Fehlerbehebung bei unbekannten Protokollverlusten in Catalyst Switches der Serie 9000
Download-Optionen
-
ePub (830.5 KB)
In verschiedenen Apps auf iPhone, iPad, Android, Sony Reader oder Windows Phone anzeigen
Inklusive Sprache
In dem Dokumentationssatz für dieses Produkt wird die Verwendung inklusiver Sprache angestrebt. Für die Zwecke dieses Dokumentationssatzes wird Sprache als „inklusiv“ verstanden, wenn sie keine Diskriminierung aufgrund von Alter, körperlicher und/oder geistiger Behinderung, Geschlechtszugehörigkeit und -identität, ethnischer Identität, sexueller Orientierung, sozioökonomischem Status und Intersektionalität impliziert. Dennoch können in der Dokumentation stilistische Abweichungen von diesem Bemühen auftreten, wenn Text verwendet wird, der in Benutzeroberflächen der Produktsoftware fest codiert ist, auf RFP-Dokumentation basiert oder von einem genannten Drittanbieterprodukt verwendet wird. Hier erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Cisco inklusive Sprache verwendet.
Informationen zu dieser Übersetzung
Cisco hat dieses Dokument maschinell übersetzen und von einem menschlichen Übersetzer editieren und korrigieren lassen, um unseren Benutzern auf der ganzen Welt Support-Inhalte in ihrer eigenen Sprache zu bieten. Bitte beachten Sie, dass selbst die beste maschinelle Übersetzung nicht so genau ist wie eine von einem professionellen Übersetzer angefertigte. Cisco Systems, Inc. übernimmt keine Haftung für die Richtigkeit dieser Übersetzungen und empfiehlt, immer das englische Originaldokument (siehe bereitgestellter Link) heranzuziehen.
Einleitung
In diesem Dokument werden häufige Ursachen für das Verwerfen unbekannter Protokolle bei Switches der Catalyst Serie 9000 beschrieben.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Cisco empfiehlt, dass Sie über Kenntnisse in folgenden Bereichen verfügen:
- Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
- LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
- Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
- Kapselung 802.1Q
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basierend auf folgenden Software- und Hardware-Versionen:
- Catalyst Switches der Serie 9000
- Cisco IOS® XE
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument beziehen sich auf Geräte in einer speziell eingerichteten Testumgebung. Alle Geräte, die in diesem Dokument benutzt wurden, begannen mit einer gelöschten (Nichterfüllungs) Konfiguration. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die möglichen Auswirkungen aller Befehle kennen.
Hintergrundinformationen
Unbekannte Protokollverluste treten auf, wenn der Ethertyp eines Frames nicht erkannt wird. Das bedeutet, dass das gekapselte Protokoll nicht unterstützt wird oder nicht an der Switch-Schnittstelle konfiguriert ist. Außerdem muss die Ziel-MAC-Adresse des Frames eine Adresse der Multicast-Kontrollebene sein, die in diesem Befehl aufgeführt sind.
Switch#show mac address-table | include CPU All 0100.0ccc.cccc STATIC CPU All 0100.0ccc.cccd STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0000 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0001 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0002 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0003 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0004 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0005 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0006 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0007 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0008 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0009 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000a STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000b STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000c STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000d STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000e STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.000f STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0010 STATIC CPU All 0180.c200.0021 STATIC CPU All ffff.ffff.ffff STATIC CPU

Hinweis: Unbekannte Protokoll-Drops werden nicht erhöht, wenn die Ziel-MAC-Adresse übertragen wird.
Fehlerbehebung
Schritt 1: Stellen Sie sicher, dass unbekannte Protokoll-Drops inkrementiert werden.
Switch#show interface ten1/0/5 | include protocol
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
85 unknown protocol drops
Switch#show interface ten1/0/5 | include protocol
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
90 unknown protocol dropsSchritt 2: Konfigurieren Sie eine Paketerfassung in der betroffenen Schnittstelle, und gleichen Sie die MAC-Zieladressen ab 01 ab.
Switch#monitor capture port5 interface ten1/0/5 in Switch#monitor capture port5 match mac any 0100.0000.0000 00ff.ffff.ffff Switch#monitor capture port5 buffer size 100
Schritt 3: Starten Sie die Paketerfassung, und überprüfen Sie den Zähler für das Verwerfen von Paketen mit unbekannten Protokollen.
Switch#monitor capture port5 start
Started capture point : port5
Switch#show interface ten1/0/5 | include protocol
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
541 unknown protocol drops
Schritt 4: Beenden Sie die Paketerfassung, nachdem einige unbekannte Protokolle verloren gegangen sind.
Switch#show interface ten1/0/5 | include protocol
TenGigabitEthernet1/0/5 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
544 unknown protocol drops
Switch#monitor capture port5 stop
Capture statistics collected at software:
Capture duration - 68 seconds
Packets received - 38
Packets dropped - 0
Packets oversized - 0
Bytes dropped in asic - 0
Capture buffer will exists till exported or cleared
Stopped capture point : port5Schritt 5: Exportieren des Inhalts der Paketerfassung
Switch#monitor capture port5 export location flash:drops.pcap Export Started Successfully Switch# Export completed for capture point port5
Schritt 6: Übertragen Sie die Paketerfassung auf Ihren Computer.
Switch#copy flash: ftp: vrf Mgmt-vrf Source filename [drops.pcap]? Address or name of remote host []? 10.10.10.254 Destination filename [drops.pcap]? Writing drops.pcap ! 4024 bytes copied in 0.026 secs (154769 bytes/sec)
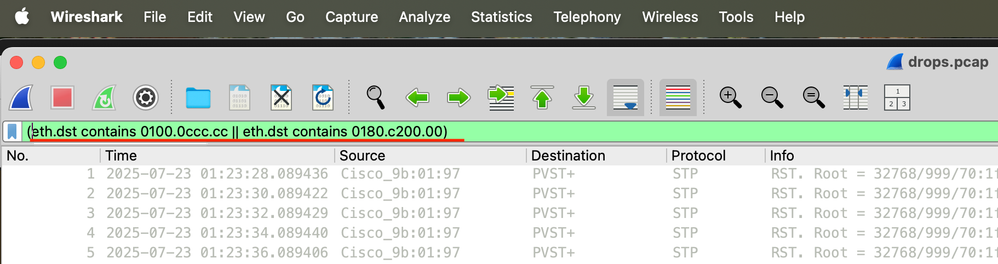
Schritt 7: Öffnen Sie die Paketerfassung in Wireshark, und verwenden Sie diesen Filter (eth.dst enthält 0100.0ccc.cc). | eth.dst enthält 0180.c200.00), um sich auf Multicast-Adressen der CPU zu konzentrieren.
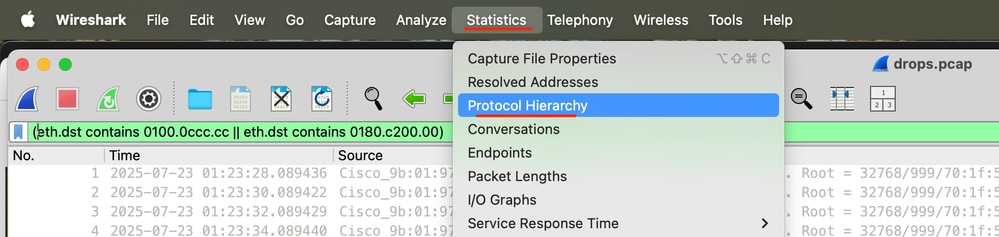
Schritt 8: Gehen Sie zu Statistik, und klicken Sie dann auf Protokollhierarchie.
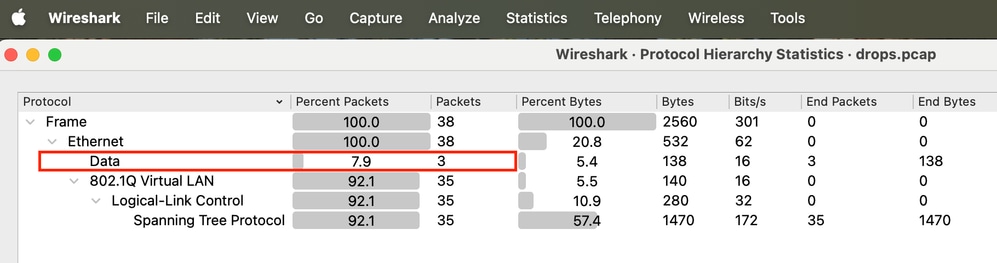
Schritt 9: Erweitern Sie den Protokollbaum, und stellen Sie sicher, dass die Switch-Schnittstelle für diese Protokolle konfiguriert ist. Alles, was als Daten bezeichnet wird, führt dazu, dass unbekannte Protokolle verloren gehen, da der Ethertyp unbekannt ist.
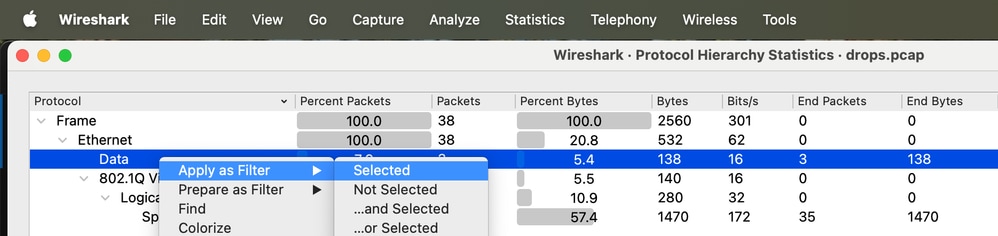
Schritt 10: Klicken Sie mit der rechten Maustaste auf Daten, navigieren Sie zu Als Filter anwenden, und klicken Sie auf Ausgewählt, um unbekannte Protokollrahmen zu filtern.
Schritt 11: Kehren Sie zum Hauptfenster von Wireshark zurück, um die Quell-MAC-Adresse und den Ethertype für unbekannte Protokolle zu ermitteln.
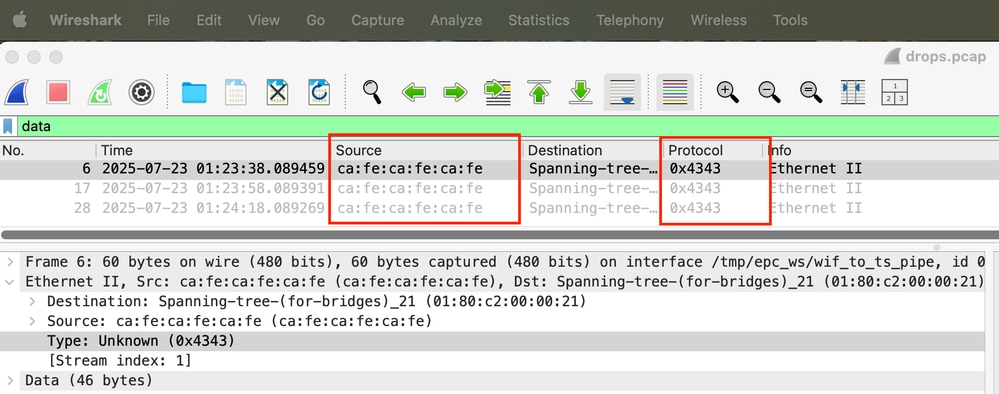
In diesem Fall führt die CAFE.CAFE.CAFE-Quelladresse zu unbekannten Protokollverlusten, da der Ethertyp 0x4343 nicht unterstützt wird.
Häufige Probleme
Die Beispiele in diesem Abschnitt basieren auf diesem Diagramm der Netzwerktopologie.
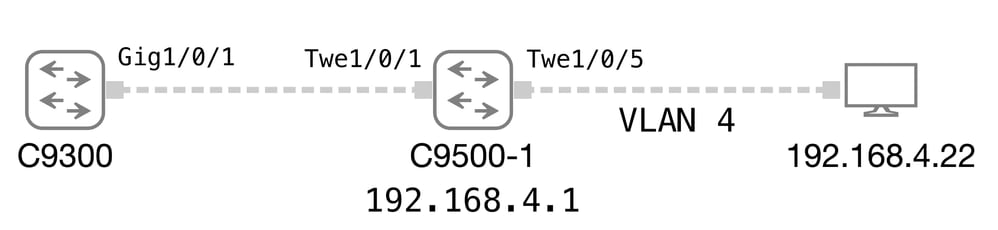
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
DTP-Nachrichten können möglicherweise unbekannte Protokollverluste verursachen, wenn sie an einem Port empfangen werden, an dem DTP deaktiviert ist. Sie können DTP aktivieren, indem Sie den Befehl no switchport nonegotiate im Schnittstellenkonfigurationsmodus verwenden.
C9500-1#show running-config interface Twe1/0/1
interface TwentyFiveGigE1/0/1
description C9300
switchport mode trunk
end
C9300#show running-config interface Gi1/0/1
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description C9500-1
switchport mode trunk
switchport nonegotiate
end
C9300#show interface gi1/0/1 | include unknown
350 unknown protocol drops LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
LLDP-Nachrichten können auch dazu führen, dass unbekannte Protokolle verloren gehen, wenn sie an einem Port empfangen werden, an dem LLDP deaktiviert ist. Sie können LLDP aktivieren, indem Sie den Befehl lldp run im globalen Konfigurationsmodus verwenden.
C9500-1#show lldp
Global LLDP Information:
Status: ACTIVE
LLDP advertisements are sent every 30 seconds
LLDP hold time advertised is 120 seconds
LLDP interface reinitialisation delay is 2 seconds
C9300#show lldp
% LLDP is not enabled
C9300#show interface gi1/0/1 | include unknown
423 unknown protocol drops Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
Ebenso können unbekannte Protokoll-Drops inkrementiert werden, wenn CDP-Nachrichten an einem Port empfangen werden, an dem CDP deaktiviert ist. Sie können CDP aktivieren, indem Sie den Befehl cdp run im globalen Konfigurationsmodus verwenden.
C9500-1#show cdp
Global CDP information:
Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds
Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds
Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled
C9300#show cdp
% CDP is not enabled
C9300#show interface gi1/0/1 | include unknown
434 unknown protocol drops VLAN-ID mit allen Nullen im 802.1Q-Header
Catalyst Switches der Serie 9000 verwerfen auch 802.1Q-Frames mit der VLAN-ID 0, wenn sie an Access-Ports empfangen werden. Diese Pakete inkrementieren jedoch nicht den Zähler für das Verwerfen unbekannter Protokolle. In diesem Beispiel wollen wir untersuchen, warum der Catalyst 9500-Switch keinen ARP-Eintrag für Host 192.168.4.22 abrufen kann.
C9500-1#ping 192.168.4.22 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.4.22, timeout is 2 seconds: ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) C9500-1#show ip arp vlan 4 Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Internet 192.168.4.1 - ecc0.18a4.b1bf ARPA Vlan4 C9500-1# C9500-1#show running-config interface Twe1/0/5 interface TwentyFiveGigE1/0/5 switchport access vlan 4 switchport mode access load-interval 30 end
Schritt 1: Starten Sie eine Paketerfassung über die Schnittstelle, die mit dem Endgerät verbunden ist.
C9500-1#show monitor capture TAC parameter monitor capture TAC interface TwentyFiveGigE1/0/5 both monitor capture TAC match any monitor capture TAC buffer size 100 circular monitor capture TAC limit pps 1000 C9500-1#monitor capture TAC start Started capture point : TAC
Schritt 2: Versuchen Sie, einen Ping an das Endgerät zu senden, um ARP-Datenverkehr zu generieren.
C9500-1#ping 192.168.4.22 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.4.22, timeout is 2 seconds: ..... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Schritt 3: Beenden Sie die Paketerfassung.
C9500-1#monitor capture TAC stop
Capture statistics collected at software:
Capture duration - 35 seconds
Packets received - 28
Packets dropped - 0
Packets oversized - 0
Bytes dropped in asic - 0
Capture buffer will exists till exported or cleared
Stopped capture point : TAC
Schritt 4: Beachten Sie, dass das Endgerät eine ARP-Antwort sendet, in diesem Fall Frame 17.
C9500-1#show monitor capture TAC buff brief | include ARP 15 19.402191 ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf b^F^R ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff ARP 60 Who has 192.168.4.22? Tell 192.168.4.1 17 21.347022 fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea b^F^R ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf ARP 60 192.168.4.22 is at fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea
Schritt 5: Beachten Sie, dass die ARP-Antwort mit der VLAN-ID 0 in einen 802.1Q-Header gekapselt wird.
C9500-1#show monitor capture TAC buff detailed | begin Frame 17
Frame 17: 60 bytes on wire (480 bits), 60 bytes captured (480 bits) on interface 0
<output omitted>
Ethernet II, Src: fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea (fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea), Dst: ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf (ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf)
Destination: ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf (ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf)
Address: ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf (ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Source: fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea (fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea)
Address: fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea (fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea)
.... ..0. .... .... .... .... = LG bit: Globally unique address (factory default)
.... ...0 .... .... .... .... = IG bit: Individual address (unicast)
Type: 802.1Q Virtual LAN (0x8100)
802.1Q Virtual LAN, PRI: 0, DEI: 0, ID: 0
000. .... .... .... = Priority: Best Effort (default) (0)
...0 .... .... .... = DEI: Ineligible
.... 0000 0000 0000 = ID: 0
Type: ARP (0x0806)
Padding: 0000000000000000000000000000
Address Resolution Protocol (reply)
Hardware type: Ethernet (1)
Protocol type: IPv4 (0x0800)
Hardware size: 6
Protocol size: 4
Opcode: reply (2)
Sender MAC address: fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea (fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea)
Sender IP address: 192.168.4.22
Target MAC address: ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf (ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf)
Target IP address: 192.168.4.1Schritt 6: Exportieren des Inhalts der Paketerfassung
C9500-1#monitor capture TAC export location flash:ARP.pcap Export Started Successfully
Schritt 7: Bestimmen Sie mithilfe des Tools zur Paketverfolgung, was der Switch mit Paket 17 macht.
C9500-1#show platform hardware fed active forward interface Twe1/0/5 pcap flash:ARP.pcap number 17 data Show forward is running in the background. After completion, syslog will be generated. C9500-1# *Sep 29 17:45:29.091: %SHFWD-6-PACKET_TRACE_DONE: R0/0: fed: Packet Trace Complete: Execute (show platform hardware fed switch <> forward last summary|detail) *Sep 29 17:45:29.091: %SHFWD-6-PACKET_TRACE_FLOW_ID: R0/0: fed: Packet Trace Flow id is 6881284
Schritt 8: Anzeigen der Ergebnisse der Paketverfolgung
C9500-1#show platform hardware fed active forward last summary
Input Packet Details:
###[ Ethernet ]###
dst = ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf
src=fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea
type = 0x8100
###[ 802.1Q ]###
prio = 0
id = 0
vlan = 0
type = 0x806
###[ ARP ]###
hwtype = 0x1
ptype = 0x800
hwlen = 6
plen = 4
op = is-at
hwsrc=fe:af:ea:fe:af:ea
psrc=192.168.4.22
hwdst = ec:c0:18:a4:b1:bf
pdst = 192.168.4.1
###[ Padding ]###
load = '00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00'
<output omitted>
Packet DROPPED
Catch-all for phf.finalFdPresent==1.

Anmerkung: Das Paket wird verworfen, da es die VLAN-ID 0 enthält.
Es gibt zwei Optionen, um diese Art von Drops zu verhindern.
Option 1: Verwenden Sie den Befehl switchport voice vlan dot1p. Auf diese Weise werden mit VLAN 0 empfangene Frames dem Zugriffs-VLAN zugewiesen.
interface TwentyFiveGigE1/0/5 switchport access vlan 4 switchport mode access switchport voice vlan dot1p load-interval 30
Option 2: Konfigurieren der Schnittstelle als Trunk-Port Auf diese Weise werden Frames, die mit VLAN 0 empfangen werden, dem nativen VLAN zugewiesen.
interface TwentyFiveGigE1/0/5 switchport trunk native vlan 4 switchport mode trunk load-interval 30 end

Anmerkung: Dies wurde häufig bei Profinet-Geräten beobachtet.
Verwandte Fehler
- Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Cisco Bug-ID CSCwe8812.
Zugehörige Informationen
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
24-Aug-2025
|
Erstveröffentlichung |
Beiträge von Cisco Ingenieuren
- Miguel PerezTAC Technical Consulting Engineer
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback