-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 3.x
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Installation and Switch Management
- Switch Configuration
-
Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
SAN Device Virtualization
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
-
Security
-
Configuring FIPS
-
Configuring Users and Common Roles
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Configuring IPv4 Access Control Lists
-
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
-
Configuring IPsec Network Security
-
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fabric Binding
-
- IP Services
- Intelligent Storage Services
- Network and Switch Monitoring
- Traffic Management
- Troubleshooting
-
Launching Fabric Manager in Cisco SAN-OS Releases Prior to 3.2(1)
-
Cisco Fabric Manager Unsupported Feature List
-
Interface Nonoperational Reason Codes
-
Managing Cisco FabricWare
-
Configuration Limits for Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.1(x) and 3.2(x)
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
Basic Gigabit Ethernet Configuration for IPv4
Configuring Interface Descriptions
Configuring the MTU Frame Size
About VLANs for Gigabit Ethernet
Configuring the VLAN Subinterface
Gigabit Ethernet IPv4-ACL Guidelines
Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports IP version 4 (IPv4) on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. This chapter describes how to configure IPv4 addresses and other IPv4 features.
This chapter includes the following topics:
•
Basic Gigabit Ethernet Configuration for IPv4
About IPv4
Both FCIP and iSCSI rely on TCP/IP for network connectivity. On each IPS module or MPS-14/2 module, connectivity is provided in the form of Gigabit Ethernet interfaces that are appropriately configured. This section covers the steps required to configure IP for subsequent use by FCIP and iSCSI.
Note
For information about configuring FCIP, see Chapter 48, "Configuring FCIP." For information about configuring iSCSI, see Chapter 42, "Configuring iSCSI."
A new port mode, called IPS, is defined for Gigabit Ethernet ports on each IPS module or MPS-14/2 module. IP storage ports are implicitly set to IPS mode, so it can only be used to perform iSCSI and FCIP storage functions. IP storage ports do not bridge Ethernet frames or route other IP packets.
Each IPS port represents a single virtual Fibre Channel host in the Fibre Channel SAN. All the iSCSI hosts connected to this IPS port are merged and multiplexed through the single Fibre Channel host.
In large scale iSCSI deployments where the Fibre Channel storage subsystems require explicit LUN access control for every host device, use of proxy-initiator mode simplifies the configuration.
Note
The Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on the MPS-14/2 module do not support EtherChannel.
Note
To configure IPv6 on a Gigabit Ethernet interface, see the "Configuring IPv6 Addressing and Enabling IPv6 Routing" section on page 46-11.
Tip
Gigabit Ethernet ports on any IPS module or MPS-14/2 module should not be configured in the same Ethernet broadcast domain as the management Ethernet port—they should be configured in a different broadcast domain, either by using separate standalone hubs or switches or by using separate VLANs.
Basic Gigabit Ethernet Configuration for IPv4
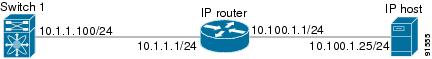
Figure 53-1 shows an example of a basic Gigabit Ethernet IP version 4 (IPv4) configuration.
Figure 53-1 Gigabit Ethernet IPv4 Configuration Example
Note
The port on the Ethernet switch to which the MDS Gigabit Ethernet interface is connected should be configured as a host port (also known as access port) instead of a switch port. Spanning tree configuration for that port (on the Ethernet switch) should disabled. This helps avoid the delay in the management port coming up due to delay from Ethernet spanning tree processing that the Ethernet switch would run if enabled. For Cisco Ethernet switches, use either the switchport host command in IOS is or the set port host in Catalyst OS. Refer to the configuration guide for your Ethernet switch.
To configure the Gigabit Ethernet interface using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Switches > Interfaces > Ethernet > IPS.
You see the Gigabit Ethernet Configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
Click the IP Addresses tab.
Step 3
Click Create Row.
You see the Create Gigabit Ethernet Interface dialog box.
Step 4
Select the switch on which you want to create the Gigabit Ethernet interface.
Step 5
Enter the interface. For example 2/2 for slot 2, port 2.
Step 6
Enter the IPv4 address (10.1.1.100) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0).
Step 7
Click Create to save these changes or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Configuring Interface Descriptions
•
Configuring the MTU Frame Size
Configuring Interface Descriptions
See the "About Interface Descriptions" section on page 20-13 for details on configuring the switch port description for any interface.
Configuring Beacon Mode
See the "About Beacon Mode" section on page 20-15 for details on configuring the beacon mode for any interface.
Configuring Autonegotiation
By default, autonegotiation is enabled all Gigabit Ethernet interface. You can enable or disable autonegotiation for a specified Gigabit Ethernet interface. When autonegotiation is enabled, the port automatically detects the speed or pause method, and duplex of incoming signals based on the link partner. You can also detect link up conditions using the autonegotiation feature.
To configure autonegotiation using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Switches > Interfaces > Ethernet > IPS.
You see the Gigabit Ethernet Configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
In the General tab, you can enable or disable the Auto Negotiate option for a specific switch.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes.
Configuring the MTU Frame Size
You can configure the interfaces on a switch to transfer large (or jumbo) frames on a port. The default IP maximum transmission unit (MTU) frame size is 1500 bytes for all Ethernet ports. By configuring jumbo frames on a port, the MTU size can be increased up to 9000 bytes.
Note
The minimum MTU size is 576 bytes.
Tip
MTU changes are disruptive, all FCIP links and iSCSI sessions flap when the software detects a change in the MTU size.
To configure the MTU frame size using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Switches > Interfaces > Ethernet > IPS.
You see the Gigabit Ethernet Configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
In the General tab, in the Mtu column, you can enter a new value to configure the MTU Frame Size for a specific switch. For example 3000 bytes. The default is 1500 bytes.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes.
Configuring Promiscuous Mode
You can enable or disable promiscuous mode on a specific Gigabit Ethernet interface. By enabling the promiscuous mode, the Gigabit Ethernet interface receives all the packets and the software then filters and discards the packets that are not destined for that Gigabit Ethernet interface.
To configure the promiscuous mode using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Expand Switches > Interfaces > Ethernet > IPS.
You see the Gigabit Ethernet Configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2
In the General tab, you can enable or disable the Promiscuous Mode option for a specific switch.
Step 3
Click Apply Changes.
VLANs
This section describes virtual LAN (VLAN) support in Cisco MDS SAN-OS and includes the following topics:
•
About VLANs for Gigabit Ethernet
•
Configuring the VLAN Subinterface
•
Interface Subnet Requirements
About VLANs for Gigabit Ethernet
Virtual LANs (VLANs) create multiple virtual Layer 2 networks over a physical LAN network. VLANs provide traffic isolation, security, and broadcast control.
Gigabit Ethernet ports automatically recognize Ethernet frames with IEEE 802.1Q VLAN encapsulation. If you need to have traffic from multiple VLANs terminated on one Gigabit Ethernet port, configure subinterfaces—one for each VLAN.
Note
If the IPS module or MPS-14/2 module is connected to a Cisco Ethernet switch, and you need to have traffic from multiple VLANs coming to one IPS port, verify the following requirements on the Ethernet switch:
- The Ethernet switch port connected to the IPS module or MPS-14/2 module is configured as a trunking port.
- The encapsulation is set to 802.1Q and not ISL, which is the default.Use the VLAN ID as a subscription to the Gigabit Ethernet interface name to create the subinterface name (the
<slot-number>/<port-number>.<VLAN-ID>).Configuring the VLAN Subinterface
To configure a VLAN subinterface (VLAN ID) using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1
Select Interface > Ethernet and iSCSI.
Step 2
Click the Sub Interfaces tab.
Step 3
Select the Gigabit Ethernet subinterface on which 802.1Q should be used.
Step 4
Click the Edit IP Address button.
Step 5
Enter the IPv4 address and subnet mask for the Gigabit Ethernet interface.
Step 6
Click Create to save the changes or you may click Close.
Interface Subnet Requirements
Gigabit Ethernet interfaces (major), subinterfaces (VLAN ID), and management interfaces (mgmt 0) can be configured in the same or different subnet depending on the configuration (see Table 53-1).
Note
The configuration requirements in Table 53-1 also apply to Ethernet PortChannels.
IPv4-ACLs
This section describes the guidelines for IPv4 access control lists (IPv4-ACLs) and how to apply them to Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
Note
For information on creating IPv4-ACLs, see Chapter 33, "Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists."
Gigabit Ethernet IPv4-ACL Guidelines
Follow these guidelines when configuring IPv4-ACLs for Gigabit Ethernet interfaces:
•
Only use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
Note
Other protocols such as User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and HTTP are not supported in Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. Applying an ACL that contains rules for these protocols to a Gigabit Ethernet interface is allowed but those rules have no effect.
•
Apply IPv4-ACLs to the interface before you enable an interface. This ensures that the filters are in place before traffic starts flowing.
•
Be aware of the following conditions:
–
If you use the log-deny option, a maximum of 50 messages are logged per second.
–
The established option is ignored when you apply IPv4-ACLs containing this option to Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
–
If an IPv4-ACL rule applies to a pre-existing TCP connection, that rule is ignored. For example if there is an existing TCP connection between A and B and an IPv4-ACL which specifies dropping all packets whose source is A and destination is B is subsequently applied, it will have no effect.
Tip
If IPv4-ACLs are already configured in a Gigabit Ethernet interface, you cannot add this interface to an Ethernet PortChannel group. See Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces for information on configuring IPv4-ACLs.
Default Settings
Table 53-2 lists the default settings for IPv4 parameters.
Table 53-2 Default IPv4 Parameters
IPv4 MTU frame size
1500 bytes for all Ethernet ports.
Autonegotiation
Enabled.
Promiscuous mode
Disabled.

 Feedback
Feedback