Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 5.2(1)SM3(1.1c)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- June 17, 2018
Chapter: Installing the Cisco Nexus 1000V
Prerequisites for Installing the VSM Software
For information about your software and platform compatibility, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V and Microsoft Hyper-V Compatibility Information document.
Before You Begin
Ensure that you have installed and configured the following components on the target setup:
- Windows Active Directory service.
- Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) 2012 R2 UR4 or later.
- Windows Server 2012 R2 hosts with 3014795 hotfix applied. For more information, see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/3014795/en-us .
- For the hosts that are running the Virtual Ethernet Module (VEM), you should enable the Hyper-V module for Windows PowerShell.
Guidelines and Limitations
It is your responsibility to monitor and install all the relevant patches from Microsoft on the Windows hosts.
Hardware Requirements
The hardware must meet the requirements set by Microsoft to run the Hyper-V role. The Cisco Nexus 1000V Virtual Supervisor Module (VSM) requires VMs with the following configuration:
- 4 GB minimum of hard disk space
- 4 GB minimum of RAM
- As a best practice, we recommend that you have four network adapters (network interface cards—NICs) on the host where Microsoft Hyper-V is installed. You can have various combinations depending on the hardware that you have. For example, you can have one NIC with four ports or four NICs with one port each.
Software Requirements
To install and bring up a Cisco Nexus 1000V, you need the following server setup:
- Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) 2012 R2 UR4 or later
- Windows 2012 R2 hosts
- Active Directory server
To configure the VSM, you need the following information:
- VSM IP address.
- VSM domain ID (1–1023)—This ID is used for high availability (HA).
- Layer 3 connectivity between a VSM and the hosts that run a VEM is required.
– Layer2 mode is not supported.
– Layer3 UDP port number 4785.
– Communication between the VSM and VEM occurs over UDP port number 4785 that uses the Cisco Nexus Control Protocol (CNCP).
VSM NIC Ordering
The VSM creates interfaces in an ascending MAC address order of the virtual NIC offered by Microsoft Hyper-V. Currently, Microsoft Hyper V provides no guarantees that this order is the same as displayed at the VSM VM Settings panel. The VSM always uses its first interface as control0 and its second interface as mgmt0. The network profiles for these two interfaces might need different VLANs. Therefore, you should verify that the interfaces are selected by the VSM in the same order that are displayed in the Settings panel.
Enter the following command on the VSM to verify the order of the management and control MAC addresses:
If the order is not the same, use the following commands to specify the preferred MAC-to-control0/mgmt0 interface mappings:
These commands require that you enter the copy running-config startup-config command afterwards to make the change persistent and effective after the next VSM reload.
If any of the preferred MACs are not available at VSM bootup, the driver picks another interface instead (following MAC ascending order). The system logs an error with a syslog as follows:
Basic Topology
Figure 1-1 displays the basic Hyper-V topology on a Cisco Nexus 1000V VEM.
Figure 1-1 Basic Topology for the Cisco Nexus 1000V
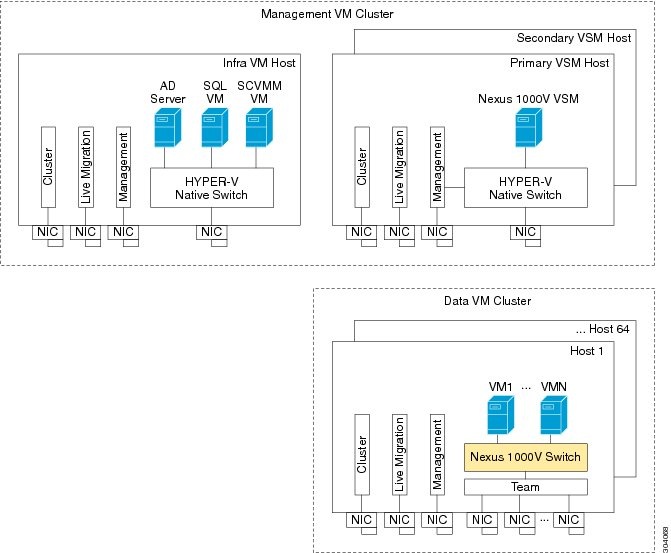

Note The management NIC is actually on the Microsoft switch. The management VM cluster is for infra VMs. The data VM cluster is for workload VMs. The minimum topology is three servers with four NICs each.
Figure 1-1 displays the Cisco Nexus 1000V deployment on two servers with the following network configuration:
- Management NIC—This network adapter is connected to an external network for the host OS connectivity.
- Microsoft virtual switch—The Microsoft virtual switch has one physical network adapter for the VSM connectivity.
- Two physical network adapters—These adapters are connected to the Cisco Nexus 1000V logical switch instance of the Hyper-V host.
Installation Workflow
Figure 1-2 displays the Cisco Nexus 1000V installation process on Microsoft SCVMM.
Figure 1-2 Cisco Nexus 1000V Installation Workflow
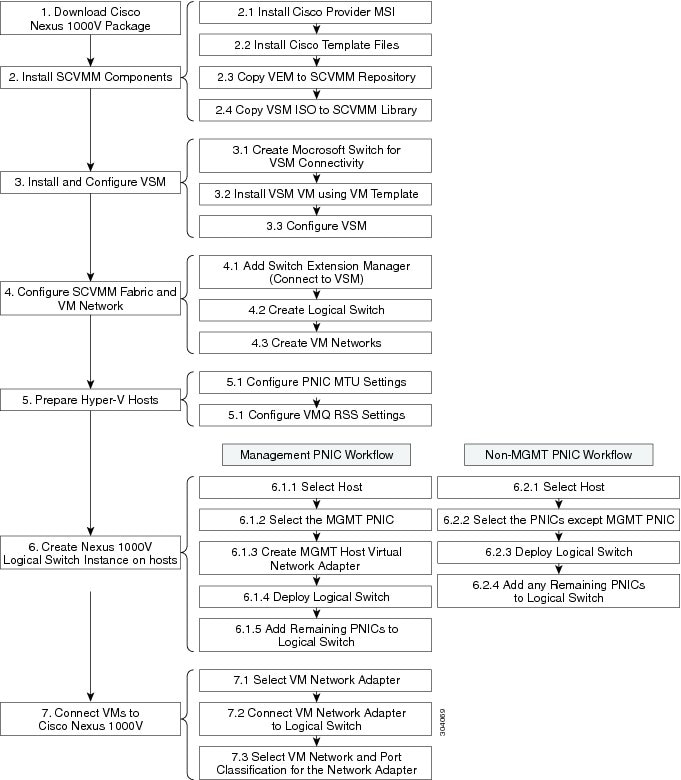
Installing the VSM Software
To install the VSM software, perform the following steps:
1. Downloading the Cisco Nexus 1000V Package.
3. Installing the VSM Certificate.
4. Preparing the Microsoft Hyper-V Hosts (Optional).
5. Adding Hosts to a Logical Switch.
6. Connecting the VM Network Adapter to the Logical Switch.
Downloading the Cisco Nexus 1000V Package
The Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V package (a zip file) is available at the download URL location provided with the software.
To download the Cisco Nexus 1000V package, download the Cisco Nexus 1000V package for Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) 2012 SP1. This package contains the following files:
- VSM ISO (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\VSM\install\Nexus-1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.iso)
- VEM MSI package (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\VEM\Nexus1000V-VEM-5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.0.msi)
- Cisco VSEM Provider MSI package (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\VMM\Nexus1000V-VSEMProvider-5.2.1.SM3.1.1c0.msi)
- Kickstart file (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\VSM\Upgrade\Nexus-1000V-kickstart.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.bin)
- System file (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\VSM\Upgrade\Nexus-1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.bin)
- PNSC-PA (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\PNSC-PA\vsmhv-pa.3.2.1e.bin)
- WSUS scripts (Nexus1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c\WSUS\)
Configuring SCVMM and VSM
This section describes how to install the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V VSM software and includes the following topics:
Installing SCVMM Components
To install the SCVMM components, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Install the Cisco Provider MSI.
a. Install the Nexus1000V-VSEMProvider-5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.0.msi from the Cisco Nexus1000V zip location on the SCVMM server in order to establish communication between SCVMM and the Cisco Nexus1000V VSM.

Note The MSI installation restarts the SCVMM service.
b. Verify that the Cisco Provider is installed properly:
- Open the SCVMM console.
- Navigate to the Settings Pane.
- Click Configuration Providers.
- Verify that the Cisco Nexus 1000V extension is displayed.
Step 2 Install the Cisco VSM template files.
After downloading the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V package, complete the following steps to install the VSM template:
- On the SCVMM server, open the PowerShell console from the SCVMM console.
- Run the script Register-Nexus1000VVSMTemplate.ps1 from the following location: %ProgramFiles%\Cisco\Nexus1000V\V2\Nexus1000V-VSMTemplate .
This script imports the Cisco VSM template in the SCVMM library.
– Navigate to the Templates tab.
– Choose Templates. On the right pane, the Nexus 1000V-VSM-Template is listed.
Step 3 Copy the VEM to the SCVMM repository.
The VEM is an MSI file that needs to be placed in the following location on the SCVMM server: %ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Switch Extension Drivers. For example, C:\ProgramData\Switch Extension Drivers. SCVMM uses the MSI file during Add host operation.

Step 4 Copy the VSM ISO file. For example, copy Nexus-1000V.5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.iso to the SCVMM library in the following location on SCVMM server: \\VMName\MSSCVMMLibrary. After copying the ISO file, make sure to refresh the SCVMM library so that SCVMM detects the copied ISO.
Installing and Configuring the VSM Workflow
To install and configure the VSM workflow, use an existing Microsoft Switch with external connectivity or create a new one, for the VSM connectivity.
Installing the VSM using a VM Template
To install the VSM using a VM template, perform the following steps:
Step 1 From the left navigation pane in the SCVMM user interface, click the VMs and Services icon and from the top menu bar, choose Create Virtual Machine. The Create Virtual Machine wizard opens.
Step 2 In the Select Source panel, choose the Use an existing virtual machine, VM template, or virtual hard disk option and click Browse.
Step 3 Choose the Nexus1000V_VSM_Template file listed under the Type: VM Template header.
Step 4 Click OK and click Next.
Step 5 In the Specify Virtual Machine Identity panel, enter the name of the virtual machine and click Next.
Step 6 In the Configure Hardware panel, configure the hardware settings for the virtual machine. If you are using a template, most of the settings have already been configured (For example, the hard drive is set to 4 GB and there are three network adapters). The only item that you have to manually configure is the ISO image.
Step 7 Click Virtual DVD drive below the Bus Configuration header in the center pane.
Step 8 Click Existing ISO image file and click Browse.
Step 9 Choose the ISO image from the SCVMM library, click OK, and click Next.
Step 10 In the Select Destination panel, keep the default settings of Place the virtual machine on a host; Destination: All Hosts and click Next.
Step 11 After the host is displayed in the Select Host panel, chose it, and click Next.
Step 12 In the Configure Settings panel, review the settings and click Next.
Step 13 In the Select Networks panel, choose the virtual switches that are used for the virtual machine. For each network adapter, select the type of the virtual switch. For example, choose Standard Switch or Logical Switch and click Next.
Step 14 In the Add Properties panel, keep the default settings of the Automatic Actions and click Next.
Step 15 In the Confirm the Settings panel in the final Summary window, review and confirm the settings.
Step 16 Click Create to begin the virtual machine creation. A progress bar is displayed in the Job Status column in the VM window.
Step 17 After the virtual machine creation is complete, right-click the Name of the virtual machine in the SCVMM user interface and choose Power On.
Step 18 Right-click the Name of the virtual machine again, click Connect or View, and choose Connect via Console.
See Table 1-1 for more information about the Cisco Nexus 1000V ISO boot options.
Install the Cisco Nexus 1000V only if the disk is unformatted, and bring up the new image |
|||
Install Cisco Nexus 1000V only if the disk is unformatted and go to the VSH shell |
Configuring the VSM
After installing VSM using a VM template, connect to a VM console and configure the VSM. We recommend that the VSM is deployed using the template provided by Cisco. After the deployment is complete, power on the VSM. The following basic inputs are required for the VSM configuration:

Note Make sure that you eject the virtual ISO image from the CD ROM.
Deploying the VSM
To deploy the VSM, perform the following steps:
Step 1 When the Virtual Machine Viewer window opens, the message “Do you want to format it? (y/n)” appears. Enter Y (yes).
Step 2 At the command prompt, when the message “Perform r/w tests (takes very long time) on target disks? (y/n)” appears, enter Y (yes).

Note The default action is taken if you do not immediately respond to the message prompts.
Step 3 After the software is copied and the CD-ROM drive is mounted, you are prompted to enter the System Administrator Account Setup. At the Enter the password for “admin”: prompt, enter the password. At the Confirm the password for “admin”: prompt, reenter the password.
Step 4 Enter the HA role at the prompt Enter HA role [standalone/primary/secondary].

Note We recommend that you create a VSM HA pair. Configure the first VM as the primary VSM and install the second VM as the secondary VSM.
If you set the HA role as secondary, the following question is displayed at the prompt: Setting HA role to secondary will cause a system reboot. Are you sure (yes/no)?: Enter Yes if you want to set the HA role to Secondary.
Step 5 At the prompt, enter the domain ID: Enter the domain ID[1-1023]; for example, 199. A domain ID is required for the VSMs to communicate with each other. While installing the secondary VSM, enter the same domain ID that was specified for the primary VSM.
Step 6 After step 5 for secondary VSM, the message is displayed: saving boot configuration and the system reloads.
Step 7 At the prompt, the Basic System Configuration Dialog is displayed. Enter Yes at the prompt.
Step 8 At the command prompt, the following message is displayed: Create another login account? [yes/no] (n). Select No to skip creating another login account.

Note The defaults are used if you do not change the values.
Step 9 Enter the switch name; for example, Nexus1000V-Eng.
Step 10 Press Y for yes when prompted to continue with the out-of-band management configuration.
Step 11 Enter the Mgmt0 IPv4 address for the VSM; for example, 10.10.10.4.
Step 12 Enter the Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask; for example, 255.255.255.0.
Step 13 At the command prompt, the following message is displayed: Configure the default gateway? Enter Y for yes.
Step 14 Enter the IPv4 address of the default gateway; for example, 10.10.10.5.
Step 15 At the command prompt, the following message is displayed: Vem feature level will be set to 5.2(1)SM3(1.1). Do you want to reconfigure? (yes/no) [n]: Press Enter at the prompt to enter the default value.
Step 16 Enter n when the following command prompt message is displayed: Configure Advanced Options? (yes/no)[n]:.
Step 17 The following message is displayed: Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Press Enter at the prompt to enter the default value.
Step 18 Enter y when the following command prompt message is displayed: Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]:.
Step 19 Complete steps 1 to 5 to configure the secondary VSM with an HA role.
Step 20 Verify the HA role using the command show system redundancy status on primary and secondary VSMs.
Configuring the VSM
After completing these steps, you are prompted to log into the VSM. Access the VSM via SSH using the IP address configured in the VSM installation section. The following minimal objects need to be created on the VSM:
- Logical network
- Network segment pool
- IP pool template
- Network segment
- Virtual Ethernet port profile
- Ethernet port profile
- Network uplink
To configure the VSM, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enter the configuration mode using the command config t.
Step 2 Create a logical network using the command nsm logical network <name> at the prompt to configure the SCVMM networking fabric; for example, nsm logical network Intranet. Type exit. You can enter any name for the logical network.
Step 3 Create a network segment pool using the command nsm network segment pool <name>; for example, nsm network segment pool IntranetSJ.
Step 4 Associate the network segment pool to the logical network using the command member-of logical-network <name>; for example, member-of logical-network Intranet. Type exit.
Step 5 Create an IP pool template using the command nsm ip pool template <name>; for example, nsm ip pool template pool10.
Step 6 Configure the IP address range and network IP address range using the commands, for example, ip address <30.0.0.2> <30.0.0.100> and network <30.0.0.2> <255.255.255.0>.Type exit.
Step 7 Create a network segment using the command nsm network segment <name>; for example, nsm network segment VMNetworkA.
Step 8 Create a VLAN inside the network segment using the command switchport access vlan <number>; for example, switchport access vlan 100.
Step 9 Associate the network segment pool to the network segment using the command member-of network segment pool <name>; for example, member-of network segment pool IntranetSJ.
Step 10 (Optional) Import the IP pool template to the network segment. Specify the IP subnet using the commands ipsubnet [ CIDRnotation ] and ip pool import template [ name ]. For example:

Note The IP subnet should be the same as the network specified in the ip pool template command.
Step 11 Publish the network segment using the command publish network segment <name>; for example, publish network segment VMNetworkA. Type exit.
Step 12 Create a virtual Ethernet port profile using the command port-profile type vethernet <name>; for example, port-profile type vethernet Veth-policy.
Step 13 Enter the no shutdown command to keep the system in a power-on state. Enter state enabled at the prompt.
Step 14 Publish the port profile using the command publish port-profile and type exit. The port profile is imported for publishing the network uplink.
Step 15 Create a virtual Ethernet port profile using the command port-profile type ethernet <name>; for example, port-profile type ethernet eth-pp-policy .
Step 16 Enter the no shutdown command to keep the system in a power-on state. Enter state enabled at the prompt.
Step 17 Create a network uplink using the command nsm network uplink NexusUplink.
Step 18 Associate the network segment pool using the command allow network segment pool IntranetSJ; for example, allow network segment pool IntranetSJ.
Step 19 Import the port profile that was created earlier using the command import port-profile <name>; for example, import port-profile eth-pp-policy.
Step 20 Publish the network uplink using the command publish network uplink <name>; for example, publish network uplink NexusUplink. Type exit.
Step 21 Copy the running configuration to the start-up configuration using the command copy running-config startup-config. The following message is displayed in the window: Copy complete, now saving to disk (please wait)
Step 22 Enter the command show running-config to verify the configuration.

Note The setup script configures the VSM to function in L3 control mode. L2 control mode is not supported with Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V. When configuring L3 control with Microsoft Hyper-V, you do not need to create a port profile with L3 control.
Configuring the SCVMM Fabric Workflow

Note The entire workflow to configure the SCVMM fabric can also be performed using scripts. For more information, see PowerShell Scripts for Configuring the SCVMM Fabric Workflow.
To install and configure the VSM workflow, create a Microsoft switch for VSM connectivity and then perform the following steps:
Connecting SCVMM to VSM
Once the VSM is up, configure the SCVMM networking fabric for the Cisco Nexus 1000V.

Note Check and turn off the proxy server settings for your LAN in the Internet Options settings window of Internet Explorer before proceeding to the next steps.
Connecting SCVMM 2012-R2 to VSM
To retrieve the objects from the VSM to SCVMM 2012 R2, perform the following steps:.
Step 1 When the VSM is up, log in to the VSM using SSH and the IP address configured in the previous section.
Step 2 From the SCVMM administrator console, navigate to the Fabric pane.
Step 3 Under Networking, select Network Service.
Step 4 Right-click to add a Add Network Service . The Add Network Service wizard is displayed.
Step 5 Enter a name for the Network Service and click Next . In the description, mention that it is a virtual switch extension.
Step 6 Step 6: In the Manufacturer and Model window, select the settings as outlined in the following steps:
a. a.Select a manufacturer, for example, Cisco Systems, Inc .
b. Select the model type, for example, Nexus 1000V Chassis 2.0 .
Step 7 Step 7: In the next window, select Run As Accoun t.
Step 8 In the Run As account field, click Browse . The Select a Run As Account window opens.
a. In the Select a Run As Account window, select an account from the available options or click Create Run As account tab to create an account for the VSM. A Create Run As account window opens.
b. In the Create Run As account window, enter the following VSM credentials:
– Enter the name of the account in the Name field as VSM_admin.
– Enter the description of the account in the Description field.
– Enter the user name in the User Name field and the password in the Password field.
– Confirm the password in the Confirm password field.
– Uncheck the Validate Domain Credentials box as the Active Directory cannot be validated with the credentials.
– The new account, for example, VSM_admin is displayed in the Select a Run As Account window. This is a one-time procedure for the VSM.
c. Select the new account and click OK in the Select a Run As Account window.
Step 9 Enter the IP address of the VSM in the connection string, for example, http://10.10.10.4. To use HTTPS, see Installing the VSM Certificate
Step 10 In the Providers window, choose the provider as Cisco Systems Nexus 1000V and click Test . This verifies the communication between the Cisco VSM and the SCVMM.
Step 11 In the Host Groups panel, select a few or all the host groups that can use the virtual switch extension manager and click Next .
Step 12 In the Summary panel, confirm the settings and click Finish.
Once the Virtual Network Service has been successfully added, it is listed in the main window in the SCVMM user interface at the path: Fabric > Networking > Network Service.
Creating a Logical Switch in SCVMM
Once the Virtual Switch Extension Manager has been added, create a logical switch on VMM. Define the extensions and port profiles for the logical switch, create classifications that contain the native port profile and a port profile for each extension as outlined in the following steps.
To create a logical switch, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the SCVMM user interface, under Networking, right-click Logical Switches and then click Create Logical Switch. The Create Logical Switch wizard appears.
Step 2 The Getting Started panel opens. Review the instructions and click Next.
Step 3 In the General panel, add a name and the description for the logical switch in the Name and Description fields; for example, N1000V_Test .
Step 5 In the Extensions panel, the virtual switch extensions are listed. Choose the extension that you created in the previous steps. This is listed as a forwarding extension. Do not change any selections of the auto-selected extensions.
Step 7 In the Uplink panel, specify the uplink port profiles that are part of this logical switch. The uplink port profiles are available for use on the hosts where an instance of the logical switch is created.
– Choose Team in the Uplink mode field to select multiple uplinks.

Note Even if you use a single uplink or multiple uplinks, the mode should always be Team.
– In the Uplink port profiles field, click Add . The Add Uplink Port Profile window opens. Select a port profile that is available for use by the host physical adapter that connects to this logical switch.
Step 8 In the Virtual Port panel, click Add . The Add Virtual Port window opens.
– Choose the VSM by checking the name that was created earlier; for example, Nexus 1000v-Test .
– Select the port profile from the drop-down menu.
– Select a port profile classification for the port profile; for example, AllAccess1 .
– Click Browse in the Port Classification field. Assign the selected port profile to a port classification in the Select a Port Profile Classification window.
– Click Create Port Classification . The Create Port Classification wizard opens. Enter the name for the port profile classification in the Name field; for example, AllAccess1 . Enter the description for the port profile classification in the Description field.
– Click OK . The selected port classification is displayed in the Select a Port Profile Classification window.
– Choose the port classification from the table.
Step 9 Click OK to finish adding the Virtual Port.
Step 10 Click Next to close the Create Logical Switch wizard.
Step 11 In the Summary panel, confirm the settings and click Finish. Now the logical switch is created.
The defined configuration is available on every host that uses the logical switch and the hosts, virtual switches, and virtual machines remain in compliance with their associated logical switch

Note If you want to add more port profiles to the VSM, you must configure the properties again. All the hosts should be configured for multiple uplinks. To update the properties and add more uplink port profiles, right-click the logical switch in the SCVMM user interface and click Properties.
Configuring the VM Network
Once the logical switch and the hosts are configured, complete the following steps to configure the VMs and associate the network segments to the VMs.
Step 1 Click VMs and Services in the left navigation panel of the SCVMM user interface.
Step 2 Click VM Networks. Right-click and select the Create VM Network option. The Create VM Network wizard opens.
Step 3 In the Name panel, specify the name for the VM network in the Name field. Enter the description for the VM network in the Description field. For example, add a name for the VM network as VM_network. If the name is same as the network-segment name, it is easy for the customers to do the mapping.
Step 4 Select the Logical Network which is created on the VSM.
Step 6 To configure VM network in SCVMM 2012 R2, do the following:
a. In the Isolation panel, select the Network manager in which is the logical switch was created.
c. In the Isolation options panel, select Specify an externally supplied VM network to configure the isolation externally. Confirm the External VM Network that was previously created; for example, VM_Network.
Step 8 In the Summary panel, confirm the settings, and click Finish.
The new VM network is displayed in the VM Networks and IP Pools panel in the SCVMM user interface.
Installing the VSM Certificate
To enable HTTPS communication between the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V VSM software and the SCVMM server, you must first install the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V VSM certificate. You can install this certificate either manually or nu using a script.
Installing the VSM Certificate Manually
To install the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V VSM software certificate, perform the following steps:
Step 1 From the SCVMM Server, open Internet Explorer, and connect to the VSM using https://vsm-ip .
The Certificate Error window opens.
Step 2 Choose the Continue to this website option.
The Cisco Nexus 1000V window opens.
Step 3 Select the Certificate Error link that is available on the address bar of the same window.
Step 4 From the Unstrusted Certificate dialog box click View Certificates .
The Cisco Nexus 1000V VSM certificate appears.
Step 5 Click the Install Certificate button.
The Certificate Import wizard opens.
Step 6 Choose Local Machine as the installation location and click Next .
Step 7 Based on the VM settings, a popup window for the User Account Control (UAC) may open.
Step 8 On the next window, select the Place all certificates in the following store option and click Browse.
Step 9 Choose the Trusted Root Certification Authorities option available on the certificate store and click OK .
Step 10 Click Next on the Certificate Import wizard.
Step 11 Review the summary on the final window and Select Finish . This completes the importing of the certificate.
Step 12 Press OK on the Certificate Import wizard.
Step 13 Press OK on the Certificate window.
Installing the VSM Certificate Using a Script
Use the following PowerShell script to install the VSM certificate:
This script is available at the following location on the SCVMM server:
PowerShell Scripts for Configuring the SCVMM Fabric Workflow
After the Cisco VSM Provider (Nexus1000V-NetworkServiceProvider-5.2.1.SM3.1.1c.0.msi) is installed from the download package on the SCVMM server, the following scripts are available in %ProgramFiles%\Cisco\Nexus1000V\V2\Scripts\VMMConfig example "C:\Program Files\Cisco\Nexus1000V\V2\Scripts\VMMConfig":
- Deploy-Nexus1000V-VSEM.ps1
- Refresh-Nexus1000V-VSEM.ps1
- Install-Nexus1000V-VSMCertificate.ps1
- Cleanup-Nexus1000V-VSEM.ps1
This script handles the following operations that you would need to do on the SCVMM server:
a. Add extension manager/network service.
c. Associate Cisco uplink port profiles with the logical switch (created in step b).
d. Associate virtual port profiles with the logical switch (created in step b).
e. Create VM networks from Cisco published network segments.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use this script if the Cisco VSEM is already added to the SCVMM server and you need to configure new objects such as port profiles, network segments, or uplink networks on the VSM. You may also need to refresh the Cisco VSEM to associate the Cisco Nexus 1000V objects on the SCVMM and make them available for usage.
This script helps you refresh the VSEM and make the necessary associations.
The following example creates a new VM network (VMNetworkB), a new port classification (Veth-policy-new), and a new uplink network (NexusUplink-New) on the Cisco VSM.

Note The following were already created on the Cisco VSM as shown in Deploy-Nexus1000V-VSEM.ps1:
- Existing VM network (VMNetworkA)
- Existing port classification (Veth-policy)
- Existing uplink network (NexusUplink)
Install-Nexus1000V-VSMCertificate.ps1
This script is used to install the Cisco Nexus1000V VSM certificate on the SCVMM server. This certificate is required to establish an HTTPS connection between the SCVMM server and the VSM.
This script is used to perform a cleanup of the Cisco Nexus 1000V components available on the SCVMM server.
This script exits if it encounters any Cisco Nexus 1000V objects.
Preparing the Microsoft Hyper-V Hosts (Optional)
Before you add hosts to the logical switch, you can prepare the Microsoft Hyper-V hosts. This step is optional.
Configuring the MTU with the Cisco Nexus 1000V
In Microsoft Hyper-V, the VSM does not manage the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) setting of VM NIC or physical adapters. All physical adapters added to the Cisco Nexus 1000V switch should have the same MTU configured and the PNIC MTU should not be changed after it is added to the switch.
To configure the MTU, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Open View Network Connections from the Server Manager or Control Panel or by typing ncpa.cpl from a command line.
Step 2 Right-click the adapter and choose Properties.
Step 3 Click Configure under the adapter properties window.
Step 4 Click the Advanced tab.
Step 5 Under Property , click Jumbo Packet and set the desired value.
Repeat this procedure for all adapters that are added to Cisco Nexus 1000V logical switch.

Note Certain adapters allow the MTU change only through their own adapter manager. For example, the MTU of the Cisco VIC cards can be changed through the UCSM or ILO.
VMQ Processor Configuration with the Cisco Nexus 1000V
VMQ allows the network traffic received on an adapter to be spread over multiple CPU cores which provides better performance. The following two factors are important in determining if the VMQ operates correctly:
- The receive side scaling (RSS) CPU number determines the lowest CPU core that can be used by RSS.
- The maximum number of RSS CPU determines how many CPU cores can be used by RSS.
The above two factors can be configured so that the same CPU core is not used by multiple NICs.

Note Changing the RSS registry is a disruptive operation and causes the Ethernet adapter to flap.
The Cisco Nexus 1000V supports the following port-channel operational modes: Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) and vPC.
The LACP utilizes the same Subgroup id for all the members of a port-channel. The RSS Base CPU and Max RSS Processors should be configured with same value for all member ports.
MAC pinning/manual pinning port-channel use multiple subgroup IDs within the members of the port-channel. Therefore, the RSS Base CPU and Max RSS processors should be configured so that the same CPU core is not used by multiple NICs.
Changing the RSS Registry
To change the RSS registry, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Open View Network Connections from the Server Manager or Control Panel or by typing ncpa.cpl from a command line.
Step 2 Right-click the adapter and choose properties .
Step 3 Under the Adapter Properties window, click Configure .
Step 4 Click the Advanced tab.
Step 5 Click Maximum Number of RSS Processor and enter a value.
Step 6 Click Starting RSS CPU and enter a value.
Repeat this procedure for all the adapters that you want VMQ to be enabled on.
The RSS setting cannot be modified through the network connections for certain adapters. For those adapters, you must set the registry keys directly using the registry editor. Check the Microsoft documentation for information about changing the registry.
Adding Hosts to a Logical Switch
After a logical switch is created, you can update the properties of the logical switch.
Step 1 In the left navigation pane, choose the server, under Fabric > Servers > All Hosts, right-click and choose Properties. The Properties window opens.
Step 2 In the left navigation pane of the Properties window, click Virtual Switch es .
Step 3 In the Virtual Switches pane, in the New Virtual Switches field, click New Logical Switch. Choose the correct logical switch and physical adapters to assign to the logical switch. The module is added to Cisco Nexus1000V VSM.

Note The MGMT PNIC can be added to the logical switch only when the switch is created. Adding it later results in a loss of host connectivity.
Step 4 Under the Physical Adapter header, choose a network adapter from the drop-down list in the Adapter field. In the Uplink Port Profile field, confirm the uplink port profile for the adapter.
Step 5 For port-channeling, click Add to add a second network adapter. Choose a different network adapter, confirm the uplink port profile, and click OK.

Note Do not use the same port profile for both adapters. If you have configured the port channels, then you can use the same port-profile on both the adapters. Refer the NSM Configuration Guide for more details.
The Cisco Nexus 1000V package that was copied on the SCVMM is installed on the host.
We recommend that you create one logical switch per VSM.
Connecting the VM Network Adapter to the Logical Switch
To connect the VM network adapter to the Logical Switch, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Choose the VM network adapter.
Step 2 Choose the server on which the VM is installed in the SCVMM user interface. In the left navigation pane under VMs and Services > All Hosts, click the Hyper-V server. In the main window, right-click the virtual machine that you have created, and choose Properties.
Step 3 In the properties file, click Hardware Configuration in the left navigation pane.
Step 4 In the Hardware Configuration panel, choose NetWork Adapter.
Step 5 In the Network Adapter 1 pane on the right, choose Connected to a VM Network.
Step 6 Browse to find the VM network created in an earlier section.
Step 8 In the Hardware Configuration pane, under Virtual Switch, choose the logical switch in the Logical Switch field. For the classification, choose the previously created port profile in the Classification field.

Note If you set the default port profile earlier as outlined in Step 8 of Creating a Logical Switch in SCVMM. If you do not select a port classification for the logical switch in this window, the default port classification is applied to the logical switch.
The Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V installation is now complete.
 Feedback
Feedback