Installation Guide for Cisco Security Manager 4.13
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- August 7, 2015
Chapter: Troubleshooting
- Startup Requirements for Cisco Security Manager Services
- Comprehensive List of Required TCP and UDP Ports
- Troubleshooting the Security Manager Server
- Troubleshooting the Security Manager Client
- Running a Server Self-Test
- Collecting Server Troubleshooting Information
- Viewing and Changing Server Process Status
- Restarting All Processes on Your Server
- Reviewing the Server Installation Log File
- Symantec Co-existence Issues
- Problems after Installing Windows Updates
- Problem Connecting to an ASA Device with Higher Encryption
- Pop-up Showing Activation.jar in Use During the Time of Installation
- How to Set the Locale for the Windows Default User Template to U.S. English
- How to disable the RMI Registry Port
Troubleshooting
CiscoWorks Common Services provides Security Manager with its framework for installation, uninstallation, and re-installation on servers. If the installation or uninstallation of Security Manager server software causes an error, see “Troubleshooting and FAQs” in the Common Services online help.
The following topics help you to troubleshoot problems that might occur when you install, uninstall, or re-install Security Manager-related software applications on a client system or on a server, including the standalone version of Cisco Security Agent.
- Startup Requirements for Cisco Security Manager Services
- Comprehensive List of Required TCP and UDP Ports
- Troubleshooting the Security Manager Server
- Troubleshooting the Security Manager Client
- Running a Server Self-Test
- Collecting Server Troubleshooting Information
- Viewing and Changing Server Process Status
- Reviewing the Server Installation Log File
- Symantec Co-existence Issues
- Problems after Installing Windows Updates
- Problem Connecting to an ASA Device with Higher Encryption
- Pop-up Showing Activation.jar in Use During the Time of Installation
- How to Set the Locale for the Windows Default User Template to U.S. English
- How to disable the RMI Registry Port
Startup Requirements for Cisco Security Manager Services
Cisco Security Manager services must be started in a specific order for Security Manager to function correctly. The initialization of these services is controlled by the Cisco Security Manager Daemon Manager service. You should not change the service startup type for any of the Cisco Security Manager services. You should also not stop or start any of the Cisco Security Manager services manually. If you need to restart a specific service, you should restart the Cisco Security Manager Daemon Manager which ensures that all the related services are stopped and started in the correct order.
Comprehensive List of Required TCP and UDP Ports
The Cisco Security Management Suite applications need to communicate with clients and other applications. Other server applications might be installed on separate computers. For successful communication, certain TCP and UDP ports need to be open and available for transmitting traffic. Normally, you need to open only those ports described in Required Services and Ports. However, if you find that the applications are not able to communicate, the following table describes additional ports that you might need to open. The list is in port number order.
|
|
|
Range of Ports |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4431 |
|||||
| Syslog2 |
|||||
Troubleshooting the Security Manager Server
This section answers questions that you might have about:
- Server Problems During Installation
- Server Problems After Installation
- Server Problems During Uninstallation
Server Problems During Installation
Q. When I install the server software, what does this installation error message mean?
Server software installation error messages and explanations appear in Table A-2, where they are sorted alphabetically by their first word.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
An earlier attempt to uninstall a Common Services-dependent application failed. |
1. 2. 3. |
|
|
Your license file is corrupted or the contents of the license file are invalid. |
|
|
|
You entered the pathname to an invalid license file for five consecutive attempts. After five failed attempts, installation continues in evaluation mode. |
Click OK to close the license error dialog box, and installation proceeds to the next screen of the wizard. |
The Windows 2012 R2 server may not have the following Microsoft Windows patches: b. Run clearcompressionflag.exe c. KB2919355, KB2932046, KB2959977, KB2937592, KB2938439, and KB2934018 These patches are required to register critical Cisco Security Manager services in this server. Ensure that you install these patches in the aforesaid order. We recommend you to install these patches before installing the Cisco Security Manager. Alternatively, you can also install these patches after installing the Cisco Security Manager, and then run the "<CSMInstalledDirectory>\CSCOpx\bin\RegisterApache.bat" CSM scripts to register the services. For more information, refer the Installation Guide for Cisco Security Manager. |
The recommended Windows Update patches may be missing in your Windows 2012 R2 server. |
Ensure you have the required patches installed in your server, before you begin installing Cisco Security Manager. You may proceed installing Cisco Security Manager, and then install these patches. However, you will be required to register Apache Services with the windows services. For more information, refer Readiness Checklist for Installation, page 4-3 . |
|
An earlier attempt to install a Common Services-dependant application failed. |
|
|
|
Your server does not meet the requirement for hard drive space. |
|
|
|
Temporary files that are supposed to be deleted automatically during software installations have not been deleted on your server. |
Search the temporary directory on your server for subdirectories with names that include the “_istmp” string. Delete all such subdirectories. |
|
|
You left Terminal Services enabled during installation, even though we do not support this. See Readiness Checklist for Installation, page 4-3 . |
To learn how to do this, see the “Terminal Server Support for Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 Server” topic in Installing and Getting Started With CiscoWorks LAN Management Solution 3.1, at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/net_mgmt/ciscoworks_lan_management_solution/3.1/install/guide/IGSG31.html |
|
|
The installation program checks the Windows account permissions during installation. If the Windows account that you are installing CiscoWorks Common Services under does not have local administrator privileges, InstallShield displays this error message. |
1. 2. |
Q. What should I do if the server installer suspends operation (hangs)?
Q. Can I install both Cisco Security Manager and Cisco Secure Access Control Server on one system?
We recommend that you do not. We do not support the coexistence of Security Manager on the same server with Cisco Secure ACS for Windows.
Q. Why does the Security Manager database backup fail?
If network management applications, such as Tivoli, were used to install Cygwin on the same system where a Security Manager server was installed, backup of the Security Manager database fails. Uninstall Cygwin.
Server Problems After Installation
Q. I want to change the hostname of the Security Manager Server. How do I achieve this?
You can change the hostname of the Security Manager Server by performing the steps detailed in (Optional) Changing the Hostname of the Security Manager Server.
Q. The Security Manager interface does not appear, or is not displayed correctly, or certain interface elements are missing. What happened?
There are several possible explanations. Investigate the scenarios in this list to understand and work around simple problems that might affect the interface:
- Some required services are not running on your server. Restart the server daemon manager, wait for all services to start completely, then restart Security Manager Client and try again to connect.
- Your server does not have enough free disk space. Confirm that the Security Manager partition on your server has at least 500 MB free.
- Your base license file is corrupted. See Getting Help with Licensing, page 2-8 .
- Your server uses the wrong Windows language. Only English, on US-English versions of Windows, and Japanese, on Japanese versions of Windows, are supported. (See Server Requirements and Recommendations, page 3-4 .) Any other language can corrupt the installed version of Security Manager, and missing GUI elements are one possible symptom. If you are using an unsupported language, you must select a supported language, then uninstall and re-install Security Manager. See Uninstalling Server Applications, page 5-21 .
- You ran the Security Manager installation utility over a network connection, but we do not support this use case (see Installing Security Manager Server, Common Services, and AUS, page 5-3 ). You must uninstall and re-install the server software. See Uninstalling Server Applications, page 5-21 .
- Your client system does not meet the minimum requirements. See Client Requirements, page 3-11 .
- You tried to use HTTP, but the required protocol is HTTPS.
- Buttons are the only missing element. You opened the Display Properties control panel on the client system, then changed one or more settings under the Appearance tab while you were simultaneously using Security Manager Client. To work around this problem, exit Security Manager Client, then restart it.
- The wrong graphics card driver software is installed on your client system. See Client Requirements, page 3-11 .
Problem When trying to open web interface to Security Manager using a web browser, a message indicates that I do not have permission to access /cwhp/LiaisonServlet on the Security Manager server. What does this mean?
Solution The following table describes common causes and suggested workarounds for this problem.
Q. Security Manager sees only the local volumes, not the mapped drives, when I use it to browse directories on my server. Why?
Microsoft includes this feature by design in Windows to enhance server security. You must place any files you need to select in Security Manager on the server, such as license files.
Q. Why is Security Manager missing from the Start menu in my Japanese version of Windows?
You might have configured the regional and language option settings on the server to use English. We do not support English as the language in any Japanese version of Windows (see Server Requirements and Recommendations, page 3-4 ). Use the Control Panel to reset the language to Japanese.
Q. My server SSL certificate is no longer valid. Also, the DCRServer process does not start. What happened?
You reset the server date or time so that it is outside the range in which your SSL certificate is valid. See Readiness Checklist for Installation, page 4-3 . To work around this problem, reset the server date/time settings.
Q. I was not prompted for the protocol to be used for communication between the server and client. Which protocol is used by default? Do I need to configure this setting manually using any other mode?
HTTPS is used as the communication protocol between the server and client, by default, when you install the client during the server installation. Because the communication is secure with the default protocol, you might not need to modify this setting manually.
An option to select HTTP as the protocol is available only when you run the client installer to install Security Manager client separately outside of the server installer. However, we recommend that you do not use HTTP as the communication protocol between the server and client. The client must use whatever protocol the server is configured to use.
Q. I am using a VMware setup, and system performance is unacceptably slow, for example, system backup takes two hours.
Ensure that you allocate two or more CPUs to the VM running Security Manager. Systems allocating one CPU have been found to have unacceptable performance for some system activities.
Q. Validation and some other operations fail with SQL query exception in logs. What happened?
It is possible that the Sybase temp directory ran out of disk space and, therefore, Sybase failed to create temp files. By default, Sybase creates temp files under the Windows temp directory. If the system variable SA_TMP is defined, then temp files are created in the directory specified by SA_TMP. Clear the disk space where the Sybase temp directory is located and then restart Security Manager.
Server Problems During Uninstallation
Q. What does this uninstallation error message mean?
Uninstallation error messages and explanations appear in Table A-4, where they are sorted alphabetically by their first word. For additional information about uninstallation error messages, see the Common Services documentation in your installation of Security Manager.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
The message might be benign, and clicking OK to dismiss it might be all that is required. Otherwise, the message might appear on servers where either or both of the following conditions apply: |
If you dismiss the message and the uninstallation fails, try either or both of these possible workarounds, then try again to uninstall: 1. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. |
|
setup.exe - Access is denied. 1 file(s) copied. |
Reboot the server, then complete the procedure described in Uninstalling Server Applications, page 5-21 . |
|
|
|
Either your organization uses WMI or someone enabled the WMI service accidentally on your server. |
Q. What should I do if the uninstaller hangs?
Q. What should I do if the uninstaller displays a message to say that the crmdmgtd service is not responding and asks “Do you want to keep waiting?”
The uninstallation script includes an instruction to stop the crmdmgtd service, which did not respond to that instruction before the script timed out. Click Yes. In most cases, the crmdmgtd service then stops as expected.
Troubleshooting the Security Manager Client
This section answers questions that you might have about:
Client Problems During Installation
Q. When I install the client software, what does this installation error message mean?
Client software installation error messages and explanations appear in Table A-5 , where they are sorted alphabetically by their first word.
Q. What should I do if the client installer suspends operation (hangs)?
Try the following. Any one of them might solve the problem:
- If antivirus software is installed on your client system, disable it, then try again to run the installer.
- Reboot the client system, then try again to run the installer.
- Use a browser on the client system to log in to the Security Manager server at http:// < server_name > :1741. If you see an error message that says “Forbidden” or “Internal Server Error,” the required Tomcat service is not running. Unless you rebooted your server recently and Tomcat has not had enough time yet to start running, you might have to review server logs or take other steps to investigate why Tomcat is not running.
Q. The installer says that a previous version of the client is installed and that it will be uninstalled. However, I do not have a previous version of the client installed. Is this a problem?
During installation or re-installation of the client, the installer might detect a previously installed client, even if no such client exists, and display an incorrect message that it will be uninstalled. This message is displayed because of the presence of certain old registry entries in your system. Although client installation proceeds normally when this message appears, use the Registry Editor to delete the following key to prevent this message from being displayed during subsequent installations: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\Cisco Security Manager Client. (To open the Registry Editor, select Start > Run and enter regedit.) Also, rename the C:\Program Files (x86)\Zero G Registry\.com.zerog.registry.xml file (any name will do).
Client Problems After Installation
Q. Why does the interface not look right?
An older video (graphics) card might fail to display the Security Manager GUI correctly until you upgrade its driver software. To test whether this problem might affect your client system, right-click My Computer, select Properties, select Hardware, click Device Manager, then expand the Display adapters entry. Double-click the entry for your adapter to learn what driver version it uses. You can then do one of the following:
–![]() If your client system uses an ATI MOBILITY FireGL video card, you might have to obtain a video driver other than the driver that came with your card. The driver that you use must be one that allows you to configure Direct 3D settings manually. Any driver lacking that capability might stop your client system from displaying elements in the Security Manager GUI.
If your client system uses an ATI MOBILITY FireGL video card, you might have to obtain a video driver other than the driver that came with your card. The driver that you use must be one that allows you to configure Direct 3D settings manually. Any driver lacking that capability might stop your client system from displaying elements in the Security Manager GUI.
–![]() For any video card, go to the web sites of the PC manufacturer and the card manufacturer to check for incompatibilities with the display of modern Java2 graphics libraries. In most cases where a known incompatibility exists, at least one of the two manufacturers provides a method for obtaining and installing a compatible driver.
For any video card, go to the web sites of the PC manufacturer and the card manufacturer to check for incompatibilities with the display of modern Java2 graphics libraries. In most cases where a known incompatibility exists, at least one of the two manufacturers provides a method for obtaining and installing a compatible driver.
Q. Why is the Security Manager Client missing from the Start menu in my Japanese version of Windows?
You might have configured the regional and language option settings to use English on the client system. We do not support English as the language in any Japanese version of Windows. Use the Control Panel to reset the language to Japanese.
Q. Why is the Security Manager Client missing from the Start menu for some or all the users on a workstation on which it is installed?
When you install the client, you select whether shortcuts will be created for just the user installing the product, for all users, or for no users. If you want to change your election after installation, you can do so manually by copying the Cisco Security Manager Client folder from Documents and Settings\<user>\Start Menu\Programs\Cisco Security Manager to Documents and Settings\All Users\Start Menu\Programs\Cisco Security Manager. If you elected to not create shortcuts, you need to manually create the shortcut in the indicated All Users folder.
Q. What can I do if my connections from a client system to the server seem unusually slow, or if I see DNS errors when I try to log in?
You might have to create an entry for your Security Manager server in the hosts file on your client system. Such an entry can help you to establish connections to your server if it is not registered with the DNS server for your network. To create this helpful entry on your client system, use Notepad or any other plain text editor to open C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts. (The host file itself contains detailed instructions for how to add an entry.)

Note![]() You might have to create an entry for your DNS additional entry which will point to the same IP address (which will be used in the Security Manager client application's “Server Name” field) in the httpd.conf configuration file under NMSROOT~/MDC/Apache/conf/ and restart the Daemon Manager. Such an entry can help you establish connections to your server. Examples:
You might have to create an entry for your DNS additional entry which will point to the same IP address (which will be used in the Security Manager client application's “Server Name” field) in the httpd.conf configuration file under NMSROOT~/MDC/Apache/conf/ and restart the Daemon Manager. Such an entry can help you establish connections to your server. Examples: ServerName, foo.example.com. [Tip: The location NMSROOT is the path to the Security Manager installation directory. The default is C:\Program Files (x86)\CSCOpx.]
Q. What is wrong with my authentication setup if my login credentials are accepted without any error message when I try to log in with Security Manager Client, but the Security Manager desktop is blank and unusable? (Furthermore, does the same problem explain why, in my web browser, Common Services on my Security Manager server accepts my login credentials but then fails to load the Cisco Security Management Suite desktop?)
You did not finish all the required steps for Cisco Secure ACS to provide login authentication services for Security Manager and Common Services. Although you entered login credentials in ACS, you did not define the Security Manager server as a AAA client. You must do so, or you cannot log in. See the ACS documentation for detailed instructions.
Q. What should I do if I cannot use Security Manager Client to log in to the server and a message says...?
Verify that your server meets the minimum hardware and software requirements. See Server Requirements and Recommendations, page 3-4 . |
|
|
|
There are two possible explanations:
a. b. |
|
|
At least one of the following services did not start correctly. On the server, select Start > Programs > Administrative Tools > Services, right-click each service named below, then select Restart from the shortcut menu:
Wait 5 minutes, then try again to start Security Manager Client. |
Q. Why is the Activity Report not displayed when I use Internet Explorer as my default browser?
This problem occurs because of invalid registry key values or inaccuracies with the location of some of the dll files associated with Internet Explorer. For information on how to work around this problem, refer to the Microsoft Knowledge Base article 281679, which is available at this URL: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/281679/EN-US.
Q. How can I clear the server list from the Server Name field in the Login window?
Edit csmserver.txt to remove unwanted entries. The file is in the directory in which you installed the Security Manager client. The default location is C:\Program Files (x86)\Cisco Systems\Cisco Security Manager Client.
Q. The Security Manager client did not load because of a version mismatch. What does this mean?
The Security Manager server version does not match the client version. To fix this, download and install the most recent client installer from the server.
Q. Where are the client log files located?
The client log files are located in C:\Program Files (x86)\Cisco Systems\Cisco Security Manager Client\logs. Each GUI session has its own log file.
Q. How do I know if Security Manager is running in HTTPS mode?
- After you log in to the server using a browser, look at the URL in the address field. If the URL starts with https, Security Manager is running in HTTPS mode.
- Go to Common Services > Server > Security > Single Server Management > Browser-Server Security Mode Setup. If you see Current Setting: Enabled, Security Manager is running in HTTPS mode. If the setting is Disabled, use HTTP.
- When logging in using the client, first try HTTPS mode (check the HTTPS checkbox). If you get the message “Login URL access is forbidden; Please make sure your protocol (HTTP, HTTPS) is correct,” the server is probably running in HTTP mode. Uncheck the HTTPS checkbox and try again.
Q. How can I enable the Client Debug log level?
In the file client.info, which is located by default in C:\Program Files (x86)\Cisco Systems\Cisco Security Manager Client\jars, modify the DEBUG_LEVEL parameters to include DEBUG_LEVEL=ALL and then restart the Security Manager client.
Q. When working with a dual-screen setup, certain windows and popup messages always appear on the primary screen, even when the Security Manager client is running on the secondary screen. For example, with the client running on the secondary screen, windows such as the Policy Object Manager always open in the primary screen. Can I fix this?
This is a known issue with the way dual-screen support is implemented in certain operating systems. We recommend running the Security Manager client on the primary screen. You should launch the client after configuring the dual-screen setup.
If a window opens on the other screen, you can move it by pressing Alt+spacebar, followed by M; you can then use the arrow keys to move the window.
Q. I cannot install or uninstall any software on a client system. Why?
If you run an installation and an uninstallation simultaneously on the client system, even if they are for different applications, you corrupt the client system InstallShield database engine and are prevented from installing or uninstalling any software. For more information, log in to your Cisco.com account, then use Bug Toolkit to view CSCsd21722 and CSCsc91430.
Running a Server Self-Test
To run a self-test that confirms whether your Security Manager server is operating correctly:
Step 1![]() From a system on which Security Manager Client is connected to your Security Manager server, select Tools > Security Manager Administration.
From a system on which Security Manager Client is connected to your Security Manager server, select Tools > Security Manager Administration.
Step 2![]() In the Administration window, click Server Security, then click any button. A new browser opens, displaying one of the security settings pages in the Common Services GUI, corresponding to the button you clicked.
In the Administration window, click Server Security, then click any button. A new browser opens, displaying one of the security settings pages in the Common Services GUI, corresponding to the button you clicked.
Step 3![]() From the Common Services page, select Admin under the Server tab.
From the Common Services page, select Admin under the Server tab.
Step 4![]() In the Admin page TOC, click Selftest.
In the Admin page TOC, click Selftest.
Step 6![]() Click the SelfTest Information at < MM-DD-YYYY HH:MM:SS > link, where:
Click the SelfTest Information at < MM-DD-YYYY HH:MM:SS > link, where:
Step 7![]() Read the entries in the Server Info page.
Read the entries in the Server Info page.
Collecting Server Troubleshooting Information
If you are experiencing problems with Security Manager, and you cannot resolve the problem after trying all the recommendations listed in the error message and reviewing this guide for a possible solution, use the Security Manager Diagnostics utility to collect server information.
The Security Manager Diagnostics utility collects server diagnostic information in a ZIP file, CSMDiagnostics.zip. You overwrite the file with new information each time you run Security Manager Diagnostics, unless you rename the file. The information in your CSMDiagnostics.zip file can help a Cisco technical support engineer to troubleshoot any problems that you might have with Security Manager or its related applications on your server.

Tip Security Manager also includes an advanced debugging option that collects information about the configuration changes that have been made with the application. To activate this option, select Tools > Security Manager Administration > Debug Options, then check the Capture Discovery/Deployment Debugging Snapshots to File check box. Bear in mind that although the additional information saved to the diagnostics file may aid the troubleshooting effort, the file may contain sensitive information, such as passwords. You should change debugging levels only if the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) asks you to change them.
You can run Security Manager Diagnostics in either of two ways.
Viewing and Changing Server Process Status
To verify that the server processes for Security Manager are running correctly:
Step 1![]() From the CiscoWorks home page, select Common Services > Server > Admin.
From the CiscoWorks home page, select Common Services > Server > Admin.
Step 2![]() In the Admin page TOC, click Processes.
In the Admin page TOC, click Processes.
The Process Management table lists all server processes. Entries in the ProcessState column indicate whether a process is running normally.
Step 3![]() If a required process is not running, restart it. See Restarting All Processes on Your Server.
If a required process is not running, restart it. See Restarting All Processes on Your Server.

Note![]() Only users with local administrator privileges can start and stop the server processes.
Only users with local administrator privileges can start and stop the server processes.
Restarting All Processes on Your Server

Note![]() You must stop all processes, then restart them all, or this method does not work.
You must stop all processes, then restart them all, or this method does not work.
Step 1![]() At the command prompt, enter net stop crmdmgtd to stop all processes.
At the command prompt, enter net stop crmdmgtd to stop all processes.
Step 2![]() Enter net start crmdmgtd to restart all processes.
Enter net start crmdmgtd to restart all processes.

Tip Alternatively, you can select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services, then restart Cisco Security Manager Daemon Manager.
Reviewing the Server Installation Log File
If responses from the server differ from the responses that you expect, you can review error and warning messages in the server installation log file.
Use a text editor to open Cisco_Prime_install_*.log.
In most cases, the log file to review is the one that has either the highest number appended to its filename or has the most recent creation date.
For example, you might see log file error and warning entries that say:
ERROR: Cannot Open C:\PROGRA~1\CSCOpx/lib/classpath/ssl.properties at C:\PROGRA~1\CSCOpx\MDC\Apache\ConfigSSL.pl line 259.
INFO: Enabling SSL....
WARNING: Unable to enable SSL. Please try later....

Note![]() In the event of a severe problem, you can send the log file to Cisco TAC. See Obtain Documentation and Submit a Service Request, page xi.
In the event of a severe problem, you can send the log file to Cisco TAC. See Obtain Documentation and Submit a Service Request, page xi.
Symantec Co-existence Issues
If you are using Symantec Antivirus Corporate Edition 10.1.5.5000 and Security Manager on the same system and observe any issues during Security Manager startup, follow this procedure:
Step 1![]() Disable Symantec Antivirus services completely.
Disable Symantec Antivirus services completely.
Step 2![]() Restart Security Manager services. (See Restarting All Processes on Your Server.)
Restart Security Manager services. (See Restarting All Processes on Your Server.)
Step 3![]() Restart the set of Symantec services (Symantec Antivirus, Symantec Antivirus Definition Watcher, Symantec Settings Manager, and Symantec Event Manager) in such a way that Symantec Event Manager is started last.
Restart the set of Symantec services (Symantec Antivirus, Symantec Antivirus Definition Watcher, Symantec Settings Manager, and Symantec Event Manager) in such a way that Symantec Event Manager is started last.
Problems after Installing Windows Updates
Problems can occur with the Security Manager Daemon Manager after installing Microsoft Windows updates. The reason is that installing Windows updates may update *.dll files that affect the functionality of Common Services and other applications that depend on them.
This problem can be recognized by the following symptoms: After a Windows update, Security Manager will start all processes; however, Security Manager will be unreachable over HTTPS and therefore from the Security Manager client, which uses HTTPS.
This problem occurs because Common Services relies on files and associations within Windows. These files can be altered to correct vulnerabilities and protect Windows from exploits. However, as an unintended side effect, these changes can cause the Security Manager server to act abnormally when it is restarted.
This problem can occur any time that Windows Update, or any other application, makes changes to Windows that affect *.dll files, executables, startup processes, Windows components, or partition sizes.
To resolve this problem in cases where changes in Windows have been made and Security Manager acts abnormally when it is restarted, Security Manager must be re-installed.
Cisco recommends backing up your Security Manager server regularly. In particular, if regular backups have not been made, or if many changes have been made to your Security Manager installation, you should back up your Security Manager server before running Windows Update or any other installer package.
Problem Connecting to an ASA Device with Higher Encryption
This troubleshooting topic may help you if you are unable to add and discover an ASA device with higher encryption. In particular, if you want to use AES-256, you must download and install the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Files. Security Manager does not include this extension, but it does support it.
Problem The problem occurs when the certificate contains a key longer than 1024 bits. The cryptography strength limitations placed by the default policy files included with Java Runtime Environment (JRE) give the highest strength cryptography algorithms and key lengths which are allowed for import to all countries.
Solution If your country does not place restrictions on the import of cryptography, you can download the unlimited strength policy files:
Step 1![]() Go to http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp.
Go to http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp.
Step 2![]() Download the “Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Files 6.”
Download the “Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy Files 6.”
Step 3![]() Follow the instructions in the README.txt file in the downloaded package.
Follow the instructions in the README.txt file in the downloaded package.
Pop-up Showing Activation.jar in Use During the Time of Installation
This troubleshooting topic may help you if, during installation, a pop-up window appears with the message “Activation.jar being used by some other service.”

Tip This problem is extremely rare.
Any anti-virus or monitoring agent process in the server should be shut down before the installation. For more information, refer to Readiness Checklist for Installation.
A pop-up window appears with the message “Activation.jar being used by some other service.”
Step 1![]() Click OK on the pop-up and complete the installation.
Click OK on the pop-up and complete the installation.
Step 2![]() Uninstall Security Manager and restart the server.
Uninstall Security Manager and restart the server.
Step 3![]() Install Security Manager again.
Install Security Manager again.
Step 4![]() Immediately after the start of the installation, enter “services.msc” at a command prompt and press Enter.
Immediately after the start of the installation, enter “services.msc” at a command prompt and press Enter.
Step 5![]() When the Services menu opens, keep refreshing it until “Cisco Security Manager Daemon Manager” appears.
When the Services menu opens, keep refreshing it until “Cisco Security Manager Daemon Manager” appears.
Step 6![]() Right-click CSM Daemon Manager > Properties > Startup type and then click Disabled.
Right-click CSM Daemon Manager > Properties > Startup type and then click Disabled.
Step 7![]() Right-click CWCS syslog service > Properties > Startup type and click Disabled.
Right-click CWCS syslog service > Properties > Startup type and click Disabled.
Step 8![]() After the installation is complete, and at the time of server restart, change the startup type of both of the above services from “Disabled” to “Automatic” mode.
After the installation is complete, and at the time of server restart, change the startup type of both of the above services from “Disabled” to “Automatic” mode.
How to Set the Locale for the Windows Default User Template to U.S. English
If you normally use a non-U.S. English Windows locale, you must change the default system locale to U.S. English before installing Security Manager; changing the default system locale and rebooting the server does not change the default profile. It is not sufficient for the current user only to have the proper settings; this is because Security Manager creates a new account (“casuser”) that runs all Security Manager server processes.
This section explains how to configure region and language settings on the Security Manager server, especially if you normally use a non-U.S. English Windows locale. The specific details apply to Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 with SP1 Enterprise—64-bit, but they are very similar for the other supported server operating systems, namely the following ones:
To ensure that all newly created users have the same settings as the current user, you need to copy the settings for the current user to new user accounts. This can be done as shown below.
Ensure that the current user has proper U.S. English locale settingsin the Region and Language dialog box. (The navigation path to this dialog box is Start > Control Panel > Region and Language.)
Figure A-1 Windows Region and Language dialog box
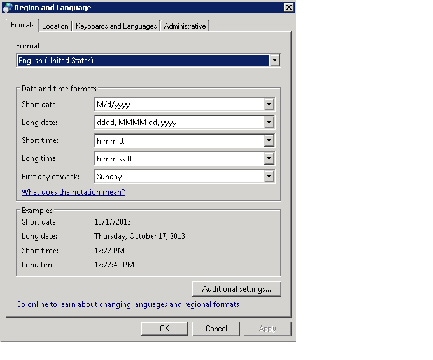
Click the Administrative tab. Find the Copy Settings... button.
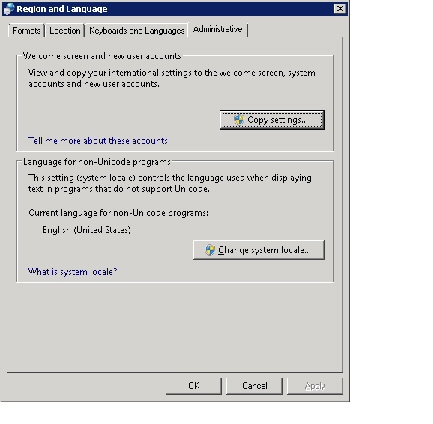
Click the Copy settings... button. The Welcome screen and new user account settings dialog box will appear.
Under “Copy your current settings to:” check the “New user accounts” box. This will ensure that all newly created users have the same configuration as the current settings.
Finally, install (or re-install) Cisco Security Manager server. In the new installation, the new account (“casuser”) that runs all Security Manager server processes will have a U.S. English default profile.
How to disable the RMI Registry Port
In a typical Cisco Security Manager configuration the RMI registry port is open by default. You may need to disable this in a typical Cisco Security Manager configuration. Follow the steps below, to disable the RMI Registry Port:
Step 1![]() Stop Cisco Security Manager Server.
Stop Cisco Security Manager Server.
Step 2![]() Export the ESS registry entry from the following Windows registry path in Cisco Security Manager Server.
Export the ESS registry entry from the following Windows registry path in Cisco Security Manager Server.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Cisco\Resource Manager\CurrentVersion\Daemons\ESS

Note![]() This is recommended, to create a backup.
This is recommended, to create a backup.
Step 3![]() Run the ESS_Reg_Edit.bat file. This file is available in Bug Search Kit (Attached in the defect CSCvc21327). The file will update the ESS registry entry by removing the JMX remote monitoring parameter in the Arguments Key.
Run the ESS_Reg_Edit.bat file. This file is available in Bug Search Kit (Attached in the defect CSCvc21327). The file will update the ESS registry entry by removing the JMX remote monitoring parameter in the Arguments Key.
Step 4![]() Locate the activemq.xml file at this location ~CSCOpx\objects\ess\conf\activemq.xml
Locate the activemq.xml file at this location ~CSCOpx\objects\ess\conf\activemq.xml
Step 5![]() Modify the "createConnector" value as false as follows:
Modify the "createConnector" value as false as follows:
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
Step 7![]() Restart Cisco Security Manager.
Restart Cisco Security Manager.
 Feedback
Feedback