to-VLAN Mappings on the VXLAN Gateway
The VLAN-to-VXLAN mappings that are configured on a gateway module can be managed by editing the port profile applied on the gateway uplink modules. To add or remove a mapping, perform these steps on the VSM.
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | vsm# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||||||
| Step 2 | vsm(config)# encapsulation profile segment name |
Creates an encapsulation profile to contain the VLAN-to-VXLAN mappings. | ||||||
| Step 3 | vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# dot1q VLAN-ID bridge-domain bd-name |
Maps a VLAN to a VXLAN. The VXLAN is specified through the bridge-domain name.
| ||||||
| Step 4 | vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# exit | Exits the current configuration mode. | ||||||
| Step 5 | vsm(config)# port-profile port-profile-name |
Specifies the name of the port-profile applied to the VXLAN Gateway uplink interface. | ||||||
| Step 6 | vsm(config-port-prof)# service instance 1 to 4096 |
Defines a place holder for mappings. The range is from 1 to 4096.
| ||||||
| Step 7 | vsm(config-port-prof-srv)# encapsulation profile name | Assigns the specified encapsulation profile to the port profile. | ||||||
| Step 8 | vsm(config-port-prof-srv)# copy running-config startup-config |
Saves the change persistently through reboots and restarts by copying the running configuration to the startup configuration. |
This example shows how to configure VXLAN-to-VLAN mappings on the VXLAN gateway:
vsm# configure terminal vsm(config)# encapsulation profile segment mgmt_mappings vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# dot1q 1555 bridge-domain vxlan6000 vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# dot1q 1557 bridge-domain vxlan6002 vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# dot1q 1558 bridge-domain vxlan6003 vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# dot1q 1559 bridge-domain vxlan6004 vsm(config-vxlan-encap-prof)# exit vsm(config)# port-profile Uplink-All-VXGW vsm(config-port-prof)# service instance 2 vsm(config-port-prof)# encapsulation profile mgmt_mappings vsm(config-prot-prof-srv)# copy running-config startup-config
vsm(config)# show run port-profile Uplink-All-VXGW
port-profile type ethernet Uplink-All-VXGW
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1545-1575,1577-1605
mtu 1550
service instance 2
encapsulation dot1q 1555 bridge-domain vxlan6000
encapsulation dot1q 1557 bridge-domain vxlan6002
encapsulation dot1q 1558 bridge-domain vxlan6003
encapsulation dot1q 1559 bridge-domain vxlan6004
no shutdown
state enabled
vsm(config)# show port-profile usage port-profile Uplink-All-VXGW port-channel1 port-channel5 Ethernet7/1 Ethernet7/3
vsm(config)# show run interface ethernet 7/1 expand-port-profile
interface Ethernet7/1
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1545-1575,1577-1605
mtu 1550
channel-group auto mode active
service instance 2
no shutdown
encapsulation dot1q 1557 bridge-domain vxlan6002
encapsulation dot1q 1555 bridge-domain vxlan6000
encapsulation dot1q 1558 bridge-domain vxlan6003
no shutdown
 Feedback
Feedback