Release Notes for Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module, Release 1.6.2
This document describes the features, limitations, and bugs for this Cisco APIC-EM controller release. For information about the features, limitations, and bugs for the supported applications for this release, see the following:
-
Cisco EasyQoS for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Network Visibility for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Path Trace for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Active Advisor for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Integrity Verification Application for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Remote Troubleshooter Application for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Cisco Wide Area Bonjour Application for APIC-EM Release Notes
-
Release Notes for Cisco Intelligent Wide Area Network Application (Cisco IWAN App)
-
Release Notes for Cisco Network Plug and Play
Introduction
The Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (Cisco APIC-EM) is a network controller that helps you manage and configure your network.
The Cisco APIC-EM can support up to the following total number of devices, hosts, and access points:
-
Network devices (routers, switches, wireless LAN controllers)—10,000
-
Hosts—100,000
-
Access Points—10,000
 Note |
For specific Cisco APIC-EM requirements based upon the number of devices, hosts, and access points within your network, see Cisco APIC-EM Scale Limits. |
What's New in Cisco APIC-EM, Release 1.6.2
There are no new features with this release.
Cisco APIC-EM System Requirements
Cisco offers a physical appliance that can be purchased from Cisco with the ISO image pre-installed and tested. The Cisco APIC-EM can also be installed and operate within a dedicated physical server (bare-metal) or a virtual machine within a VMware vSphere environment. The Cisco APIC-EM has been tested and qualified to run on the following Cisco UCS servers:
-
Cisco UCS C220 M4S Server
-
Cisco UCS C220 M3S Server
-
Cisco UCS C22 M3S Server
In addition to the above servers, the Cisco APIC-EM may also run on any Cisco UCS servers that meet the minimum system requirements (see Cisco APIC-EM Physical Server Requirements). We also support running the product in a virtual machine that meets the minimum system requirements on VMware vSphere (see Cisco APIC-EM VMware vSphere Requirement).
 Note |
The Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 64-bit operating system is included in the ISO image and is a requirement for the successful installation and operation of the Cisco APIC-EM. Prior to installing the Cisco APIC-EM on your Cisco UCS server, click the following link and review the online matrix to confirm that your hardware supports Ubuntu 14.04 LTS: http://www.ubuntu.com/certification/server/ |
Cisco APIC-EM Physical Server Requirements
The following table lists the minimum system requirements for a successful Cisco APIC-EM server (bare-metal hardware) installation. Review the minimum system requirements for a server installation.
 Note |
For Cisco APIC-EM scale limits based upon the number of devices, hosts, and access points within your network, see Cisco APIC-EM Scale Limits. |
The minimum system requirements for each server in a multi-host deployment are the same as in a single-host deployment, except that the multi-host deployment requires two or three servers. Two servers are required for software high availability. Three servers are required for both software and hardware high availability. With multiple servers (two or three servers), all of the servers must reside in the same subnet. For additional information about a multi-host deployment, see Supported Multi-Host Configurations.
 Caution |
You must dedicate the entire server for the Cisco APIC-EM. You cannot use the server for any other software programs, packages, or data. During the Cisco APIC-EM installation, any other software programs, packages, or data on the server will be deleted. |
|
Physical Server Options |
Server image format |
Bare Metal/ISO |
||
|
Hardware |
CPU (cores) |
6
|
||
|
CPU (speed) |
2.4 GHz |
|||
|
Memory |
32 GB |
|||
|
Disk Capacity |
200 GB of available/usable storage after hardware RAID |
|||
|
RAID Level 1 |
Hardware-based RAID at RAID Level 10 |
|||
|
Disk I/O Speed |
200 MBps |
|||
|
Network Adapter |
1 |
|||
|
Networking |
Web Access |
Required |
||
|
Browser |
The following browsers are supported when viewing and working with the Cisco APIC-EM:
|
Cisco APIC-EM VMware vSphere Requirement
You must configure at a minimum 32 GB RAM for the virtual machine that contains the Cisco APIC-EM when a single host is being deployed. The single-host server that contains the virtual machine must have this much physical RAM available.
For a multi-host deployment (2 or 3 hosts), only 32 GB of RAM is required for each of the virtual machines that contains the Cisco APIC-EM. Two servers are required for software high availability. Three servers are required for both software and hardware high availability. With multiple servers (two or three servers), all of the servers must reside in the same subnet. For additional information about a multi-host deployment, see Supported Multi-Host Configurations.
 Note |
For Cisco APIC-EM scale limits based upon the number of devices, hosts, and access points within your network, see Cisco APIC-EM Scale Limits. |
 Note |
As with running an application on any virtualization technology, you might observe a degradation in performance when you run the Cisco APIC-EM in a virtual machine compared to running the Cisco APIC-EM directly on physical hardware. |
|
Virtual Machine Options |
VMware ESXi Version |
5.1/5.5/6.0/6.5 |
|
|
Server Image Format |
ISO |
||
|
Virtual CPU (vCPU) |
6
|
||
|
Datastores |
We recommend that you do not share a datastore with any defined virtual machines that are not part of the designated Cisco APIC-EM cluster. If the datastore is shared, then disk I/O access contention may occur and cause a significant reduction of disk bandwidth throughput and a significant increase of I/O latency to the cluster. |
||
|
Hardware Specifications |
CPU (speed) |
2.4 GHz |
|
|
Memory |
32 GB |
||
|
Disk Capacity |
200 GB |
||
|
Disk I/O Speed |
200 MBps |
||
|
Network Adapter |
1 |
||
|
Networking |
Web Access |
Required |
|
|
Browser |
The following browsers are supported when viewing and working with the Cisco APIC-EM:
|
||
|
Network Timing |
To avoid conflicting time settings, we recommend that you disable the time synchronization between the guest VM running the Cisco APIC-EM and the ESXi host. Instead, configure the timing of the guest VM to a NTP server.
|
VMware Resource Pools
When installing the Cisco APIC-EM on a VMware virtual machine, then we also recommend that you configure resource pools with the following settings.
-
Resource Pools—CPU Resources:
-
Shares—Normal
-
Reservation—Minimum 14400 MHz
-
Reservation Type—Expandable
-
Limit—Maximum limit
-
-
Resource Pools—Memory Resources:
-
Shares—Normal
-
Reservation—32 GB or 64 GB minimum depending upon your hardware
-
Reservation Type—Expandable
-
Limit—Maximum limit
-
For examples on how to create and configure both resource pools and a virtual machine for the Cisco APIC-EM, see Appendix A, "Preparing Virtual Machines for Cisco APIC-EM" in the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide.
Cisco APIC-EM Scale Limits
The following table lists the Cisco APIC-EM appliance scale limits for deployment.
|
Hardware Appliance2 |
Cores |
RAM |
Hard Disk |
RAID |
Scale Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
APIC-EM-APL-R-K9 |
10 |
64 GB |
4 X SAS HDD of 900 GB each |
RAID 10 |
|
|
APIC-EM-APL-G-K9 |
20 |
128 GB |
8 X SAS HDD of 900 GB each |
RAID 10 |
|
 Note |
The supported scale numbers do not change if you deploy either a single-host appliance or a multi-host cluster (with up to three host appliances). The scale numbers are also the same for either the APIC-EM-APL-R-K9 appliance or the APIC-EM-APL-G-K9 appliance. The reason for installing a larger appliance (APIC-EM-APL-G-K9) with 128 GB RAM is to plan and invest in the future of your network. The smaller appliance (APIC-EM-APL-R-K9) provides 64 GB RAM, which is enough for today's use cases, but the scale and number of applications used by the controller will increase over time. |
For a Cisco APIC-EM deployment using Cisco UCS servers, you should match the virtual specifications listed in the following tables: Table 2 and Table 3.
The following table lists the Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine scale limits for deployment.
|
Virtual Appliance |
Cores |
RAM3 |
Hard Disk |
CPU Clock Speed |
RAID |
Scale Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco APIC-EM installed on a Virtual Machine (32 GB) |
12 |
32 GB |
200 GB Internal data store Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Cisco APIC-EM installed on a Virtual Machine (64 GB) |
8 |
64 GB |
500 GB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Cisco APIC-EM installed on a Virtual Machine (64 GB) |
12 |
64 GB |
1 TB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Cisco APIC-EM installed on a Virtual Machine (128 GB) |
20 |
128 GB |
2 TB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
The following table lists the Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine scale limits for a three-host (multi-host) deployment.
|
Virtual Appliance |
Cores |
RAM |
Hard Disk |
CPU Clock Speed |
RAID |
Scale Limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Three hosts forming a Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine cluster; each host having 32 GB of RAM |
6 |
32 GB for each host |
200 GB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Three hosts forming a Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine cluster; each host having 32 GB of RAM |
6 |
32 GB for each host |
500 GB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Three hosts forming a Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine cluster; each host having 32 GB of RAM |
8 |
32 GB for each host |
1 TB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
|
Three hosts forming a Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine cluster; each host having 64 GB of RAM |
10 |
64 GB for each host |
2 TB Disk speed 15000 RPM |
2.9 GHz |
RAID 10 (configured on the hardware) |
|
Supported Multi-Host Configurations
The Cisco APIC-EM supports a single-host, two-host, or three-host cluster configuration. With a single-host configuration, 32 GB of RAM is required for that host. With a two or three-host cluster configuration, 32 GB of RAM is required for each host in the cluster.
 Note |
Cisco APIC-EM does not support a cluster with more than three hosts. For example, a multi-host cluster with five or seven hosts is not currently supported. |
The three-host cluster provides both software and hardware high availability. The single or two-host cluster only provides software high availability and does not provide hardware high availability. For this reason, we strongly recommend that you use three hosts for a multi-host configuration.
A hardware failure occurs when the physical host malfunctions or fails. A software failure occurs when a service on a host fails. Software high availability involves the ability of the services on the hosts to be reinstantiated and restarted. For example, on a single host, if a service fails then that service is reinstantiated and restarted on that host. In a two-host cluster, if a service fails on one host then that service is reinstantiated and restarted on the remaining host. In a three-host cluster, if a service fails on one host, then that service is reinstantiated and restarted on one of the two remaining hosts.
When setting up a two-host or three-host cluster, you should never set up the hosts to span a LAN across slow links. This may impact the recovery time if a service fails on one of the hosts. Additionally, when configuring either a two-host or three-host cluster, all of the hosts in that cluster must reside in the same subnet.
 Note |
For additional detailed information about Cisco APIC-EM multi-host configurations, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide. |
Supported Applications
Cisco APIC-EM supports the applications listed below.
|
Application |
Introduced in Release |
Bundled |
Enabled by Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cisco EasyQoS |
1.1.0.x |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Cisco Active Advisor |
1.4.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco Command Runner 4 |
1.4.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco IWAN |
1.0.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco Network PnP 5 |
1.0.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco Network Visibility 6 |
1.0.0.x |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Cisco Path Trace |
1.0.0.x |
✓ |
✓ |
| Cisco Wide Area Bonjour |
1.4.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco Integrity Verification |
1.5.0.x |
— |
— |
|
Cisco Remote Troubleshooter |
1.5.0.x |
✓ |
— |
Cisco APIC-EM Licensing
The following are the licensing requirements for Cisco APIC-EM and its applications (apps):
-
Cisco APIC-EM controller software and its basic apps (for example, Inventory, Topology, and EasyQoS):
-
No fee-based license is required. The controller software and basic apps are offered at no cost to the user.
-
You can download the controller software (ISO Image) and run it on bare-metal Cisco UCS servers or run the ISO image on a virtual machine in a VMware ESXi environment. In both cases, you need to ensure the required CPU, memory, and storage resources are available.
-
-
Solution apps (for example, IWAN and any similar Cisco-developed solution app):
-
A per-device license is required to run the solution apps.
-
The solution apps licenses can only be acquired by purchasing Cisco® Enterprise Management 3.x device licenses, which also include the Cisco Prime™ Infrastructure licenses. The process for acquiring Cisco Prime Infrastructure 3.x device licenses is explained in the Cisco Enterprise Management Ordering Guide:
Cisco Enterprise Management 3.x, Prime Infrastructure 3. x APIC-EM Ordering and Licensing Guides

Note
The same license-acquisition process will also provide you with the right-to-use (RTU) licenses for APIC-EM solution apps. RTU licenses do not involve license files.
-
Cisco APIC-EM Technical Support
The following Cisco APIC-EM technical support options are provided:
-
Cisco APIC-EM hardware appliance:
Hardware support is provided through the Cisco SMARTnet® Service.
-
Cisco APIC-EM controller, basic apps, and services:
If you have SMARTnet on any Cisco networking device, Cisco® TAC support is offered at no additional cost.
-
Cisco APIC-EM solutions apps and services:
TAC support is offered at no additional cost, if you have a SWSS (maintenance contract) on Cisco® Enterprise Management 3.x device licenses.
Supported Platforms and Software Requirements
For information about the network devices and software versions supported for this release, see Supported Platforms for the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module.
Securing the Cisco APIC-EM
The Cisco APIC-EM provides many security features for the controller itself, as well as the hosts and network devices that it monitors and manages. We strongly suggest that the following security recommendations be followed when deploying the controller.
|
Security Recommendations |
Reference |
|---|---|
|
Deploy the controller behind a firewall that does not expose the controller's management ports (for example, ports 22 and14141) to an untrusted network, such as the Internet. |
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide, Security chapter, "Cisco APIC-EM Port Reference" for information about the key controller ports. |
|
Configure IPSec tunneling for communications between the hosts in a multi-host configuration. |
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide, Security chapter, "Configuring IPSec Tunneling for Multi-Host Communications" for information about configuring IPSec tunneling. |
|
Configure Cisco APIC-EM HTTPS services to use TLS 1.1 or TLS 1.2, instead of TLS 1.0 (current default). TLS 1.2 is strongly preferred. However, ensure that your devices – especially those that will be introduced into the network using the Cisco APIC-EM PnP application – also support TLS 1.1 and/or TLS 1.2 before choosing a TLS version above 1.0. Additionally, make sure that any NB API consumers including the browser used to access the controller's UI are capable of communicating with TLS 1.1 or TLS 1.2. All of the browser clients supported by Cisco APIC-EM already support TLS 1.1 and above. |
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide, Security chapter, "Configuring the TLS Version Using the CLI" for information about configuring the TLS version. |
|
Replace the self-signed server certificate from the controller with one signed by a well-known Certificate Authority. |
For this security recommendation, do one of the following:
|
|
Configure a proxy gateway between the controller and the network devices it monitors and manages. |
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide, Settings chapter, "Importing a Proxy Gateway Certificate" for information about importing and using the proxy gateway's certificate for the controller. |
|
When using the controller's discovery functionality, use SNMPv3 with authentication and privacy enabled for the network devices. |
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide, Settings chapter, "Configuring SNMP" for information about configuring SNMPv3 for the controller. |
Deploying the Cisco APIC-EM
You can deploy Cisco APIC-EM using the following methods:
-
As a dedicated Cisco APIC-EM physical appliance purchased from Cisco with the ISO image pre-installed.
-
As a downloadable ISO image that you can burn to a dual-layer DVD or a bootable USB flash drive. You then install the ISO image into a server that meets the Cisco APIC-EM physical server system requirements.

Note
The USB flash drive must be bootable. You can use a third-party utility to create a bootable USB flash drive using the ISO image. You cannot boot from the USB flash drive if you copy the ISO to the flash drive.
-
As a downloadable ISO image that you can install into a virtual machine within a VMware vSphere environment that meets the Cisco APIC-EM virtual machine system requirements.
To deploy the Cisco APIC-EM using any of the above methods, refer to the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide. For information about the network devices supported for this release, see Supported Platforms for the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module.
 Note |
Before you deploy the Cisco APIC-EM, make sure that the time on the controller's system clock is current or that you are using a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server that is keeping the correct time. |
Upgrading to Cisco APIC-EM, Release 1.6.2
You can upgrade to this Cisco APIC-EM release using the Update functionality of the controller's GUI. This upgrade procedure requires that you upload and update the new release, as described below.
Before you begin
Review the following list of pre-requisites and perform the recommended procedures before upgrading your Cisco APIC-EM:
-
You must have administrator (ROLE_ADMIN) permissions and access to all devices (RBAC Scope set to ALL) to perform this procedure.
For information about the user permissions required to perform tasks using the Cisco APIC-EM, see the chapter, Managing Users and Roles in the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide.
-
You can only upgrade to the new Cisco APIC-EM release from one of the earlier software or software patch releases listed below. If your current Cisco APIC-EM release version is not one of these releases, then first upgrade to one of these releases before upgrading to this release.
Supported upgrade paths to Release 1.6.2:
-
1.6.1.30163
-
1.6.0.30151
-
1.5.1.1054
-
1.5.0.1368
-
1.4.3.1009

Note
If you are upgrading from any of these release versions and have already configured NIC bonding, then just upgrade to release 1.6.1.x. There is no need to run the configuration wizard again to reconfigure your NIC bonding.
-
-
For this specific release your upgrade may fail if the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application is installed and enabled. As a workaround, perform the following tasks:
-
Disable the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application in the App Management window of the controller's GUI.
-
Install the Cisco APIC-EM software upgrade.
-
Return to the App Management window and enable the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application.
-
-
If you have not already done so, review the system requirements for your Cisco APIC-EM upgrade (see Cisco APIC-EM System Requirements). The system requirements may have changed for this release from a previous release and may require that you make changes to your deployment.
-
If you have not already done so, review the security recommendations for the Cisco APIC-EM (see Securing the Cisco APIC-EM).
-
Create a backup of your Cisco APIC-EM database. For information about backing up and restoring the controller, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide.
-
Prior to beginning the software update process for the Cisco APIC-EM, we recommend that you configure the idle timeout value in the Auth Timeout GUI window for at least an hour. If a user is logged out due to an idle timeout during the software update process, then this process will fail and need to be re-initiated again. For information about the procedure used to configure an idle timeout value, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide.
-
Allocate the appropriate time for the upgrade process; upgrading from earlier releases to this Cisco APIC-EM release may take up to an hour to complete.
-
If the upgrade fails, see the "Recovering from Upgrade Failures" chapter in the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Upgrade Guide for assistance.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Download the Cisco APIC-EM upgrade package for this release from the Cisco website at the Download Software link. |
| Step 2 |
Upload the upgrade package to the controller using the Update functionality of the GUI. For additional information about this step, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Upgrade Guide. |
| Step 3 |
Update the controller's software with the upgrade package using the Update functionality of the GUI. For additional information about this step, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Upgrade Guide. |
| Step 4 |
After updating the controller's software with the upgrade package in the previous step, proceed to clear your web browser's cache. |
| Step 5 |
Check the controller’s software version number in the GUI SYSTEM INFO tab, located in the Home window. The SYSTEM INFO tab should display the new software version. |
Caveats
Open Caveats
The following table lists the open caveats for the Cisco APIC-EM controller for this release.
 Note |
For information about open and resolved caveats for a specific application, refer to the release notes for that application. |
|
Caveat ID Number |
Headline |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A get VLAN and get Topology by VLAN does not work for the Cisco Catalyst 5000 and the Cisco Catalyst 3850. Workaround: There is no workaround at this time. |
|||||
|
When upgrading from 1.5.0.1368 to 1.5.11037 on a single node, some of the services do not come up, even though the cluster is accessible. The error, "Page Temporarily Unavailable. This page is temporarily unavailable because task-service is in the process of starting, please try again at a later time." Workaround Disable the REO, upgrade the cluster to 1.5.1, and then enable REO after all the services are up. |
|||||
|
While installing the ISO image, the installation fails with the error message below. The mapping to the drive to image is also disassociated and unmounted. Error message: Finish the Installation Failed to run preseeded command Workaround: Unmount the ISO image and mount it again. Next, try to reload the image and install it again. This issue may also occur due to an image corruption, so be sure to verify the checksum as well. |
|||||
| CSCvd14000 |
When pushing a policy to 2000 devices under a full scale of 10,000 devices, the CPU utilization rises to between 98 and 100 percent. Workaround: There is no workaround at this time. |
||||
|
Reset grapevine local needs to be performed multiple times to remove the node in MN. Workaround: In this case, reset grapevine local was performed 3 times to remove from node. |
|||||
|
Any Cisco APIC-EM users who have been authenticated/authorized by an external server and who are locked out of the controller for whatever reason, cannot be manually unlocked.
Workaround: There are two workarounds available:
|
|||||
|
Details of an application remains visible in the controller even after the application has been deleted. Workaround: There is no workaround at this time. |
|||||
|
If multiple devices have the same Unique Serial Number, then APIC-EM will consider only the first device, and ignore other devices with the same number. Workaround: There is no workaround at this time. |
|||||
|
After provisioning HUB sites, devices go to Workaround: There is no workaround at this time. |
|||||
|
When a single node G Series appliance with over 500 service filters and 80 agents, has a single instance of Wide Area Bonjour running, then at 130,000 service instances, when the interface withdraws are sent and the TTL0 messages are a large object, then error messages are seen in the sdg-services.log file. |
|||||
|
Unable to grow any services on the node after power on/off on the node in 3N Nic-bonding cluster. Workaround There are two approaches to restore:
The second approach may require additional steps to harvest the clients with service instances stuck in "unresponsive" state.
To check the service instance status, use the command |
|||||
|
Services struck in starting state on a scaled 3N NIC-bonding cluster Workaround: Need to harvest the client on which the service instances were placed manually, after which the services grows on a new client and it goes to running state. To check the service instance status, use command |
Resolved Caveats
The following table lists the resolved caveats for this release.
 Note |
For a list of caveats resolved in an earlier software release, see the Cisco APIC-EM release notes for the specific release. |
|
Caveat ID Number |
Headline |
|---|---|
|
While trying to remove a node from a 3N cluster, config-wizard gets exited with errors due to the rabbitmq queue not mirrored to the remaining two nodes. Workaround: Rebuild the cluster from scratch and restore the last backup data. |
|
|
While trying to issue Workaround: Issues |
|
|
After the upgrade from 1.6.0 to 1.6.1, the error "https://op2-prd1-dprox.cisco.com is not accessible." is seen while trying to launch the active-advisor application. Workaround Execute the command |
|
|
After removing a node from a 3N cluster for the second time, the stale host-id is seen in the grape host status output. It will still be present even after adding the node back. Workaround To remove the stale host record, run |
Using the Bug Search Tool
Use the Bug Search tool to search for a specific bug or to search for all bugs in this release.
Procedure
| Step 1 |
Go to http://tools.cisco.com/bugsearch. |
||
| Step 2 |
At the Log In screen, enter your registered Cisco.com username and password; then, click Log In. The Bug Search page opens.
|
||
| Step 3 |
To search for a specific bug, enter the bug ID in the Search For field and press Return. |
||
| Step 4 |
To search for bugs in the current release: |
Limitations and Restrictions
Cisco APIC-EM limitations and restrictions are described in the following sections:
 Note |
For information about the limitations and restrictions for a specific application, refer to the release notes for that application. |
General Limitations
-
When performing a Cisco APIC-EM discovery using an IP range, the ping sweep protocol (ICMP ping) is required. If ICMP ping is not enabled in your network, then use either the CDP discovery option for a discovery or directly add devices to the Cisco APIC-EM Device Inventory using the controller's GUI.
-
Path Trace: Cisco Performance Routing or PfR is not supported with DMVPN tunnels for this release.
-
The web GUI may take a few seconds to begin after the controller is started.
-
When working with the Cisco APIC-EM in a network with several thousand supported devices, the Topology window may load slowly. Additionally, filtering within the other controller windows may also proceed slowly.
-
Up to 4096 IP addresses are supported per discovery scan.

Note
The IP address limit applies for one or more configured IP ranges in the controller’s GUI.
-
The Cisco APIC-EM does not support duplicate IP addresses across VRFs in this release.
-
Inventory and Topology VRF filters are only supported for Cisco IOS devices. Cisco non-IOS devices such as the Nexus devices are not supported with VRF filters.
-
In a deployment with multiple inventory service instances running, re-sharding (rebalancing the devices to a remaining inventory instance when one of the inventory instances fails) occurs if any single inventory service instance fails. During this time, any device controlled by the failed service inventory instance displays in an inventory-collection pending state for a longer time than usual. Eventually, an inventory sync should occur without any issue.
-
After deleting a user from the controller's database, we recommend that you do not reuse that username when creating a new user for at least 6 hours. This waiting period is required to ensure that the deleted user's access rights and privileges are not inherited when reusing the username.
-
Cisco APIC-EM uses a master-slave database management system for the multi-host cluster. If the master host fails for any reason, then you will experience a 10 to 11 minute time interval when the controller UI is unavailable. This is due to the other two hosts recovering from that failure and re-establishing communications. If one of the slave hosts fails, there is no impact to the controller UI.
-
If the interfaces of a switch connected to a 3 host APIC-EM cluster are shut down for 30 minutes (which disconnects the Cisco APIC-EM from the network), and then brought up, it takes a very long time for controller's GUI to become accessible.
Multi-Host Limitations
-
When power-cycling Cisco APIC-EM cluster hosts, the recommended procedure is to first power on the host that gets powered off last, and then power on the rest of the hosts within 30 seconds. This avoids any possible clustering issues. If this timing recommendation is exceeded, the host power-up sequence is not maintained, or any other problem occurs, then the best way to recover is to run the reset_grapevine command on one of the hosts in the cluster. When prompted, answer "n" to all questions.
-
For a multi-host configuration with Cisco APIC-EM located behind a firewall that NATs the IP address of the controller, note the following information and requirement:
-
The Virtual IP address of the Cisco APIC-EM controller is used as a destination address for HTTP(S) traffic such as Cisco PnP and PKI download requests.
-
Any outbound connections initiated from the Cisco APIC-EM controller, such as during a Discovery, Inventory Collection, etc., will use the host IP address of one of the three Cisco APIC-EM hosts.
-
Therefore, you need to PAT (Port Address Translation) the host IP addresses of the Cisco APIC-EM hosts to a global public facing IP address for outbound connections from Cisco APIC-EM controller.
The following illustration depicts an example of a Cisco APIC-EM multi-host or multi-node (N1, N2, N3) configuration with the Cisco APIC-EM deployed behind a firewall/NAT. Also depicted are examples of the NAT Public IP-to-VIP and PAT-to-Public IP settings.
Figure 1. Cisco APIC-EM Configuration Example for Firewall/NAT 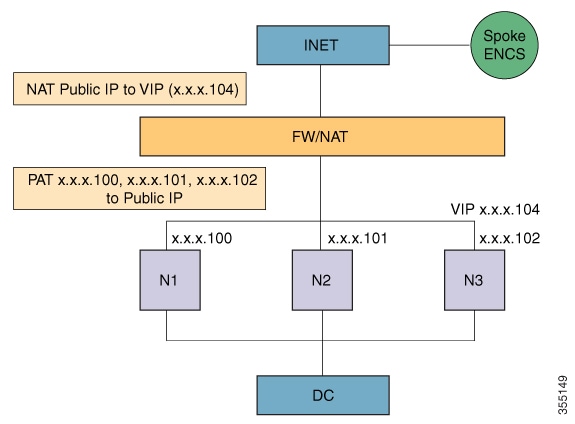
-
-
If a host fails within a multi-host configuration, the time for the cluster to recover is usually 20 minutes. The time to recover may change depending upon the Cisco APIC-EM disk I/O configuration. The recommended disk I/O speed is 200 MBps for a Cisco APIC-EM configuration.
-
If you need to replace an existing 10 GB NIC card in a Cisco APIC-EM appliance that is part of a multi-host cluster, you need to first remove that host from the multi-host cluster, then power-off the appliance and replace the 10 GB NIC card, then re-install the Cisco APIC-EM ISO on the appliance. After these steps are finished, then rejoin the host to the multi-host cluster. For information about the procedures to remove and add a host to a multi-host cluster, see the Cisco Application Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Troubleshooting Guide.
-
In a multi-host cluster with three hosts, if a single host (host A) is removed from the cluster for any reason, and the second host (host B) fails, then the last host (host C) will also immediately fail. To work around this limitation, perform the following procedure:
-
Log into the last active host (host C) and run the config_wizard command.
-
In the configuration wizard display, choose <Remove a faulted host from this APIC-EM cluster>.
-
In the configuration wizard display, choose <Revert to single-host cluster>.
The Grapevine services underpinning the original multi-host cluster are then removed and restarted.
-
Access the displayed IP address with a browser to view the Grapevine developer console and view the progress as each service restarts.
-
After host C is up and running, then proceed to reconfigure the multi-host cluster.

Note
For information about configuring a multi-host cluster, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide.
-
-
To enable external authentication with a AAA server in a multi-host environment, you must configure all individual Cisco APIC-EM host IP addresses and the Virtual IP address for the multi-host cluster on the AAA server. For additional information about external authentication with the Cisco APIC-EM, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide.
-
In certain circumstances, you may have only two operational hosts within a multi-host cluster (three hosts). For example, when in the process of setting up a multi-host cluster, you may have only two hosts set up before configuring the third or if a single host fails in your existing multi-host cluster. In these cases, the following functionality is unsupported for a multi-host cluster (three hosts) consisting of only two operational hosts:
-
Upgrading the software version
-
Installing the applications
-
Restoring a backup file
-
Restarting the cluster
-
Removing an active host, when there is an already a faulty host that exists and there is no reachability (IP connectivity) to the multi-host cluster
-
The reset grapevine command is not supported on a two-host cluster (either a 2 host multi-host cluster or 3 host multi-host cluster with one faulty host)

Important
The above functionality is only supported on a multi-host cluster that consists of three hosts.
-
-
Simultaneous removal of two hosts from a multi-host cluster (three hosts) at once or a simultaneous addition of two hosts to a multi-host cluster (three hosts) at once is not supported.
-
Cisco APIC-EM does not support shutting down 2 hosts in a 3 host cluster running a High Availability (HA) configuration. Only a single host at a time can be shut down and restarted when performing maintenance or troubleshooting in a 3 host cluster with HA.
Application Separation Limitations
-
The restore of a controller backup file should only be done on a Cisco APIC-EM controller running the same software version with same set of applications as that used to create the backup
-
When enabling or disabling an application on the controller, user downtime may result. For this reason, we recommend that you only perform these procedures during a maintenance time period.
-
Once enabled, an application cannot be subsequently revoked and returned to its previous version or disabled status.
- You should not attempt to enable or disable an application on a host within a multi-host cluster if any one of the hosts within the multi-host cluster is down. If you do attempt to enable or disable an application in this situation, then the attempt will fail and a message will be displayed that the operation cannot be performed until all the hosts are up and running.
-
As part of the application upgrade process, the controller only deletes the existing application that it successfully upgraded from in the controller's grape application display command output. The controller does not delete the record of any failed application upgrade attempts (stale application entries) in the controller's grape application display command output.
For example, assume the last successful application installation version is 5.10 and attempts have been made to upgrade to other application versions (5.13, 5.14, and 5.15) which all failed due to various reasons. Assume that a successful upgrade was made to version 5.16. The following information will appear in the grape application display command output:
$ grape application display apic-core enable_time "Tue Aug 02, 2016 10:39:37 PM" apic-core enabled true apic-core enabled_by_default true apic-core in_transition false apic-core last_error_code null apic-core last_result "Successfully upgraded application=apic-core from version=5.10.1 to version=5.16" $ grape application status APPLICATION VERSION ENABLED ENABLE TIME ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ apic-core 5.13 No None apic-core 5.14 No None apic-core 5.15 No None apic-core 5.16 Yes Tue Aug 02, 2016 10:39:37 PMYou can remove the stale application entries by using the grape application remove command, but this is not required for controller application separation functionality.
The stale application entries will only appear in the controller's CLI command output. The stale application entries do not appear in the controller's GUI.
Security Limitations
-
With this release, the default option for intra-host communications is IPSec and not GRE. If you choose not to use the default option and to configure GRE using the configuration wizard, then privacy is not enabled for all of the communications that occur between the hosts. For this reason, we strongly recommend that any multi-host cluster that is not configured with IPSec tunneling be set up and located within a secure network environment.
-
The Cisco APIC-EM should never be directly connected to the Internet. It should not be deployed outside of a NAT configured or protected datacenter environment. Additionally, when using the IWAN or PNP solution applications in a manner that is open to the Internet, you must configure a white-listing proxy or firewall to only allow incoming connections from your branch IP pools.
-
The Cisco APIC-EM platform management service (Grapevine) no longer supports port 14141.
-
Ensure that any external access to the Cisco APIC-EM using SSH (through port 22) is strictly controlled. We recommend that stringent measures be used, such as a segmented subnet as well as strict source address-based access policies in the port's access path.
-
Ensure that the strict physical security of the Cisco APIC-EM appliance or server is enforced. For Cisco APIC-EM deployed within a virtual machine, ensure that strong and audited access restrictions are in place for the hypervisor management console.
-
The Cisco APIC-EM backups are not encrypted when they are downloaded from the controller. If you download the backups from the controller, ensure that they are stored in a secure storage server and/or encrypted for storage.
-
The Update button in the controller's Trustpool GUI window will become active when an updated version of ios.p7b file is available and Internet access is present. The Update button will remain inactive if there is no Internet access.
-
As with any network management application, it is a general best practice to ensure that the traffic sent from Cisco APIC-EM to the managed devices is controlled in such a way as to minimize any security risks. More secure protocols (such as SSHv2 and SNMPv3) should be used rather than less secure ones (TELNET, SNMPv2), and network management traffic should be controlled (for example via access control lists or other types of network segmentation) to ensure that the management traffic is restricted to devices and segments of the network where it is needed.
-
If you are currently using the Device PKI certificate management functionality for the network devices (for example, when using the IWAN App) and want to take advantage of the new feature to convert the private (internal) device PKI CA in the Cisco APIC-EM from Root CA mode to a Subordinate CA (or Intermediate CA to an external CA), then you must re-provision any of the Cisco APIC-EM provisioned network devices so they obtain the new PKCS12 bundle issued from this newly subordinated CA. If you later decide to convert the Cisco APIC-EM device PKI CA back to Root CA from Subordinate CA (also referred to as SubCA), then you need to reset the controller in order to accomplish this. Additionally, any devices provisioned with certificates by the Cisco APIC-EM in SubCA mode, need to be reprovisioned. For information about the new Cisco APIC-EM PKI certificate management functionality, see the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide.
-
The Cisco APIC-EM controller does not provide a GUI or an API for replacing a subordinate CA certificate. Once SubCA mode is enabled using the controller, then the only way to replace the certificate of the Device PKI CA is to do a complete reset that brings the controller back to default root CA mode. You must then redo the conversion to subordinate CA mode using a new subordinate CA certificate. Before converting the controller back to the SubCA mode, you must also remove all device ID certificates and keys issued to network devices under the previous configuration of the Device PKI CA. The devices must be taken off line before converting the controller to SubCA mode with the new subordinate CA certificate, and then all devices will need to be reprovisioned by the PKI broker service using the new configuration of the Device PKI CA.
-
Currently, there is no subordinate CA certificate rollover capability available for the Cisco APIC-EM device PKI. This capability is targeted for a near future release. For this reason, we strongly recommend that the subordinate CA certificate lifetime be set to at least two years. This will prevent any disruption to the device PKI due to a CA certificate expiration.
-
When using the northbound REST API and creating a POST /trust-point request, this request must provide a trustProfileName attribute that has sdn-network-infra-iwan as its value (default). In the current release, no other values are valid for this required attribute.
-
Due to a Cisco IOS XE crypto PKI import limitation, Cisco devices running certain IOS versions cannot import a PKCS bundle (made up of a device certificate, device key and the subordinate CA certificate) exceeding 4KB size.

Note
Cisco devices running the following Cisco IOS versions or a higher version will not encounter this issue:
-
16.5(0.132)
-
16.3(2.11)
-
15.5(03)M4.1
This problem occurs when the Cisco APIC-EM device PKI CA is changed to SubCA mode with a subordinate CA certificate that has several and/or lengthy X509 attributes defined, thereby increasing the size of the device PKCS bundle beyond 4KB. To circumvent this issue, get the subordinate CA certificate issued with very minimal attributes. For example, do not include CDP distribution and OCSP settings.
The following command output is provided as an example of content from a subordinate CA certificate that can impact the file size, as well as the fields within the certificate where content should be minimized:
Certificate: Data: Version: 3 (0x2) Serial Number: 2e:00:00:00:0e:28:d7:1f:24:a1:1e:ef:70:00:00:00:00:00:0e Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: DC=com, DC=apic-em, CN=apic-em-CA Validity Not Before: Oct 18 19:56:54 2016 GMT Not After : Oct 19 19:56:54 2016 GMT Subject: CN=sdn-network-infra-subca Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption Public-Key: (2048 bit) Modulus: 00:cd:a7:65:a4:c4:64:e6:e0:6b:f2:39:c0:a2:3b: <snip> 85:a3:44:d1:a2:b3:b1:f5:ff:28:e4:12:41:d3:5f: bf:e9 Exponent: 65537 (0x10001) X509v3 extensions: X509v3 Subject Key Identifier: D2:DD:FA:E4:A5:6A:3C:81:29:51:B2:17:ED:82:CE:AA:AD:91:C5:1D X509v3 Authority Key Identifier: keyid:62:6F:C7:83:42:82:5F:54:51:2B:76:B2:B7:F5:06:2C:76:59:7F:F8 X509v3 Basic Constraints: critical CA:TRUE X509v3 Key Usage: critical Digital Signature, Certificate Sign, CRL Sign 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.21.7: 0-.%+.....7.....#...I......^...Q...._...S..d... Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption 18:ce:5b:90:6b:1d:5b:b4:df:fa:d3:8e:80:51:6f:46:0d:19: -
Software Update Limitations
-
For this specific release your upgrade may fail if the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application is installed and enabled. As a workaround, perform the following tasks:
-
Disable the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application in the App Management window of the controller's GUI.
-
Install the Cisco APIC-EM software upgrade.
-
Return to the App Management window and enable the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application.
-
-
Updating from earlier Cisco APIC-EM releases to this latest release may take up to an hour to complete.
-
When updating Cisco APIC-EM in a virtual machine within a VMware vSphere environment, you must ensure that the time settings on the ESXi host are also synchronized to the NTP server. Failure to ensure synchronization will cause the upgrade to fail.
-
Prior to beginning the software update process for the Cisco APIC-EM, we recommend that you configure the idle timeout value in the Auth Timeout GUI window for at least an hour. If a user is logged out due to an idle timeout during the software update process, then this process will fail and need to be re-initiated again.
In case a failure occurs on a multi-host cluster during any software updates (Linux files) and you have not increased the idle timeout using the GUI, then perform the following steps:
-
Log into each host and enter the following command: $ sudo cat /proc/net/xt_recent/ROGUE | awk '{print $1}’

Note
This command will list all IP addresses that have been automatically blocked by the internal firewall because requests from these IP addresses have exceeded a predetermined threshold.
-
If the command in Step 1 returns an IP address, then perform a reboot on the host where the above command has been entered (same host as the user is logged in).

Note
The hosts should be rebooted in a synchronous order and never two hosts rebooted at the same time.
-
After the host or hosts reboot, upload the software update package file to the controller again using the GUI.
-
Back Up and Restore
 Important |
For the IWAN solution application, you must review the Software Configuration Guide for Cisco IWAN on APIC-EM before attempting a back up and restore. There is important and detailed information about how these processes work for the IWAN application that includes what is backed up, what is not backed up, recommendations, limitations, and caveats. |
-
Before attempting a back up and restore with a host in a multi-host cluster, note the following:
-
You cannot take a back up from a single host (not in a multi-host cluster) and then restore it to a host in a multi-host cluster.
-
You cannot take a back up from a host in a multi-host cluster and restore it to a single host (not in a multi-host cluster).
-
-
When a user restores the controller from a backup file using the Cisco APIC-EM GUI, the password of that user and all other users will be reset to what is in the backup file.
-
You can only restore a backup from a controller that is the same version from which the backup was taken. In addition to the controller version being the same as the backup, the enabled applications and version on the controller also need to be the same as the one on which the backup was taken.
-
If you have configured a multi-host cluster with two or three hosts and not all of the hosts are running when you initiate a restore operation, then the restore operation will fail. All of the hosts that comprise the cluster must be in the cluster and operational at the time of the restore.
-
Prior to beginning the backup and restore process for the Cisco APIC-EM, we recommend that you log out and then log back into the controller. This will ensure that the default forced session timeout for the Cisco APIC-EM does not occur during this process.
-
Prior to beginning the backup and restore process for the Cisco APIC-EM, we recommend that you configure the idle timeout value in the Auth Timeout GUI window for at least an hour. If a user is logged out due to an idle timeout during the restore file upload process, then the restore process will fail and need to be re-initiated again.
Deployment Limitations
-
The default timezone (Universal Time Coordinated or UTC) should not be changed for the Cisco APIC-EM controller.
-
Before deploying Cisco APIC-EM for NIC bonding setup, ensure that the port-channel in the switch side is in Bundled state.
-
For a multi-host deployment, when joining a host to a cluster there is no merging of the data on the two hosts. The data that currently exists on the host that is joining the cluster is erased and replaced with the data that exists on the cluster that is being joined.
-
For a multi-host deployment, when joining additional hosts to form a cluster be sure to join only a single host at a time. You should not join multiple hosts at the same time, as doing so will result in unexpected behavior.
-
For a multi-host deployment, you should expect some service downtime when adding or removing hosts to a cluster, since the services are then redistributed across the hosts. Be aware that during the service redistribution, there will be downtime.
-
The controller GUI starts up and becomes accessible prior to all the Cisco APIC-EM services starting up and becoming active. For this reason, you need to wait a few minutes before logging into the controller GUI under the following circumstances:
-
Fresh ISO image installation
-
Resetting the controller using the reset_grapevine command
-
Power failure and the controller restarts
-
-
If you are installing the Cisco APIC-EM ISO image on a physical server using local media, you can use either a DVD drive, a bootable USB device, or a mounted VirtualMedia via CIMC (Cisco Integrated Management Controller for a Cisco UCS server). If you use a mounted VirtualMedia via CIMC, the installation process may take up to an hour. If you use a DVD drive or a bootable USB device, the installation process may take approximately 15 minutes.
-
If you burn the APIC-EM ISO to a bootable USB flash drive and then boot the server from the USB flash drive, a “Detect and mount CD-ROM” error might display during installation. This typically occurs when you perform the installation on a clean, nonpartitioned hard drive. The workaround for the above issue is to perform the following steps:
-
Press Alt+F2 to access the shell prompt.
-
Enter the mount command to determine the device that is attached to the /media mount point. This should be your USB flash drive.
-
Enter the umount /media command to unmount the USB flash drive.
-
Enter the mount /dev/ device_path /cdrom command (where device_path is the device path of the USB flash drive) to mount the USB flash drive to the CD-ROM. For example:
mount /dev/sda1 /cdrom -
Press Alt+F1 to return to the installation error screen.
-
Click “Yes” to retry mounting the CD-ROM.
-
-
When the configuration wizard is run to deploy the Cisco APIC-EM and the <save & exit> option is selected at the end of the configuration process instead of the proceed>> option, then you should always run the reset_grapevine command to bring the Cisco APIC-EM to an operational state. Failure to run the reset_grapevine command at the end of the deployment process after choosing the <save & exit> option in the configuration wizard will cause certain services to fail. The services that will fail are services that are brought up in the new VMs that are created and that depend upon the PKI certificates and stores. Services that do not depend upon the PKI certificates and stores will function properly.
User Account Limitations
-
We strongly recommend that when creating usernames for the Cisco APIC-EM, that you always use lower case characters. Do not create two usernames that are the same, but have a different case. For example, do not create the following usernames: USER123 and user123.
-
This version of the Cisco APIC-EM has been tested for external authentication with Cisco ISE based AAA servers, but it may support integration with other types of AAA servers.
-
An installer (ROLE_INSTALLER) uses the Cisco Plug and Play Mobile App to access the Cisco APIC-EM controller remotely for the purposes of and triggering device deployment and viewing device status. An installer cannot access the Cisco APIC-EM GUI directly. If an installer needs to change his or her password, the admin must delete the user then create a new user with the same username and a new password.
-
Users who are working with the controller's IWAN and PnP applications to monitor and manage devices and hosts must have their Groups values set to All. The IWAN and PnP applications do not support Custom groups. You set both roles and groups when configuring internal users in the Settings | Internal Users GUI window.
Service and Support
Troubleshooting
See the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Troubleshooting Guide, for troubleshooting procedures.
Related Documentation
The following publications are available for the Cisco APIC-EM:
Cisco APIC-EM Controller Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including new features, system requirements, and open and resolved caveats. |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Release Notes |
|
Installation and configuration of the controller, including post-installation tasks. |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide |
|
Introduction to the Cisco APIC-EM GUI and its applications. |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Quick Start Guide 7 |
|
Configuration of user accounts, RBAC scope, security certificates, authentication and password policies, and global discovery settings. Monitoring and managing Cisco APIC-EM services. Backup and restore. Cisco APIC-EM APIs. |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Administrator Guide |
|
Troubleshooting the controller, including the installation, services, and passwords. Developer console. How to contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC). |
Cisco Application Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Troubleshooting Guide |
|
Tasks to perform before updating the controller to the latest version. Software update instructions. Tasks to perform after an update. |
Cisco Application Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Upgrade Guide |
Cisco Network Visibility Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Network Visibility application. |
Cisco Network Visibility Application for APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Supported platforms and software releases. |
Cisco Network Visibility Application for APIC-EM Supported Platforms |
|
Installation of the application. (This application is installed as part of the Cisco APIC-EM controller software.) |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide |
|
Network discovery, device and host management, topology maps. |
Cisco Network Visibility Application for APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco EasyQoS Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco EasyQoS application. |
Cisco EasyQoS Application for APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Supported platforms and software releases. |
Cisco EasyQoS Application for APIC-EM Supported Platforms |
|
Installation of the application. (This application is installed as part of the Cisco APIC-EM controller software.) |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide |
|
Configuration of quality of service policies on the network devices in your network. |
Cisco EasyQoS Application for APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco Path Trace Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Path Trace application. |
Cisco Path Trace Application for APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Supported platforms and software releases. |
Cisco Path Trace Application for APIC-EM Supported Platforms |
|
Installation of the application. (This application is installed as part of the Cisco APIC-EM controller software.) |
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module Installation Guide |
|
Procedures for performing path traces and information about how to understand the path trace results. |
Cisco Path Trace Application for APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco IWAN Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco IWAN application. |
Cisco IWAN Application on APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Using the Cisco IWAN application. |
Cisco IWAN Application on APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco Integrity Verification Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Integrity Verification application. |
Cisco Integrity Verification Application (Beta) on APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Using the Cisco Integrity Verification application. |
Cisco Integrity Verification Application (Beta) on APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco Remote Troubleshooter Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application. |
Cisco Remote Troubleshooter Application on APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Using the Cisco Remote Troubleshooter application. |
Cisco Remote Troubleshooter Application on APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco Active Advisor Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Active Advisor application. |
Cisco Active Advisor for APIC-EM Release Notes |
Cisco Wide Area Bonjour Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Wide Area Bonjour application. |
Cisco Wide Area Bonjour Application for APIC-EM Release Notes |
|
Installation, configuration, troubleshooting, and usage of the application. |
Cisco Wide Area Bonjour Application for APIC-EM User Guide |
Cisco Network Plug and Play Application Documentation
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
Release information, including open and resolved caveats for the Cisco Plug and Play application. Supported Cisco devices for Cisco Network Plug and Play. |
Release Notes for Cisco Network Plug and Play |
|
Configuration of devices using Cisco Network Plug and Play. |
Configuration Guide for Cisco Network Plug and Play on Cisco APIC-EM Cisco Network Plug and Play Agent Configuration Guide or Cisco Open Plug-n-Play Agent Configuration Guide (depending on the Cisco IOS XE release) |
|
Cisco Network Plug and Play solution overview. Main workflows used with the Cisco Network Plug and Play solution. Deployment of the Cisco Network Plug and Play solution. Tasks for using proxies with the Cisco Network Plug and Play solution. Configuration of a DHCP server for APIC-EM controller auto-discovery. Troubleshooting procedures for the Cisco Network Plug and Play solution. |
Solution Guide for Cisco Network Plug and Play |
|
Information about using the Cisco Plug and Play Mobile App. |
Mobile Application User Guide for Cisco Network Plug and Play (also accessible in the app through Help) |
Cisco APIC-EM Developer Documentation
The Cisco APIC-EM developer website is located on the Cisco DevNet website
|
For this type of information... |
See this document... |
|---|---|
|
API functions, parameters, and responses. |
|
|
Tutorial introduction to controller GUI, DevNet sandboxes and APIC-EM NB REST API. |
Getting Started with Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (APIC-EM) |
|
Hands-on coding experience calling APIC-EM NB REST API from Python. |
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation at:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation as an RSS feed and delivers content directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service.
 Feedback
Feedback