- About This Book
-
- Getting Started
- Setting Up the Prime Fulfillment Services for L2VPN
- Creating a FlexUNI/EVC Ethernet Policy
- Creating a FlexUNI/EVC Ethernet Service Request
- Creating a FlexUNI/EVC ATM-Ethernet Interworking Policy
- Creating a FlexUNI/EVC ATM-Ethernet Interworking Service Request
- Creating an L2VPN Policy
- Creating an L2VPN Service Request
- Creating a VPLS Policy
- Creating a VPLS Service Request
- Deploying, Monitoring, and Auditing Service Requests
- Using Auto Discovery for L2 Services
- Sample Configlets
- Setting Up VLAN Translation
-
- Getting Started with MPLS VPN
- Setting Up the Prime Fulfillment Services
- Independent VRF Management
- IPv6 and 6VPE Support in MPLS VPN
- MPLS VPN Service Policies
- MPLS VPN Service Requests
- Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
- Provisioning Multi-VRFCE PE-CE Links
- Provisioning Management VPN
- Provisioning Cable Services
- Provisioning Carrier Supporting Carrier
- Provisioning Multiple Devices
- Spanning Multiple Autonomous Systems
- Sample Configlets
- Troubleshooting MPLS VPNs
Cisco Prime Fulfillment User Guide 6.1
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- March 20, 2015
Chapter: Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
Provisioning Regular PE-CE Links
This chapter describes how to configure MPLS VPN PE-CE links in the Prime Fulfillment provisioning process.
MPLS VPN PE-CE Link Overview
To provision an MPLS VPN service in Prime Fulfillment, you must first create an MPLS VPN Service Policy. In Prime Fulfillment, a Service Policy is a set of default configurations for creating and deploying a service request.
Prime Fulfillment supports two MPLS VPN Service Policy Types: Regular PE-CE and MVRFCE PE-CE. The following scenarios focus on the Regular PE-CE Policy Type.
The Regular PE-CE Policy Type is a normal PE to CE link between two devices. This Policy Type has two options:
•![]() CE Present enabled (One PE with one CE; two devices)
CE Present enabled (One PE with one CE; two devices)
•![]() CE Present disabled (PE Only with no CE; one device)
CE Present disabled (PE Only with no CE; one device)
Figure 27-1 shows an example of a normal PE to CE link between two devices.
Figure 27-1 PE to CE link with CE Present
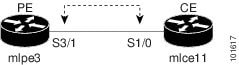
In a PE to CE link with CE Present enabled, interfaces S3/1 and S1/0 are configured as an MPLS VPN link in the service request process.
Figure 27-2 shows an example of a PE Only link with no CE.
Figure 27-2 PE to CE link with No CE

In a PE to CE link with CE Present disabled, interface FE0/0 is configured as an MPLS VPN link in the service request process.
Network Topology
Figure 27-3 shows an overview of the network topology in which the MPLS VPN PE-CE links are created.
Figure 27-3 Network Topology for MPLS VPN PE-CE Scenarios.
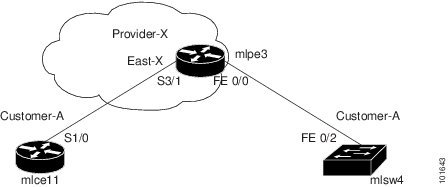
The network topology in Figure 27-3 illustrates the lab environment of a service provider (Provider-X) and one customer (Cust-A). There is one Region (East-X) and one PE (mlpe3.cisco.com). Each customer device (one CE and one CLE) represents a Site (mlce11-Site and mlsw4-Site).
Prerequisite Tasks
Before you can create a Service Policy in Prime Fulfillment, you must complete the following Service Inventory tasks:
Step 1 ![]() Set up a Customer with a Site (see Chapter 21, "Creating Customers, Sites, and CPEs").
Set up a Customer with a Site (see Chapter 21, "Creating Customers, Sites, and CPEs").
Step 2 ![]() Set up a Provider with a Region (see Chapter 21, "Creating Providers, Regions, and PEs").
Set up a Provider with a Region (see Chapter 21, "Creating Providers, Regions, and PEs").
Step 3 ![]() Import, create, or discover Devices (see Chapter 21, "Creating Devices").
Import, create, or discover Devices (see Chapter 21, "Creating Devices").
Step 4 ![]() Create CPE and PE (see Chapter 21, "Creating CPEs").
Create CPE and PE (see Chapter 21, "Creating CPEs").
Step 5 ![]() Collect Configurations (see Chapter 21, "Collecting Configurations").
Collect Configurations (see Chapter 21, "Collecting Configurations").
Step 6 ![]() Create Resource Pools (see Chapter 21, "Creating Resource Pools").
Create Resource Pools (see Chapter 21, "Creating Resource Pools").
Step 7 ![]() Create Route Target(s) (see Chapter 21, "Creating Route Target(s)").
Create Route Target(s) (see Chapter 21, "Creating Route Target(s)").
Step 8 ![]() Define a MPLS VPN (see Chapter 21, "Creating an MPLS VPN").
Define a MPLS VPN (see Chapter 21, "Creating an MPLS VPN").
Defining a VPN for the PE-CE Link
During service deployment, Prime Fulfillment generates the Cisco IOS commands to configure the logical VPN relationships. At the beginning of the provisioning process, before creating a Service Policy, a VPN must be defined within Prime Fulfillment.
To define a VPN, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Choose Inventory > Logical Inventory > VPNs.
Choose Inventory > Logical Inventory > VPNs.
The VPNs window appears.
Step 2 ![]() Click Create to create a VPN.
Click Create to create a VPN.
The Create New VPN window appears.
Step 3 ![]() In the Name field, enter the VPN name.
In the Name field, enter the VPN name.
It is recommended not to use special characters (' ` " < > ( ) [ ] { } / \ & ^ ! ? ~ * % = , . + |) in the VPN name, as this may cause misconfiguration of the VRF name for certain devices, if the VPN name is used to autogenerate a VRF name.
Step 4 ![]() In the Customer field, click Select.
In the Customer field, click Select.
The Select Customer window appears.
Step 5 ![]() Check to choose a Customer and click Select.
Check to choose a Customer and click Select.
The VPNs window reappears where the new VPN Name is associated with a Customer in this new VPN definition.
Step 6 ![]() Click Save.
Click Save.

Note ![]() You can also set VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined independent VRF object. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management."
You can also set VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined independent VRF object. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management."

Note ![]() For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policies
This section contains the following sections:
•![]() PE-CE Service Policy Overview
PE-CE Service Policy Overview
•![]() Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
•![]() Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
PE-CE Service Policy Overview
Figure 27-4 shows an example of the PE-CE link that is defined in the PE-CE Service Policy scenario.
Figure 27-4 PE-CE Topology
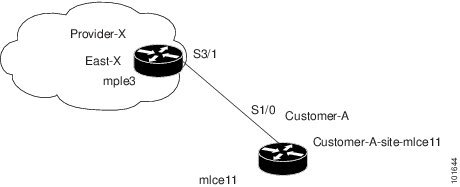
Creating a PE-CE Service Policy
To create a PE-CE service policy, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Choose Service Design > Policies > MPLS.
Choose Service Design > Policies > MPLS.
The MPLS window appears as shown in Figure 27-5.
Figure 27-5 MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type
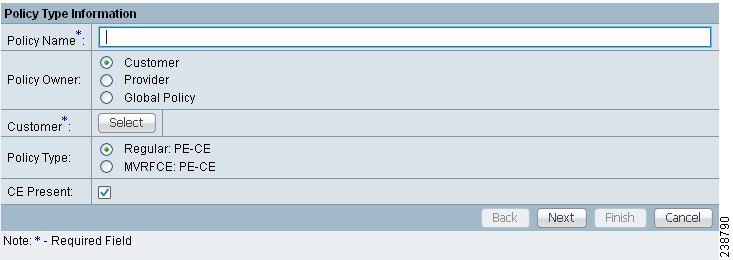
Step 2 ![]() Edit the following attributes:
Edit the following attributes:
•![]() Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
•![]() Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
•![]() Customer:
Customer:
–![]() Click Select to specify a Customer.
Click Select to specify a Customer.
The Customer for MPLS Policy window appears.
–![]() Check to choose a Customer and click Select.
Check to choose a Customer and click Select.
•![]() Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type. (Regular PE-CE)
Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type. (Regular PE-CE)
Step 3 ![]() CE Present: Check to set CE as present.
CE Present: Check to set CE as present.
Step 4 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 27-6.
Figure 27-6 The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface
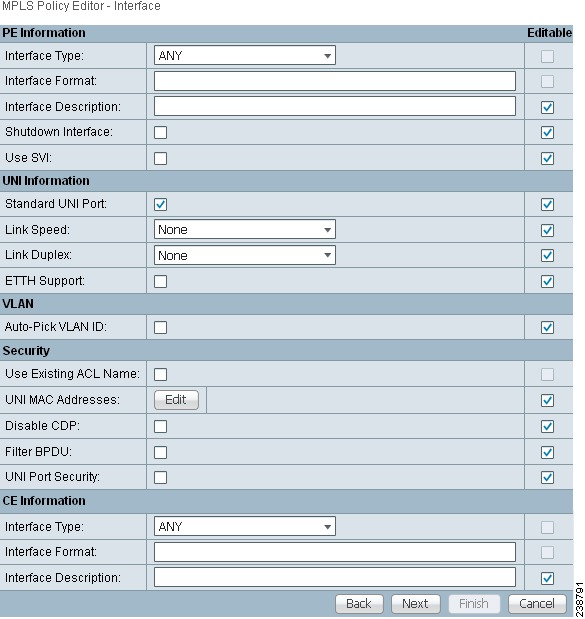
Step 5 ![]() Click Next to accept the defaults.
Click Next to accept the defaults.
The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears.

Note ![]() Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the service request process.
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the service request process.
Step 6 ![]() Edit all applicable attributes.
Edit all applicable attributes.

Note ![]() If you check Automatically Assign IP Address, the screen refreshes and adds a forth attribute: IP Address Pool.
If you check Automatically Assign IP Address, the screen refreshes and adds a forth attribute: IP Address Pool.
Step 7 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information window appears.
Step 8 ![]() Click Next to accept the defaults.
Click Next to accept the defaults.
The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window appears.

Note ![]() For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".

Note ![]() If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
Step 9 ![]() To enable template association for the policy, click the Next button in MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window.
To enable template association for the policy, click the Next button in MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window.
The Template Association window appears. In this window, you can enable template support and, optionally, associate templates and data files with the policy. For instructions about associating templates with policies and how to use the features in this window, see Chapter 49, "Using Templates and Data Files with Policies and Service Requests" When you have completed setting up templates and data files for the policy per the instructions in the appendix, click Finish in the Template Association window to close it.
The Policies window appears.
Step 10 ![]() If you did not enable templates, click Finish in the MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN window.
If you did not enable templates, click Finish in the MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN window.
The Policies window reappears.
The MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Policy is complete.
Creating a PE-NoCE Service Policy
To create a PE-NoCE service policy, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Choose Service Design > Policies > MPLS.
Choose Service Design > Policies > MPLS.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Policy Type window appears.
Step 2 ![]() Edit the following attributes:
Edit the following attributes:
•![]() Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
Policy Name: Enter the policy name.
•![]() Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
Policy Owner: Choose the Policy Owner.
•![]() Customer:
Customer:
–![]() Click Select to specify a Customer.
Click Select to specify a Customer.
The Customer for MPLS Policy window appears.
–![]() Choose a Customer and click Select.
Choose a Customer and click Select.
•![]() Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type. (Regular PE-CE)
Policy Type: Choose the Policy Type. (Regular PE-CE)
•![]() CE Present: Do not check to set CE as not present (NoCE).
CE Present: Do not check to set CE as not present (NoCE).
Step 3 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Interface window appears.
Step 4 ![]() Click Next to accept the defaults.
Click Next to accept the defaults.
The MPLS Policy Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears.

Note ![]() Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the service request process.
Make sure the Editable check boxes are checked, so you can edit these attributes in the service request process.
The field values displayed in this dialog box reflect the values specified in the service policy associated with this service.
For details on the IP address scheme fields, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the IP Address Scheme".
Step 5 ![]() Edit all applicable attributes.
Edit all applicable attributes.

Note ![]() If you check Automatically Assign IP Address, the screen refreshes and adds a forth attribute: IP Address Pool.
If you check Automatically Assign IP Address, the screen refreshes and adds a forth attribute: IP Address Pool.
Step 6 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Policy Editor - Routing Information window appears.
Step 7 ![]() Click Next to accept the defaults.
Click Next to accept the defaults.
The MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window appears.

Note ![]() For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".

Note ![]() If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
Step 8 ![]() To enable template association for the policy, click the Next button in MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window.
To enable template association for the policy, click the Next button in MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN Membership window.
The Template Association window appears. In this window, you can enable template support and, optionally, associate templates and data files with the policy. For instructions about associating templates with policies and how to use the features in this window, see Chapter 49, "Using Templates and Data Files with Policies and Service Requests" When you have completed setting up templates and data files for the policy per the instructions in the appendix, click Finish in the Template Association window to close it.
The Policies window appears.
Step 9 ![]() If you did not enable templates, click Finish in the MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN window.
If you did not enable templates, click Finish in the MPLS Policy Editor - VRF and VPN window.
The Policies window reappears.
The MPLS VPN PE-NoCE Service Policy is complete.
Creating MPLS VPN PE-CE Service Requests
This section contains the following sections:
•![]() Creating PE-CE Service Requests
Creating PE-CE Service Requests
•![]() Creating PE-NoCE Service Requests
Creating PE-NoCE Service Requests
Creating PE-CE Service Requests
To create a PE-CE service request, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Choose Operate > Service Requests > MPLS.
Choose Operate > Service Requests > MPLS.
The MPLS Policy Selection window appears.
Step 2 ![]() Choose an MPLS PE-CE type policy.
Choose an MPLS PE-CE type policy.
Step 3 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 4 ![]() Click Add Link.
Click Add Link.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 5 ![]() Click Select CE.
Click Select CE.
The CPE for MPLS VPN Link window appears.
Step 6 ![]() Choose a CPE device and click Select.
Choose a CPE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 7 ![]() Choose a CE Interface from the drop-down list.
Choose a CE Interface from the drop-down list.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 8 ![]() Click Select PE.
Click Select PE.
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window appears.
Step 9 ![]() Choose a PE device and click Select.
Choose a PE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 10 ![]() Choose a PE Interface from the drop-down list.
Choose a PE Interface from the drop-down list.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 11 ![]() Click Select PE.
Click Select PE.
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window reappears.
Step 12 ![]() In the Link Attribute cell, click Add.
In the Link Attribute cell, click Add.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 27-7.
Figure 27-7 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
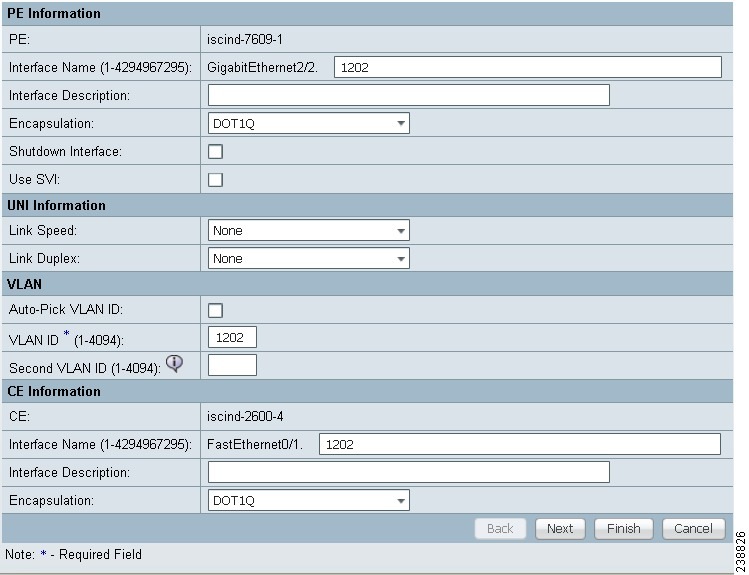
PE Information
Step 13 ![]() Interface Name: Enter a value to identify the interface.
Interface Name: Enter a value to identify the interface.
Step 14 ![]() Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Step 15 ![]() Shutdown Interface: When you check this check box, the PE interface is configured in a shutdown state.
Shutdown Interface: When you check this check box, the PE interface is configured in a shutdown state.
Step 16 ![]() Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
The selections available in the drop-down list are determined by the interface type.
Step 17 ![]() VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID. The VLAN ID is shared between the PE and CE, so there is one VLAN ID for both.
VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID. The VLAN ID is shared between the PE and CE, so there is one VLAN ID for both.
Step 18 ![]() Auto-Pick VLAN ID: Check this check box if you would like Prime Fulfillment to autopick a VLAN ID from the VLAN pool.
Auto-Pick VLAN ID: Check this check box if you would like Prime Fulfillment to autopick a VLAN ID from the VLAN pool.
If this box is checked, the VLAN ID field is not visible in the GUI.
Step 19 ![]() Second VLAN ID: The Second VLAN ID is an optional attribute that provides a method to match the Q-in-Q second VLAN tag of incoming frames on the PE interface.
Second VLAN ID: The Second VLAN ID is an optional attribute that provides a method to match the Q-in-Q second VLAN tag of incoming frames on the PE interface.
For usage details about this attribute, see Chapter 25, "Notes on the VLAN ID and Second VLAN ID Attributes".
Step 20 ![]() Use SVI: Check this box to have Prime Fulfillment terminate VRF on SVI.
Use SVI: Check this box to have Prime Fulfillment terminate VRF on SVI.
CE Information
Step 21 ![]() Interface Name: Enter a value from to identify the interface.
Interface Name: Enter a value from to identify the interface.
Step 22 ![]() Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Step 23 ![]() Encapsulation: Choose the CE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
Encapsulation: Choose the CE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
The selections available in the drop-down list are determined by the interface type.
Step 24 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears.
Step 25 ![]() Accept the defaults and click Next.
Accept the defaults and click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window appears, as shown in Figure 27-8.
Figure 27-8 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information
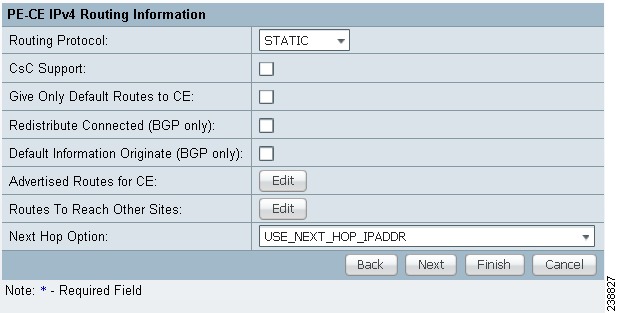

Note ![]() For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
Step 26 ![]() Choose a Next Hop Option:
Choose a Next Hop Option:
•![]() USE_OUT_GOING_INTF_NAME
USE_OUT_GOING_INTF_NAME
•![]() USE_NEXT_HOP_IPADDR
USE_NEXT_HOP_IPADDR
•![]() OUTGOING_INTF_NAME+NEXT_HOP_IPADDR
OUTGOING_INTF_NAME+NEXT_HOP_IPADDR

Note ![]() If this interface is dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6), you will be prompted to enter the routing information for both IPv4 and IPv6 independently. The fields in the IPv6 Routing Information window are slightly different from the IPv4 version. For information on setting up the routing information for IPv6, see Chapter 25, "Setting Static Routing Protocol Attributes (for IPv4 and IPv6)".
If this interface is dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6), you will be prompted to enter the routing information for both IPv4 and IPv6 independently. The fields in the IPv6 Routing Information window are slightly different from the IPv4 version. For information on setting up the routing information for IPv6, see Chapter 25, "Setting Static Routing Protocol Attributes (for IPv4 and IPv6)".
Step 27 ![]() To continue, click Next.
To continue, click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window appears.

Note ![]() If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.

Note ![]() For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
Step 28 ![]() Click Add to join a VPN.
Click Add to join a VPN.
The Select CERCs window appears.
Step 29 ![]() Choose a Customer from the drop-down list.
Choose a Customer from the drop-down list.
Step 30 ![]() Choose a VPN from the drop-down list.
Choose a VPN from the drop-down list.
Step 31 ![]() Check to choose a VPN from the list.
Check to choose a VPN from the list.
Step 32 ![]() Click Join As Hub or Join As Spoke.
Click Join As Hub or Join As Spoke.
Step 33 ![]() Click Done.
Click Done.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window reappears.
Step 34 ![]() Click the Next button to associate templates or data files to the service request.
Click the Next button to associate templates or data files to the service request.

Note ![]() This step assumes the policy on which the service request is based has template association enabled. If not, there will be no Next button visible in the GUI. In that case, click Finish and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window and proceed with Step 37, below.
This step assumes the policy on which the service request is based has template association enabled. If not, there will be no Next button visible in the GUI. In that case, click Finish and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window and proceed with Step 37, below.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Template Association window appears. In this window, you can associate templates and data files with a device by clicking the Add button in Template/Data File column for the device. When you click the Add button, the Add/Remove Templates window appears. For instructions about associating templates with service requests and how to use the features in this window, see Chapter 49, "Using Templates and Data Files with Policies and Service Requests"
Step 35 ![]() When you have completed setting up templates and data files for any device(s), click Finish in the Template Association window to close it and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window.
When you have completed setting up templates and data files for any device(s), click Finish in the Template Association window to close it and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window.
You can define multiple links in this service request, following the instructions outlined in previous steps.
Step 36 ![]() To save your work, click Save.
To save your work, click Save.
The MPLS Service Requests window reappears showing that the MPLS VPN PE-CE service request is in the Requested state and ready to deploy.
Creating PE-NoCE Service Requests
To create a PE-NoCE service request, perform the following steps.
Step 1 ![]() Choose Operate > Service Requests > MPLS.
Choose Operate > Service Requests > MPLS.
Step 2 ![]() Choose an MPLS PE-NoCE type policy.
Choose an MPLS PE-NoCE type policy.
Step 3 ![]() Click OK.
Click OK.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 4 ![]() Click Add Link.
Click Add Link.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 5 ![]() Click Select PE.
Click Select PE.
The PE for MPLS VPN Link window appears.
Step 6 ![]() Choose a PE device and click Select.
Choose a PE device and click Select.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 7 ![]() Choose the PE Interface from the drop-down list.
Choose the PE Interface from the drop-down list.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window appears.
Step 8 ![]() In the Link Attribute cell, Click Add.
In the Link Attribute cell, Click Add.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface window appears, as shown in Figure 27-9.
Figure 27-9 MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Interface
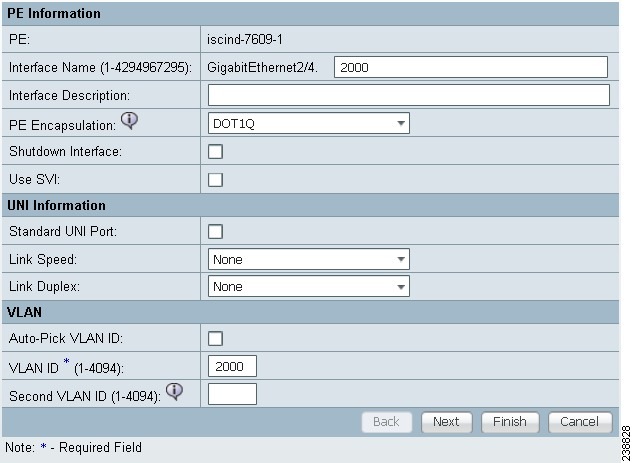
Step 9 ![]() Interface Name: Enter a value to identify the interface.
Interface Name: Enter a value to identify the interface.
Step 10 ![]() Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Interface Description: Optionally, you can enter a description of the PE interface.
Step 11 ![]() Shutdown Interface: When you check this check box, the PE interface is configured in a shutdown state.
Shutdown Interface: When you check this check box, the PE interface is configured in a shutdown state.
Step 12 ![]() PE Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
PE Encapsulation: Choose the PE Encapsulation from the drop-down list.
The selections available in the drop-down list are determined by the interface type. This field is needed for deciding PE/UNI encapsulation.
Step 13 ![]() VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID. The VLAN ID is shared between the PE and CE, so there is one VLAN ID for both.
VLAN ID: Enter the VLAN ID. The VLAN ID is shared between the PE and CE, so there is one VLAN ID for both.
Step 14 ![]() Auto-Pick VLAN ID: Check this check box if you would like Prime Fulfillment to autopick a VLAN ID from the VLAN pool.
Auto-Pick VLAN ID: Check this check box if you would like Prime Fulfillment to autopick a VLAN ID from the VLAN pool.
If this box is checked, the VLAN ID field is not visible in the GUI.
Step 15 ![]() Second VLAN ID: The Second VLAN ID is an optional attribute that provides a method to match the Q-in-Q second VLAN tag of incoming frames on the PE interface.
Second VLAN ID: The Second VLAN ID is an optional attribute that provides a method to match the Q-in-Q second VLAN tag of incoming frames on the PE interface.
For usage details about this attribute, see Chapter 25, "Notes on the VLAN ID and Second VLAN ID Attributes".
Step 16 ![]() Use SVI: Check this box to have Prime Fulfillment terminate VRF on SVI.
Use SVI: Check this box to have Prime Fulfillment terminate VRF on SVI.
Step 17 ![]() Standard UNI Port: Check this box to access additional UNI security parameters.
Standard UNI Port: Check this box to access additional UNI security parameters.
Step 18 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - IP Address Scheme window appears.
Step 19 ![]() Accept the defaults and click Next.
Accept the defaults and click Next.

Note ![]() If this interface is dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6), you will be prompted to enter the routing information for both IPv4 and IPv6 independently.
If this interface is dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6), you will be prompted to enter the routing information for both IPv4 and IPv6 independently.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Routing Information window appears.
Step 20 ![]() Set attributes for the routing information as needed for your configuration.
Set attributes for the routing information as needed for your configuration.

Note ![]() For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
For information about protocol types, see Chapter 24, "Specifying the Routing Protocol for a Service".
Step 21 ![]() Click Next.
Click Next.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - VRF and VPN window appears.

Note ![]() If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.
If you want to set the VRF and VPN attributes via a previously defined VRF object, check the Use VRF Object check box. For more information on this feature, see Chapter 22, "Independent VRF Management." That chapter describes how to use independent VRF objects in MPLS VPN service policies and service requests.

Note ![]() For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
For more information on setting the VRF and VPN attributes in MPLS VPN service requests, see Chapter 25, "Defining VRF and VPN Attributes in an MPLS Service Request".
Step 22 ![]() Click Add to join the VPN.
Click Add to join the VPN.
The Join VPN dialog box appears.
Step 23 ![]() Check to choose the VPN.
Check to choose the VPN.
Step 24 ![]() Click Join as Hub or Join as Spoke.
Click Join as Hub or Join as Spoke.
Step 25 ![]() Click Done.
Click Done.
The MPLS Service Request Editor window reappears.
Step 26 ![]() Click the Next button to associate templates or data files to the service request.
Click the Next button to associate templates or data files to the service request.

Note ![]() This step assumes the policy on which the service request is based has template association enabled. If not, there will be no Next button visible in the GUI. In that case, click Finish and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window and proceed with Step 30, below.
This step assumes the policy on which the service request is based has template association enabled. If not, there will be no Next button visible in the GUI. In that case, click Finish and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window and proceed with Step 30, below.
The MPLS Link Attribute Editor - Template Association window appears. In this window, you can associate templates and data files with a device by clicking the Add button in Template/Data File column for the device. When you click the Add button, the Add/Remove Templates window appears. For instructions about associating templates with service requests and how to use the features in this window, see Chapter 49, "Using Templates and Data Files with Policies and Service Requests"
Step 27 ![]() When you have completed setting up templates and data files for any device(s), click Finish in the Template Association window to close it and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window.
When you have completed setting up templates and data files for any device(s), click Finish in the Template Association window to close it and return to the MPLS Service Request Editor window.
You can define multiple links in this service request, following the instructions outlined in previous steps.
Step 28 ![]() To save your work, click Save.
To save your work, click Save.
The MPLS Service Requests window reappears showing that the MPLS VPN PE-NoCE Service Request is in the Requested state and ready to deploy.
 Feedback
Feedback