MP-EBGP-Konfigurationsbeispiel
Inhalt
Einleitung
Dieses Dokument enthält Informationen zur Konfiguration des erweiterten Multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol (MP-EBGP) auf Cisco IOS-Routern. MP-BGP ist ein erweitertes BGP, das es dem BGP ermöglicht, Routing-Informationen für mehrere Netzwerkschichtprotokolle, IPv6, VPNv4 und andere, zu übertragen. MP-BGP ermöglicht eine von einer Multicast-Routing-Topologie verschiedene Unicast-Routing-Topologie, die die Kontrolle von Netzwerk und Ressourcen erleichtert.
Voraussetzungen
Anforderungen
Es gibt keine spezifischen Anforderungen für dieses Dokument.
Verwendete Komponenten
Dieses Dokument ist nicht auf bestimmte Software- und Hardware-Versionen beschränkt.
Die Konfigurationen in diesem Dokument basieren auf dem Cisco Router der Serie 3700, auf dem die Cisco IOS® Software, Version 12.4 (15)T 13, ausgeführt wird.
Konventionen
Weitere Informationen zu Dokumentkonventionen finden Sie unter Cisco Technical Tips Conventions (Technische Tipps von Cisco zu Konventionen).
Konfigurieren
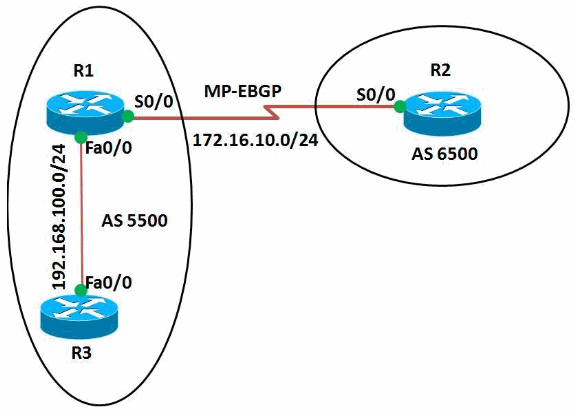
In diesem Beispiel sind die R1- und R3-Router so konfiguriert, dass sie zum AS 5500 gehören und iBGP bilden. Der R2-Router ist für den AS 6500 konfiguriert. Die R1- und R2-Router kommunizieren miteinander über MP-EBGP. Alle Router sind mit Loopback-Adressen konfiguriert.
Hinweis: Verwenden Sie das Tool für die Suche nach Befehlen (nur für registrierte Kunden), um weitere Informationen zu den in diesem Dokument verwendeten Befehlen zu erhalten.
Netzwerkdiagramm
In diesem Dokument wird die folgende Netzwerkeinrichtung verwendet:
Konfigurationen
In diesem Dokument werden folgende Konfigurationen verwendet:
| Konfiguration auf Router R1 |
|---|
R1#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R1 ! ip cef ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 10.10.10.10 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.100.10 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0 ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0 mpls ip clock rate 2000000 ! router bgp 5500 no synchronization bgp router-id 10.10.10.10 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 192.168.100.0 redistribute connected neighbor 172.16.10.2 remote-as 6500 neighbor 172.16.10.2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor 192.168.100.11 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 172.16.10.2 activate neighbor 172.16.10.2 send-community both !--- Sends the community attribute to a BGP neighbor. exit-address-family ! ! end |
| Konfiguration auf Router R2 |
|---|
R2#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R2 ! ip cef ! ip vrf WAN rd 2020:1 route-target export 2020:1 route-target import 2020:1 ! ! interface Loopback0 ip vrf forwarding WAN !--- Associates a VRF instance with an interface or subinterface. ip address 20.20.20.20 255.255.255.255 ! interface Serial0/0 ip vrf forwarding WAN ip address 172.16.10.2 255.255.255.0 mpls ip clock rate 2000000 ! router bgp 6500 no synchronization bgp router-id 20.20.20.20 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! ! address-family vpnv4 neighbor 172.16.10.1 activate neighbor 172.16.10.1 send-community both exit-address-family ! address-family ipv4 vrf WAN redistribute connected redistribute static neighbor 172.16.10.1 remote-as 5500 neighbor 172.16.10.1 activate no synchronization exit-address-family ! ! ! end |
| Konfiguration auf Router R3 |
|---|
R3#show run Building configuration... ! version 12.4 ! hostname R3 ! ip cef ! ! ! interface Loopback0 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.100.11 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! router bgp 5500 no synchronization bgp router-id 11.11.11.11 bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 192.168.100.10 remote-as 5500 no auto-summary ! end |
Überprüfung
Um Einträge in der (BGP)-Routing-Tabelle anzuzeigen, verwenden Sie den Befehl show ip bgp.
| IP-BGP anzeigen |
|---|
Auf Router R1 R1#show ip bgp 172.16.10.2
BGP routing table entry for 172.16.10.2/32, version 14
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.10.10)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
!--- Displays the routing table entries for the host 172.16.10.2
R1#sh ip bgp 192.168.100.11
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.100.0/24, version 4
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table)
Advertised to update-groups:
1 2
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (10.10.10.10)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, local, best
!--- Displays the entries for the host 192.168.100.11
Auf Router R3 R3#sh ip bgp 192.168.100.10
BGP routing table entry for 192.168.100.0/24, version 4
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table Default-IP-Routing-Table, RIB-failure(17))
Not advertised to any peer
Local
192.168.100.10 from 192.168.100.10 (10.10.10.10)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
!--- Displays the entries for the host 192.168.100.10
|
Verwenden Sie im Router R2 den Befehl show ip bgp vpnv4, um die (VPNv4)-Adressinformationen aus der (BGP)-Tabelle anzuzeigen.
| show ip bgp vpnv4 |
|---|
Auf Router R2 R2#sh ip bgp vpnv4 vrf WAN
BGP table version is 24, local router ID is 20.20.20.20
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, I - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: I - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 2020:1 (default for vrf WAN)
*> 10.10.10.0/24 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 20.20.20.20/32 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
* 172.16.10.0/24 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
r> 172.16.10.2/32 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 ?
*> 192.168.100.0 172.16.10.1 0 0 5500 I
!--- Displays prefixes associated with the (VRF) instance WAN.
R2#show ip bgp vpnv4 vrf WAN 172.16.10.1
BGP routing table entry for 2020:1:172.16.10.0/24, version 7
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table WAN)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
5500
172.16.10.1 from 172.16.10.1 (10.10.10.10)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external
Extended Community: RT:2020:1
mpls labels in/out 18/nolabel
Local
0.0.0.0 from 0.0.0.0 (20.20.20.20)
Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 32768, valid, sourced, best
Extended Community: RT:2020:1
mpls labels in/out 18/aggregate(WAN)
!--- Displays prefixes associated with neighbor 172.16.10.1
|
MP-EBGP wird zwischen den R1- und R2-Routern eingerichtet. Verwenden Sie den Befehl ping, um die Erreichbarkeit von R1 zu R2 und umgekehrt zu überprüfen.
| Ping |
|---|
Auf Router R1 R1#ping 172.16.10.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.10.2, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/64/208 ms R1#ping 192.168.100.11 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.100.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 12/41/96 ms !--- Router R1 can successfully ping the routers R2 and R3.Auf Router R2 R2#ping vrf WAN 172.16.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/32/96 ms R2#ping vrf WAN 192.168.100.11 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.100.11, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/73/204 ms !--- Router R2 can successfully reach router R1 and R3. |
Zugehörige Informationen
Revisionsverlauf
| Überarbeitung | Veröffentlichungsdatum | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-May-2012
|
Erstveröffentlichung |
 Feedback
Feedback