Cisco ACI GOLF
The Cisco ACI GOLF feature (also known as Layer 3 EVPN Services for Fabric WAN) enables much more efficient and scalable ACI fabric WAN connectivity. It uses the BGP EVPN protocol over OSPF for WAN routers that are connected to spine switches.
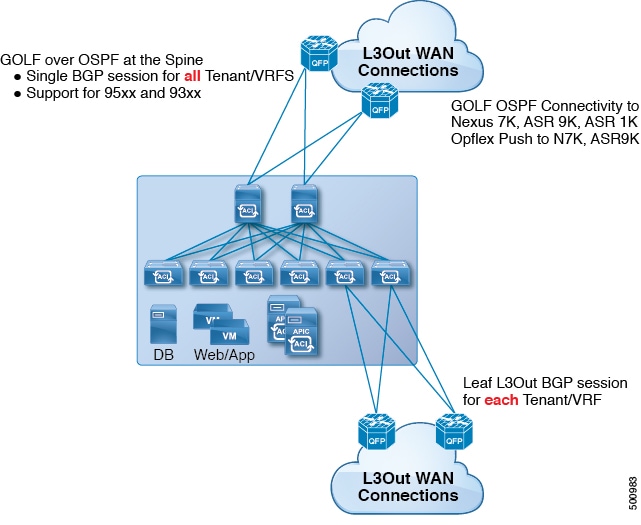
All tenant WAN connections use a single session on the spine switches where the WAN routers are connected. This aggregation of tenant BGP sessions towards the Data Center Interconnect Gateway (DCIG) improves control plane scale by reducing the number of tenant BGP sessions and the amount of configuration required for all of them. The network is extended out using Layer 3 subinterfaces configured on spine fabric ports. Transit routing with shared services using GOLF is not supported.
A Layer 3 external outside network (L3extOut) for GOLF physical connectivity for a spine switch is specified under the infra tenant, and includes the following:
-
LNodeP(l3extInstPis not required within the L3Out in the infra tenant. ) -
A provider label for the
L3extOutfor GOLF in the infra tenant. -
OSPF protocol policies
-
BGP protocol policies
All regular tenants use the above-defined physical connectivity. The L3extOut defined in regular tenants requires the following:
-
An
l3extInstP(EPG) with subnets and contracts. The scope of the subnet is used to control import/export route control and security policies. The bridge domain subnet must be set to advertise externally and it must be in the same VRF as the application EPG and the GOLF L3Out EPG. -
Communication between the application EPG and the GOLF L3Out EPG is governed by explicit contracts (not Contract Preferred Groups).
-
An
l3extConsLblconsumer label that must be matched with the same provider label of anL3Outfor GOLF in theinfratenant. Label matching enables application EPGs in other tenants to consume theLNodePexternalL3OutEPG. -
The BGP EVPN session in the matching provider
L3extOutin theinfratenant advertises the tenant routes defined in thisL3Out.
Guidelines and Limitations for Cisco ACI GOLF
Observe the following Cisco ACI GOLF guidelines and limitations:
-
GOLF does not support shared services.
-
GOLF does not support transit routing.
-
GOLF routers must advertise at least one route to Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) to accept traffic. No tunnel is created between leaf switches and the external routers until Cisco ACI receives a route from the external routers.
-
All Cisco Nexus 9000 Series Cisco ACI-mode switches and all of the Cisco Nexus 9500 platform Cisco ACI-mode switch line cards and fabric modules support GOLF. With Cisco APIC, release 3.1(x) and higher, this includes the N9K-C9364C switch.
-
At this time, only a single GOLF provider policy can be deployed on spine switch interfaces for the whole fabric.
-
Up to Cisco APIC release 2.0(2), GOLF is not supported with Cisco ACI Multi-Pod. In release 2.0 (2), the two features are supported in the same fabric only over Cisco Nexus 9000 switches without "EX" on the end of the switch name; for example, N9K-9312TX. Since the 2.1(1) release, the two features can be deployed together over all the switches used in the Cisco ACI Multi-Pod and EVPN topologies.
-
When configuring GOLF on a spine switch, wait for the control plane to converge before configuring GOLF on another spine switch.
-
A spine switch can be added to multiple provider GOLF outside networks (GOLF L3Outs), but the provider labels have to be different for each GOLF L3Out. Also, in this case, the OSPF Area has to be different on each of the
L3extOuts and use different loopback addresses. -
The BGP EVPN session in the matching provider
L3Outin theinfratenant advertises the tenant routes defined in thisL3extOut. -
When deploying three GOLF Outs, if only 1 has a provider/consumer label for GOLF, and 0/0 export aggregation, Cisco APIC will export all routes. This is the same as existing
L3extOuton leaf switches for tenants. -
If you have an ERSPAN session that has a SPAN destination in a VRF instance, the VRF instance has GOLF enabled, and the ERSPAN source has interfaces on a spine switch, the transit prefix gets sent from a non-GOLF L3Out to the GOLF router with the wrong BGP next-hop.
-
If there is direct peering between a spine switch and a data center interconnect (DCI) router, the transit routes from leaf switches to the ASR have the next hop as the PTEP of the leaf switch. In this case, define a static route on the ASR for the TEP range of that Cisco ACI pod. Also, if the DCI is dual-homed to the same pod, then the precedence (administrative distance) of the static route should be the same as the route received through the other link.
-
The default
bgpPeerPfxPolpolicy restricts routes to 20,000. For Cisco ACI WAN Interconnect peers, increase this as needed. -
In a deployment scenario where there are two
L3extOuts on one spine switch, and one of them has the provider labelprov1and peers with the DCI 1, the secondL3extOutpeers with DCI 2 with provider labelprov2. If the tenant VRF instance has a consumer label pointing to any 1 of the provider labels (either prov1 or prov2), the tenant route will be sent out both DCI 1 and DCI 2. -
When aggregating GOLF OpFlex VRF instances, the leaking of routes cannot occur in the Cisco ACI fabric or on the GOLF device between the GOLF OpFlex VRF instance and any other VRF instance in the system. An external device (not the GOLF router) must be used for the VRF leaking.
 Note |
Cisco ACI does not support IP fragmentation. Therefore, when you configure Layer 3 Outside (L3Out) connections to external routers, or Multi-Pod connections through an Inter-Pod Network (IPN), it is recommended that the interface MTU is set appropriately on both ends of a link. On some platforms, such as Cisco ACI, Cisco NX-OS, and Cisco IOS, the configurable MTU value does not take into account the Ethernet headers (matching IP MTU, and excluding the 14-18 Ethernet header size), while other platforms, such as IOS-XR, include the Ethernet header in the configured MTU value. A configured value of 9000 results in a max IP packet size of 9000 bytes in Cisco ACI, Cisco NX-OS, and Cisco IOS, but results in a max IP packet size of 8986 bytes for an IOS-XR untagged interface. For the appropriate MTU values for each platform, see the relevant configuration guides. We highly recommend that you test the MTU using CLI-based commands. For example, on the Cisco NX-OS CLI, use a command such as |
Using Shared GOLF Connections Between Multi-Site Sites
APIC GOLF Connections Shared by Multi-Site Sites
For APIC Sites in a Multi-Site topology, if stretched VRFs share GOLF connections, follow these guidelines to avoid the risk of cross-VRF traffic issues.
Route Target Configuration between the Spine Switches and the DCI
There are two ways to configure EVPN route targets (RTs) for the GOLF VRFs: Manual RT and Auto RT. The route target is synchronized between ACI spines and DCIs through OpFlex. Auto RT for GOLF VRFs has the Fabric ID embedded in the format: – ASN: [FabricID] VNID
If two sites have VRFs deployed as in the following diagram, traffic between the VRFs can be mixed.
|
Site 1 |
Site 2 |
|---|---|
|
ASN: 100, Fabric ID: 1 |
ASN: 100, Fabric ID: 1 |
|
VRF A: VNID 1000 Import/Export Route Target: 100: [1] 1000 |
VRF A: VNID 2000 Import/Export Route Target: 100: [1] 2000 |
|
VRF B: VNID 2000 Import/Export Route Target: 100: [1] 2000 |
VRF B: VNID 1000 Import/Export Route Target: 100: [1] 1000 |
Route Maps Required on the DCI
Since tunnels are not created across sites when transit routes are leaked through the DCI, the churn in the control plane must be reduced as well. EVPN type-5 and type-2 routes sent from GOLF spine in one site towards the DCI should not be sent to GOLF spine in another site. This can happen when the DCI to spine switches have the following types of BGP sessions:
Site1 — IBGP ---- DCI ---- EBGP ---- Site2
Site1 — EBGP ---- DCI ---- IBGP ---- Site2
Site1 — EBGP ---- DCI ---- EBGP ---- Site2
Site1 — IBGP RR client ---- DCI (RR)---- IBGP ---- Site2
To avoid this happening on the DCI, route maps are used with different BGP communities on the inbound and outbound peer policies.
When routes are received from the GOLF spine at one site, the outbound peer policy towards the GOLF spine at another site filters the routes based on the community in the inbound peer policy. A different outbound peer policy strips off the community towards the WAN. All the route-maps are at peer level.
Recommended Shared GOLF Configuration Using the NX-OS Style CLI
Use the following steps to configure route maps and BGP to avoid cross-VRF traffic issues when sharing GOLF connections with a DCI between multiple APIC sites that are managed by Multi-Site.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Configure the inbound route map Example: |
|
Step 2 |
Configure the outbound peer policy to filter routes based on the community in the inbound peer policy. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
Configure the outbound peer policy to filter the community towards the WAN. Example: |
|
Step 4 |
Configure BGP. Example: |
Configuring ACI GOLF Using the GUI
The following steps describe how to configure infra GOLF services that any tenant network can consume.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
On the menu bar, click Tenants, then click infra to select the infra tenant. |
|
Step 2 |
In the Navigation pane, expand the option and perform the following actions: |
|
Step 3 |
In the section of the Navigation pane, click to select the Golf policy just created. Enter a Provider Label, (for example, golf) and click Submit. |
|
Step 4 |
In the Navigation pane for any tenant, expand the and perform the following actions: |
Cisco ACI GOLF Configuration Example, Using the NX-OS Style CLI
These examples show the CLI commands to configure GOLF Services, which uses the BGP EVPN protocol over OSPF for WAN routers that are connected to spine switches.
Configuring the infra Tenant for BGP EVPN
The following example shows how to configure the infra tenant for BGP EVPN, including the VLAN domain, VRF, Interface IP addressing, and OSPF:
configure
vlan-domain evpn-dom dynamic
exit
spine 111
# Configure Tenant Infra VRF overlay-1 on the spine.
vrf context tenant infra vrf overlay-1
router-id 10.10.3.3
exit
interface ethernet 1/33
vlan-domain member golf_dom
exit
interface ethernet 1/33.4
vrf member tenant infra vrf overlay-1
mtu 1500
ip address 5.0.0.1/24
ip router ospf default area 0.0.0.150
exit
interface ethernet 1/34
vlan-domain member golf_dom
exit
interface ethernet 1/34.4
vrf member tenant infra vrf overlay-1
mtu 1500
ip address 2.0.0.1/24
ip router ospf default area 0.0.0.200
exit
router ospf default
vrf member tenant infra vrf overlay-1
area 0.0.0.150 loopback 10.10.5.3
area 0.0.0.200 loopback 10.10.4.3
exit
exit
Configuring BGP on the Spine Node
The following example shows how to configure BGP to support BGP EVPN:
Configure
spine 111
router bgp 100
vrf member tenant infra vrf overlay- 1
neighbor 10.10.4.1 evpn
label golf_aci
update-source loopback 10.10.4.3
remote-as 100
exit
neighbor 10.10.5.1 evpn
label golf_aci2
update-source loopback 10.10.5.3
remote-as 100
exit
exit
exit
Configuring a Tenant for BGP EVPN
The following example shows how to configure a tenant for BGP EVPN, including a gateway subnet which will be advertised through a BGP EVPN session:
configure
tenant sky
vrf context vrf_sky
exit
bridge-domain bd_sky
vrf member vrf_sky
exit
interface bridge-domain bd_sky
ip address 59.10.1.1/24
exit
bridge-domain bd_sky2
vrf member vrf_sky
exit
interface bridge-domain bd_sky2
ip address 59.11.1.1/24
exit
exit
Configuring the BGP EVPN Route Target, Route Map, and Prefix EPG for the Tenant
The following example shows how to configure a route map to advertise bridge-domain subnets through BGP EVPN.
configure
spine 111
vrf context tenant sky vrf vrf_sky
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target export 100:1
route-target import 100:1
exit
route-map rmap
ip prefix-list p1 permit 11.10.10.0/24
match bridge-domain bd_sky
exit
match prefix-list p1
exit
evpn export map rmap label golf_aci
route-map rmap2
match bridge-domain bd_sky
exit
match prefix-list p1
exit
exit
evpn export map rmap label golf_aci2
external-l3 epg l3_sky
vrf member vrf_sky
match ip 80.10.1.0/24
exit
Configuring GOLF Using the REST API
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
The following example shows how to deploy nodes and spine switch interfaces for GOLF, using the REST API: Example: |
|
Step 2 |
The XML below configures the spine switch interfaces and infra tenant provider of the GOLF service. Include this XML structure in the body of the POST message. Example: |
|
Step 3 |
The XML below configures the tenant consumer of the infra part of the GOLF service. Include this XML structure in the body of the POST message. Example: |
 Feedback
Feedback