Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series Installation Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform 6
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- December 16, 2015
Chapter: Overview
- Releases Included in the Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series
- Information About Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM on Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform
- Information About the Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform Installer
- Supported Network Topologies
- OpenStack Hosts and Services
Overview
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Releases Included in the Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series
- Information About Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM on Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform
- Information About the Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform Installer
- Supported Network Topologies
- OpenStack Hosts and Services
Releases Included in the Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series
The following releases are a part of the Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM, Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2x) Series:
-
Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2b)
-
Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2a)

Note
Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2a) is not compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform, Release 7.2. Use Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2b) for new deployments to Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform, Release 7.2 or later.
-
Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2)

Note
Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2) is not compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform, Release 6.0.4. Use Release 5.2(1)SK3(2.2a) for new deployments to Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform, Release 6.0.4 or later.
Information About Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM on Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform
-
Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM)—A software component that is deployed on each KVM host. Each VM on the host is connected to the VEM through virtual Ethernet (vEth) ports. The VEM is a hypervisor-resident component and is tightly integrated with the KVM architecture.
-
Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM)—The Management component that controls multiple VEMs and helps in the definition of VM-focused network policies. It is deployed either as a virtual appliance on any KVM host or on the Cisco Cloud Services Platform appliance. The VSM is integrated with OpenStack using the OpenStack Neutron Plug-in.
-
Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform (RHEL-OSP)—Red Hat Enterprise's Linux operating system with the Red Hat's implementation of the OpenStack Juno. RHEL-OSP provides interacting services that control its computing, storage, and networking resources and is the foundation on which to build a private or public Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) cloud.
Information About the Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform Installer
The Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM uses Redhat’s deployment management tool called Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform Installer (RHEL-OSP Installer) to install the Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM on RHEL in an OpenStack cloud environment.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack Platform provides the foundation to build a private or public Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) cloud on top of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
Supported Network Topologies
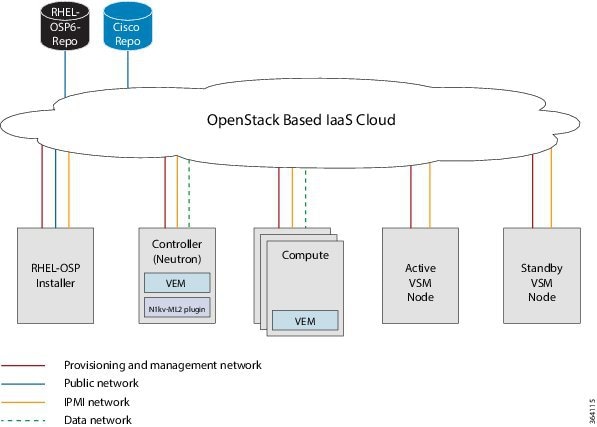
Topology with OpenStack in Standalone Mode
The Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM can be deployed with OpenStack in standalone mode (not functioning in high-availability (HA) mode). However, we recommend that you always deploy the VSM in active/standby HA mode. The following topology diagram illustrates this deployment.
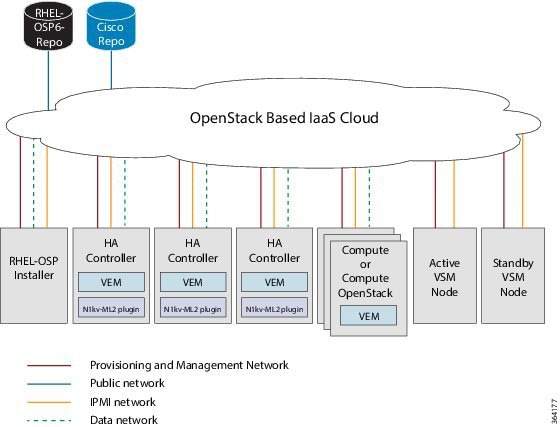
Topology with OpenStack in High-Availability Mode
The Cisco Nexus 1000V for KVM can be deployed with OpenStack in high-availability (HA) mode. We recommend that you always deploy the VSM in active/standby HA mode. The following topology diagram illustrates this deployment.
OpenStack Hosts and Services
Hosts and Services Used in OpenStack Standalone Deployments
The following table lists and describes the primary OpenStack hosts and services that you need when deploying OpenStack in standalone mode.
|
Hosts |
OpenStack Service |
|---|---|
|
OpenStack Platform Installer |
Deploys the OpenStack services |
|
Controller (Neutron) |
Neutron Server |
|
Database (MySQL) |
|
|
Messaging (RabbitMQ/QPID) |
|
|
Heat |
|
|
Ceilometer |
|
|
Keystone |
|
|
Glance |
|
|
Nova |
|
|
Cinder |
|
|
Horizon or OpenStack Dashboard |
|
|
Layer 3 Agent |
|
|
DHCP Agent |
|
|
Metadata Agent |
|
|
VEM |
|
|
Compute (Neutron) |
Ceilometer Agent |
|
Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM) |
|
|
Nova-compute |
Hosts and Services Used in OpenStack High-Availability Deployments
The following table lists and describes the primary OpenStack hosts and services that you need when deploying OpenStack in HA mode are same as those in a standalone mode. For more information, see Hosts and Services Used in OpenStack Standalone Deployments.
HA deployment is defined by the number of controller. A single controller indicates that it is a non-HA setup, while three controllers indicate that it is a HA setup.
 Feedback
Feedback