Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 5.x
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- December 19, 2014
Chapter: Configuring IGMP Snooping
Contents
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Information about IGMP Snooping
- Introduction
- IGMPv1 and IGMPv2
- IGMPv3
- Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
- Default Settings
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Globally for the VSM
- Configuring IGMP Snooping on a VLAN
- Verifying the IGMP Snooping Configuration
- Example Configuration IGMP Snooping
- Feature History for IGMP Snooping
Configuring IGMP Snooping
This chapter contains the following sections:
- Information about IGMP Snooping
- Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
- Default Settings
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Verifying the IGMP Snooping Configuration
- Example Configuration IGMP Snooping
- Feature History for IGMP Snooping
Information about IGMP Snooping
Introduction
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping software examines Layer 2 IP multicast traffic within a VLAN to discover the ports where interested receivers reside. Using the port information, IGMP snooping can reduce bandwidth consumption in a multi-access LAN environment to avoid flooding the entire VLAN. The IGMP snooping feature tracks which ports are attached to multicast-capable routers to help the routers forward IGMP membership reports. The IGMP snooping software responds to topology change notifications. By default, IGMP snooping is enabled on the device.
The following figure shows an IGMP snooping switch that sits between the host and the IGMP router. The IGMP snooping switch snoops the IGMP membership reports and Leave messages and forwards them only when necessary to the connected IGMP routers.
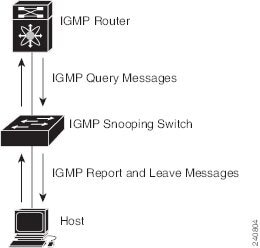
The IGMP snooping software operates upon IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 control plane packets where Layer 3 control plane packets are intercepted and influence the Layer 2 forwarding behavior.
The Cisco Nexus 1000V IGMP snooping implementation has the following proprietary features:
Multicast forwarding based on an IP address rather than a MAC address.
Optimized multicast flooding (OMF) that forwards unknown traffic to routers only and performs no data driven state creation.
For more information about IGMP snooping, see RFC 4541.
IGMPv1 and IGMPv2
If no more than one host is attached to each VLAN switch port, you can configure the fast leave feature in IGMPv2. The fast leave feature does not send last member query messages to hosts. As soon as the software receives an IGMP leave message, the software stops forwarding multicast data to that port.
IGMPv1 does not provide an explicit IGMP leave message, so the software must rely on the membership message timeout to indicate that no hosts remain that want to receive multicast data for a particular group.
Report suppression is not supported and is disabled by default.
 Note | The software ignores the configuration of the last member query interval when you enable the fast leave feature because it does not check for remaining hosts. |
IGMPv3
IGMPv3 snooping provides constrained flooding based on the group IP information in the IGMPv3 reports.
By default, the software tracks hosts on each VLAN port. The explicit tracking feature provides a fast leave mechanism. Because every IGMPv3 host sends membership reports, report suppression limits the amount of traffic that the switch sends to other multicast-capable routers.
Even though the IGMPv3 membership reports provide a full accounting of group members on a LAN segment, when the last host leaves, the querier sends a membership query. You can configure the parameter last member query interval. If no host responds before the timeout, the software removes the group state. If the querier specifies a mean-response-time (MRT) value in the query, it overrides the last member query interval configuration.
Prerequisites for IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping has the following prerequisites:
You are logged in to the switch.
A querier must be running on the uplink switches on the VLANs that contain multicast sources and receivers.
When the multicast traffic does not need to be routed, you must configure an external switch to query membership. On the external switch, define the query feature in a VLAN that contains multicast sources and receivers but no other active query feature. In the Cisco Nexus 1000V, report suppression is not supported and is disabled by default.
When an IGMP snooping query feature is enabled , it sends out periodic IGMP queries that trigger IGMP report messages from hosts wanting to receive IP multicast traffic. IGMP snooping listens to these IGMP reports to identify accurate forwarding.
Default Settings
| Parameters | Default |
|---|---|
IGMP snooping |
Enabled |
IGMPv3 Explicit tracking |
Enabled |
IGMPv2 Fast leave |
Disabled |
Last member query interval |
1 second |
Link-local groups suppression |
Enabled |
Snooping querier |
Disabled |
IGMPv1/v2 Report suppression |
Disabled |
IGMPv3 Report suppression |
Disabled |
Configuring IGMP Snooping
Enabling or Disabling IGMP Snooping Globally for the VSM
Use this procedure to enable or disable IGMP snooping globally for the VSM. IGMP snooping is enabled globally on the VSM (the default). If enabled globally, you can turn it on or off per VLAN.
You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
switch# configure terminal
switch(config)# no ip igmp snooping
switch(config)# show ip igmp snooping
Global IGMP Snooping Information:
IGMP Snooping enabled
IGMPv1/v2 Report Suppression disabled
IGMPv3 Report Suppression disabled
Link Local Groups Suppression enabled
IGMP Snooping information for vlan 1
IGMP snooping enabled
IGMP querier none
Switch-querier disabled
IGMPv3 Explicit tracking enabled
IGMPv2 Fast leave disabled
IGMPv1/v2 Report suppression disabled
IGMPv3 Report suppression disabled
Link Local Groups suppression enabled
Router port detection using PIM Hellos, IGMP Queries
Number of router-ports: 0
Number of groups: 0
Active ports:
--More--
switch(config)#
Configuring IGMP Snooping on a VLAN
Use this procedure to configure IGMP snooping on a VLAN. IGMP snooping is enabled by default for all VLANs in the VSM.
You are logged in to the CLI in EXEC mode.
 Note | If IGMP snooping is disabled globally, it takes precedence over the VLAN state. |
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | switch# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 2 | switch(config)# vlan configuration vlan-id | Enters configuration mode for the specified VLAN. | ||
| Step 3 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping | Enables or disables IGMP snooping in the running configuration for the specific VLAN. If IGMP snooping is enabled for the VSM, then IGMP snooping is enabled for the VLAN by default.
| ||
| Step 4 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping explicit-tracking | (Optional) Tracks IGMPv3 membership reports from individual hosts for each port on a per-VLAN basis in the running configuration. The default is enabled. | ||
| Step 5 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping fast-leave | (Optional) Enables fast-leave for the specified VLAN in the running configuration. Fast-leave supports IGMPv2 hosts that cannot be explicitly tracked because of the host report suppression mechanism of the IGMPv2 protocol. Enables the software to remove the group state when it receives an IGMP Leave report without sending an IGMP query message. This parameter is used for IGMPv2 hosts when no more than one host is present on each VLAN port. When you enable fast leave, the IGMP software assumes that no more than one host is present on each VLAN port. The default is disabled. | ||
| Step 6 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping last-member-query-interval seconds | (Optional) Sets the interval the software waits after sending an IGMP query to verify that no hosts that want to receive a particular multicast group remain on a network segment. If no hosts respond before the last member query interval expires, the software removes the group from the associated VLAN port. Values range from 1 to 25 seconds. The default is 1 second. | ||
| Step 7 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping mrouter interface type if_id | (Optional) Configures a static connection for the VLAN to a multicast router in the running configuration. The interface to the router must be in the specified VLAN. You can specify the interface by the type and the number, such as ethernet slot/port. vEths are not supported as router ports. | ||
| Step 8 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping static-group group-ip-addr interface type if_id | (Optional) Configures a VLAN Layer 2 port as a static member of a multicast group in the running configuration. You can specify the interface by the type and the number, such as ethernet slot/port. | ||
| Step 9 | switch(config-vlan-config)# [ no ] ip igmp snooping link-local-groups-suppression | (Optional) Configures link-local groups suppression. The default is enabled.
| ||
| Step 10 | switch(config-vlan-config)# show ip igmp snooping [ vlan vlan-id ] | (Optional) Displays the configuration for verification. | ||
| Step 11 | switch(config-vlan-config)# copy running-config startup-config | (Optional) (Optional) Saves the running configuration persistently through reboots and restarts by copying it to the startup configuration. |
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# vlan configuration 2 switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping explicit-tracking switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping fast-leave switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping last-member-query-interval 3 switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping mrouter interface ethernet 2/1 switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping static-group 230.0.0.1 interface ethernet 2/1 switch(config-vlan-config)# ip igmp snooping link-local-groups-suppression switch(config-vlan-config)# show ip igmp snooping vlan 2 IGMP Snooping information for vlan 2 IGMP snooping enabled IGMP querier none Switch-querier disabled IGMPv3 Explicit tracking enabled IGMPv2 Fast leave enabled IGMPv1/v2 Report suppression disabled IGMPv3 Report suppression disabled Link Local Groups suppression enabled Router port detection using PIM Hellos, IGMP Queries Number of router-ports: 0 Number of groups: 0 Active ports: switch(config-vlan)#
Verifying the IGMP Snooping Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the IGMP snooping configuration information.
| Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
show ip igmp snooping [ vlan vlan-id ] |
Displays IGMP snooping configuration by VLAN. |
show ip igmp snooping groups [ vlan vlan-id ] [ detail ] |
Displays IGMP snooping information about groups by VLAN. |
show ip igmp snooping querier [ vlan vlan-id ] |
Displays IGMP snooping queriers by VLAN. |
show ip igmp snooping mroute [ vlan vlan-id ] |
Displays multicast router ports by VLAN. |
show ip igmp snooping explicit-tracking [ vlan vlan-id ] |
Displays IGMP snooping explicit tracking information by VLAN. |
For detailed information about commands and their output, see the Cisco Nexus 1000V for Microsoft Hyper-V Command Reference.
Example Configuration IGMP Snooping
This example shows how to enable IP IGMP snooping for the VSM, and make the following optional configurations for VLAN 2:
Feature History for IGMP Snooping
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
IGMP Snooping |
5.2(1)SM1(5.1) |
This feature was introduced. |