ASA/PIX: Konfiguration und Fehlerbehebung für die RRI (Reverse Route Injection)
Inhalt
Einführung
Dieses Dokument beschreibt die Konfiguration und Fehlerbehebung von RRI (Reverse Route Injection) auf der Cisco Security Appliance (ASA/PIX).
Hinweis: Weitere Informationen zur VPN-Konfiguration des Remote-Zugriffs auf ASA/PIX und dem Cisco VPN-Client 4.x mit Windows 2003 finden Sie im Konfigurationsbeispiel für die RADIUS-Authentifizierung (gegen Active Directory) unter PIX/ASA 7.x und Cisco VPN-Client.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Für dieses Dokument bestehen keine speziellen Anforderungen.
Verwendete Komponenten
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf den folgenden Software- und Hardwareversionen:
-
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) der Serie 5500 mit Softwareversion 8.0
-
Cisco VPN Client Software Version 5.0
Die Informationen in diesem Dokument wurden von den Geräten in einer bestimmten Laborumgebung erstellt. Alle in diesem Dokument verwendeten Geräte haben mit einer leeren (Standard-)Konfiguration begonnen. Wenn Ihr Netzwerk in Betrieb ist, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die potenziellen Auswirkungen eines Befehls verstehen.
Zugehörige Produkte
Diese Konfiguration kann auch mit der Cisco PIX Firewall der Serie 500 verwendet werden, die die Softwareversion 7.x und höher ausführt.
Konventionen
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie unter Cisco Technical Tips Conventions (Technische Tipps zu Konventionen von Cisco).
Hintergrundinformationen
Reverse Route Injection (RRI) wird zum Füllen der Routing-Tabelle eines internen Routers verwendet, auf dem das OSPF-Protokoll (Open Shortest Path First) oder das Routing Information Protocol (RIP) für Remote-VPN-Clients oder LAN-²LAN-Sitzungen ausgeführt wird.
Konfigurieren
In diesem Abschnitt erhalten Sie Informationen zum Konfigurieren der in diesem Dokument beschriebenen Funktionen.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie das Command Lookup Tool (nur registrierte Kunden), um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Abschnitt verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten.
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die folgende Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
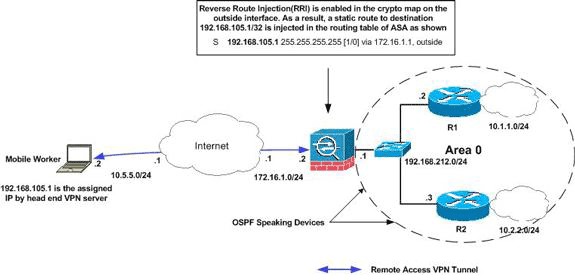
Hinweis: Die in dieser Konfiguration verwendeten IP-Adressierungsschemata sind im Internet nicht rechtlich routbar. Es handelt sich um RFC 1918-Adressen, die in einer Laborumgebung verwendet wurden.
Hinweis: Sie können RRI im LAN-zu-LAN VPN-Tunnel und in Easy VPN-Szenarien verwenden.
Konfigurationen
In diesem Dokument werden folgende Konfigurationen verwendet:
| Cisco ASA |
|---|
ciscoasa(config)#access-list split extended permit ip 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0
192.168.105.0 255.255.255.00
ciscoasa(config)#access-list redistribute standard permit 192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
ciscoasa(config)#ip local pool clients 192.168.105.1-192.168.105.10 mask 255.255.255.0
ciscoasa(config)#route-map redistribute permit 1
ciscoasa(config-route-map)#match ip address redistribute
ciscoasa(config-route-map)#exit
ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup internal
ciscoasa(config)#group-policy clientgroup attributes
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#split-tunnel-network-list value split
ciscoasa(config-group-policy)#exit
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp nat-traversal 10
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp enable outside
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 encryption 3des
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 hash sha
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 group 2
ciscoasa(config)#isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400
ciscoasa(config)#crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
ciscoasa(config)#crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
ciscoasa(config)#crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set reverse-route
!--- Command to enable RRI
ciscoasa(config)#crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic outside_dyn_map
ciscoasa(config)#crypto map outside_map interface outside
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group vpn-test type ipsec-ra
ciscoasa(config)#tunnel-group vpn-test general-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#address-pool clients
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#default-group-policy clientgroup
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-general)#tunnel-group vpn-test ipsec-attributes
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-ipsec)#pre-shared-key cisco123
ciscoasa(config-tunnel-ipsec)#exit |
| Cisco ASA |
|---|
ciscoasa#show running-config
: Saved
:
ASA Version 8.0(2)
!
hostname ciscoasa
enable password 8Ry2YjIyt7RRXU24 encrypted
names
!
interface Ethernet0
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet1
nameif inside
security-level 100
ip address 192.168.212.1 255.255.255.0
!
!---Output Suppressed
!
passwd 2KFQnbNIdI.2KYOU encrypted
ftp mode passive
access-list split extended permit ip 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0
192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
!--- Split-tunneling ACL
access-list redistribute standard permit 192.168.105.0 255.255.255.0
!--- Match the traffic sourced from 192.168.105.0 network
pager lines 24
mtu outside 1500
mtu insi 1500
ip local pool clients 192.168.105.1-192.168.105.10 mask 255.255.255.0
no failover
icmp unreachable rate-limit 1 burst-size 1
no asdm history enable
arp timeout 14400
!
route-map redistribute permit 1
match ip address redistribute
!
!
router ospf 1
network 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
log-adj-changes
redistribute static subnets route-map redistribute
!--- Redistribute the static routes sourced from 192.168.105.0 !--- network into OSPF Autonomous System (AS).
!
route outside 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.1 1
!---Output Suppressed
crypto ipsec transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set transform-set ESP-3DES-SHA
crypto dynamic-map outside_dyn_map 20 set reverse-route
!--- Command to enable RRI
crypto map outside_map 65535 ipsec-isakmp dynamic outside_dyn_map
crypto map outside_map interface outside
crypto isakmp enable outside
crypto isakmp policy 10
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
crypto isakmp policy 65535
authentication pre-share
encryption 3des
hash sha
group 2
lifetime 86400
!---Output Suppressed
service-policy global_policy global
group-policy clientgroup internal
group-policy clientgroup attributes
split-tunnel-policy tunnelspecified
split-tunnel-network-list value split
username vpnuser password gKK.Ip0zetpjju4R encrypted
tunnel-group vpn-test type remote-access
tunnel-group vpn-test general-attributes
address-pool clients
default-group-policy clientgroup
tunnel-group vpn-test ipsec-attributes
pre-shared-key *
prompt hostname context
Cryptochecksum:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
: end |
Fehlerbehebung
Dieser Abschnitt enthält Informationen zur Fehlerbehebung in Ihrer Konfiguration.
Ausgabe der Routing-Tabelle, bevor RRI in der ASA aktiviert wird
Hinweis: Nehmen Sie an, der VPN-Tunnel wird von einem mobilen Remote-Benutzer eingerichtet, und 192.168.105.1 ist die zugewiesene IP-Adresse von ASA.
ASA-Routing-Tabelle
ciscoasa#show route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.105.1 255.255.255.255 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
C 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, insi
C 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, outside
S 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
O 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 2:09:24, insi
O 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 2:09:24, insi
Tipp: Auch wenn RRI nicht konfiguriert ist, wird die statische Route des angeschlossenen Clients in die Routing-Tabelle des VPN-Servers (ASA/PIX) eingespeist. Sie wird jedoch nicht an den internen Router weiterverteilt, der dynamische Routing-Protokolle wie OSPF und EIGRP ausführt (wenn Sie ASA 8.0 ausführen).
Routing-Tabelle Router R1
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.2.2.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 02:11:52, Ethernet0
Router R2-Routing-Tabelle
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.2.2.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.1.1.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 02:13:03, Ethernet0
Ausgabe der Routing-Tabelle nach Aktivierung von RRI in der ASA
Hinweis: Nehmen Sie an, der VPN-Tunnel wird von einem mobilen Remote-Benutzer eingerichtet, und 192.168.105.1 ist die zugewiesene IP-Adresse von ASA.
ASA-Routing-Tabelle
ciscoasa#show route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
S 192.168.105.1 255.255.255.255 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
C 192.168.212.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, insi
C 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, outside
S 10.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1, outside
O 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 2:09:24, insi
O 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 2:09:24, insi
Routing-Tabelle Router R1
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.105.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.105.1 [110/20] via 192.168.212.1, 00:03:06, Ethernet0
!--- Redistributed route
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.2.2.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.3, 02:11:52, Ethernet0
Router R2-Routing-Tabelle
R2#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.105.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 192.168.105.1 [110/20] via 192.168.212.1, 00:04:17, Ethernet0
!--- Redistributed route
C 192.168.212.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.2.2.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.1.1.1/32 [110/11] via 192.168.212.2, 02:13:03, Ethernet0
Zugehörige Informationen
Cisco kontaktieren
- Eine Supportanfrage öffnen

- (Erfordert einen Cisco Servicevertrag)
 Feedback
Feedback