-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide, Release 3.3(3)
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Installation and Switch Management
- Switch Configuration
-
Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
SAN Device Virtualization
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
-
Security
-
Configuring FIPS
-
Configuring Users and Common Roles
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
-
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
-
Configuring IPsec Network Security
-
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fabric Binding
-
- IP Services
- Intelligent Storage Services
- Network and Switch Monitoring
- Traffic Management
- Troubleshooting
-
Configuration Limits for Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.x
-
Table Of Contents
Cisco MDS 9500 Series Multilayer Directors
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Fabric Switches
Cisco MDS 9216i Multiprotocol Fabric Switch
Cisco MDS 9222i, Cisco MDS 9216A and Cisco MDS 9216 Multilayer Fabric Switches
Cisco MDS 9100 Series Fixed Configuration Fabric Switches
Cisco SAN-OS Software Configuration
Tools for Software Configuration
Software Configuration Overview
Product Overview
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family of multilayer directors and fabric switches offers intelligent fabric-switching services that realize maximum performance while ensuring high reliability levels. They combine robust and flexible hardware architecture with multiple layers of network and storage management intelligence. This powerful combination enables highly available, scalable storage networks that provide intelligent networking features such as multiprotocol and multitransport integration, virtual SANs (VSANs), advanced security, sophisticated debug analysis tools, and unified SAN management.
This chapter lists the hardware features for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family and describes its software features. It includes the following sections:
•
Cisco SAN-OS Software Configuration
Hardware Overview
This section provides an overview of the following Cisco MDS 9000 Family of multilayer directors and fabric switches:
•
Cisco MDS 9500 Series multilayer directors
–
Cisco MDS 9513 multilayer director
–
Cisco MDS 9509 multilayer director
–
Cisco MDS 9506 multilayer director
•
Cisco MDS 9200 Series fabric switches
–
Cisco MDS 9222i multilayer fabric switch
–
Cisco MDS 9216i multilayer fabric switch
–
Cisco MDS 9216A multilayer fabric switch
–
Cisco MDS 9216 multilayer fabric switch
•
Cisco MDS 9100 Series fixed configuration fabric switches
–
Cisco MDS 9140 multilayer switch
–
Cisco MDS 9134 multilayer switch
–
Cisco MDS 9124 multilayer switch
–
Cisco MDS 9120 multilayer switch
–
Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem
–
Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter
Cisco MDS 9500 Series Multilayer Directors
The Cisco MDS 9500 Series includes the following multilayer, modular directors:
•
The Cisco MDS 9513 Director, which has thirteen slots, two of which (slot 7 and slot 8) are reserved for the Supervisor-2 modules, and can accommodate up to eleven hot-pluggable switching or services modules.
•
The Cisco MDS 9509 Director, which has nine slots, two of which (slot 5 and slot 6) are reserved for the Supervisor-1 modules or Supervisor-2 modules, and can accommodate up to seven hot-pluggable switching or services modules.
•
The Cisco MDS 9506 Director, which has six slots, two of which (slot 5 and slot 6) are reserved for the Supervisor-1 modules or Supervisor-2 modules, and can accommodate up to four hot-pluggable switching or services modules.
Note
Supervisor-1 modules and Supervisor-2 modules can only operate in the same chassis during migration. See the "Migrating from Supervisor-1 Modules to Supervisor-2 Modules" section on page 8-32.
The two supervisor modules ensure high availability and traffic load balancing capabilities. The standby supervisor module provides redundancy if the active supervisor module fails. Supervisor-1 modules provide management access through a 10/100BASE-T Ethernet port switch and an RS-232 serial port. Supervisor-2 modules provide management access through a 10/100/1000BASE-T Ethernet port switch and an RS-232 serial port.
Note
As of Cisco MDS SAN-OS release 3.2(1), the USB ports on the Supervisor-2 module are supported. USB flash drives connected to these ports may be used for the same functions as media in the external compact flash slot.
The Cisco MDS 9500 Series directors support the following switching and services modules:
•
48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
18/4-port Multiservice module (MSM-18/4)
•
18/4-port Multiservice module FIPS
•
18-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
16-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module
•
8-port IP Storage Services (IPS-8) module
•
4-port IP Storage Services (IPS-4) module
•
Storage Services Module (SSM)
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9500 Series Hardware Installation Guide.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Fabric Switches
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series includes the following multilayer switches supporting multiprotocol capabilities:
•
Cisco MDS 9222i
•
Cisco MDS 9216i
•
Cisco MDS 9216A
•
Cisco MDS 9216
Cisco MDS 9216i Multiprotocol Fabric Switch
The Cisco MDS 9216i multiprotocol fabric switch has two slots, one of which is reserved for the integrated supervisor module and the other for switching or services modules. The supervisor module provides supervisor functions and has 14 standard Fibre Channel ports and two multiprotocol ports that can support FCIP and iSCSI protocols simultaneously.
The Cisco MDS 9200 multilayer fabric switches support the following switching and services modules:
•
48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
16-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module
•
8-port IP Storage Services (IPS-8) module
•
4-port IP Storage Services (IPS-4) module
•
Storage Services Module (SSM)
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide.
Cisco MDS 9222i, Cisco MDS 9216A and Cisco MDS 9216 Multilayer Fabric Switches
The Cisco MDS 9222i, Cisco MDS 9216A and Cisco MDS 9216 multilayer fabric switches have two slots, one of which is reserved for the integrated supervisor module and the other for a switching or services module. The supervisor module provides supervisor functions and has 16 standard Fibre Channel ports.
The Cisco MDS 9222i multilayer fabric switch supports the following switching and services modules:
•
12-port, 24-port, and 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching modules
•
4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
18/4-port Multiservice Module
•
18/4-port Multiservice FIPS Module with Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2 Level-3 validation
•
32-port Storage Services Module
•
8-port IP Storage Services Module
The Cisco MDS 9216A multilayer fabric switch supports the following switching and services modules:
•
48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
16-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module
•
8-port IP Storage Services (IPS-8) module
•
4-port IP Storage Services (IPS-4) module
The Cisco MDS 9216 multilayer fabric switch supports the following switching and services modules:
•
32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
16-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module
•
14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module
•
8-port IP Storage Services (IPS-8) module
•
4-port IP Storage Services (IPS-4) module
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide and the Cisco MDS 9216 Switch Hardware Installation Guide.
Cisco MDS 9100 Series Fixed Configuration Fabric Switches
Cisco MDS 9100 Series includes the following multilayer, fixed configuration (non-modular) switches:
•
Cisco MDS 9140 with 40 ports (8 full-rate ports, 32 host-optimized ports)
•
Cisco MDS 9134 with 34 ports (24-port base with 8-port license for growth; two 10 Gbps ports can be activated independently in 24-port or 32-port configurations)
–
On-demand port activation licensing
–
Non-disruptive upgrades
•
Cisco MDS 9124 with 24 ports (8 base ports, which can go upto 8 or 16 additional ports)
Also includes:
–
On-demand port activation licensing
–
Non-disruptive upgrades
•
Cisco MDS 9120 with 20 ports (4 full-rate ports, 16 host-optimized ports)
•
Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem (24 ports; 16 internal 2/4 Gbps, and 8 full-rate ports)
•
Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter (20 ports; 14 internal 2/4 Gbps, and 6 external full-rate ports)
These fixed configuration switches are packaged in 1 RU enclosures and provide 1-Gbps, 2-Gbps, 4-Gbps, or 10 Gbps autosensing Fibre Channel ports. Besides Telnet access, a 10/100BASE-T Ethernet port provides switch access.
Note
Switches in the Cisco MDS 9100 Series do not have a COM1 port (RS-232 serial port).
Refer to the Cisco MDS 9100 Series Hardware Installation Guide.
Cisco SAN-OS Software Configuration
This section describes the tools you can use to configure SAN-OS software, and provides an overview of the software configuration process with links to the appropriate chapters.
This section includes the following topics:
•
Tools for Software Configuration
•
Software Configuration Overview
Tools for Software Configuration
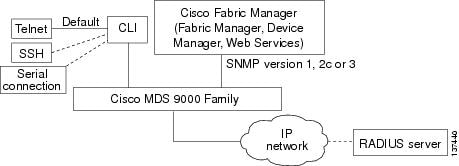
You can use one of two configuration management tools to configure your SANs (see Figure 1-1).
•
The command-line interface (CLI) can manage Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches using Telnet, SSH, or a serial connection.
•
The Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric Manager, a Java-based graphical user interface, can manage Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches using SNMP.
Figure 1-1 Tools for Configuring Cisco SAN-OS Software
CLI
With the CLI, you can type commands at the switch prompt, and the commands are executed when you press the Enter key. The CLI parser provides command help, command completion, and keyboard sequences that allow you to access previously executed commands from the buffer history.
Continue reading this document for more information on configuring the Cisco MDS switch using the CLI.
Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric Manager
The Cisco Fabric Manager is a set of network management tools that supports Secure Simple Network Management Protocol version 3 (SNMPv3) and legacy versions. The Cisco Fabric Manager applications are:
•
Fabric Manager Client—provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that displays real-time views of your network fabric, and lets you manage the configuration of Cisco MDS 9000 Family devices and third-party switches.
•
Fabric Manager Server—performs advanced monitoring, troubleshooting, and configuration for multiple fabrics. It must be started before running the Fabric Manager Client. It can be accessed by up to 16 Fabric Manager Clients at a time.
•
Device Manager—presents two views of a switch.
–
Device View displays a continuously updated physical representation of the switch configuration, and provides access to statistics and configuration information for a single switch.
–
Summary View presents real-time performance statistics of all active interfaces and channels on the switch for Fibre Channel and IP connections.
•
Fabric Manager Web Services—allows operators to monitor MDS events, performance, and inventory, and perform minor configuration tasks from a remote location using a web browser.
•
Performance Manager—provides detailed traffic analysis by capturing data with SNMP. This data is compiled into various graphs and charts that can be viewed with any web browser using Fabric Manager Web Services.
The Cisco Fabric Manager applications are an alternative to the CLI for most switch configuration commands.
Note
Resource Manager Essentials (RME) versions 3.4 and 3.5 provide support for switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family. Device Updates (DU) are available on Cisco.com (http://www.cisco.com/).
For more information on configuring the Cisco MDS switch using the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Software Configuration Overview
This section provides an overview of the Cisco SAN-OS configuration process and includes the following topics:
Basic Configuration
These sections contain the minimum information you need to get your switch up and running.
•
Preparing to configure the switch (Chapter 2, "Before You Begin")
•
Installing licenses (Chapter 3, "Obtaining and Installing Licenses")
•
Activating additional ports (Chapter 4, "On-Demand Port Activation Licensing")
•
Configuring the minimum requirements:
–
Initial configuration (Chapter 5, "Initial Configuration")
–
VSANs (Chapter 20, "Configuring and Managing VSANs.")
–
Interfaces (Chapter 13, "Configuring Interfaces")
–
Zones and zone sets (Chapter 24, "Configuring and Managing Zones.")
Advanced Configuration
These sections contain additional configuration information for SAN-OS software and the MDS 9000 Family of switches and includes the following topics:
•
Network and Switch Monitoring
Switch Configuration
•
On-demand port activation licensing (Chapter 4, "On-Demand Port Activation Licensing")
•
N Port virtualization (Chapter 14, "Configuring N Port Virtualization")
•
Generation 2 switching modules (Chapter 15, "Configuring Generation 2 Switches and Modules")
•
High Availability (Chapter 10, "Configuring High Availability")
•
Trunking (Chapter 16, "Configuring Trunking")
•
PortChannels (Chapter 17, "Configuring PortChannels")
•
Domains (Chapter 18, "Configuring Domain Parameters")
•
Schedule maintenance jobs (Chapter 19, "Scheduling Maintenance Jobs")
Fabric Configuration
•
Dynamic VSANs (Chapter 22, "Creating Dynamic VSANs")
•
SAN device virtualization (Chapter 21, "SAN Device Virtualization")
•
Inter-VSAN Routing (Chapter 23, "Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing")
•
Device alias distribution (Chapter 25, "Distributing Device Alias Services")
•
FSPF (Chapter 26, "Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols")
•
FLOGI (Chapter 27, "Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases")
•
SCSI (Chapter 28, "Discovering SCSI Targets")
•
FICON (Chapter 29, "Configuring FICON")
•
Switch interoperability (Chapter 30, "Advanced Features and Concepts")
Security
•
Users and Roles (Chapter 39, "Configuring Users and Common Roles")
•
SNMP (Chapter 33, "Configuring SNMP")
•
RADIUS and TACACS+ (Chapter 34, "Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+")
•
Access lists for IPv4 and IPv6 (Chapter 35, "Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists")
•
Digital certificates (Chapter 36, "Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates")
•
IPsec for network security (Chapter 37, "Configuring IPsec Network Security")
•
FC-SP for fabric security (Chapter 38, "Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP")
•
Port security (Chapter 39, "Configuring Port Security")
•
Fabric binding (Chapter 40, "Configuring Fabric Binding")
IP Services
•
FCIP (Chapter 41, "Configuring FCIP")
•
SAN extension tuner (Chapter 42, "Configuring the SAN Extension Tuner")
•
iSCSI (Chapter 43, "Configuring iSCSI")
•
IP services (Chapter 44, "Configuring IP Services")
•
IP storage (Chapter 45, "Configuring IP Storage")
•
IPv4 (Chapter 46, "Configuring IPv4 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces"
•
IPv6 (Chapter 47, "Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces")
Intelligent Storage Services
•
SCSI flow services (Chapter 48, "Configuring SCSI Flow Services and Statistics")
•
Fibre Channel write acceleration (Chapter 49, "Configuring Fibre Channel Write Acceleration"
•
SANTap (Chapter 50, "Configuring SANTap")
•
NASB (Chapter 51, "Configuring NASB")
Network and Switch Monitoring
•
RMON (Chapter 52, "Configuring RMON")
•
SPAN (Chapter 53, "Monitoring Network Traffic Using SPAN")
•
System message logging (Chapter 54, "Configuring System Message Logging")
•
Call Home (Chapter 55, "Configuring Call Home")
•
Fabric configuration servers (Chapter 56, "Configuring Fabric Configuration Servers")
Traffic Management
•
QoS (Chapter 57, "Configuring Fabric Congestion Control and QoS")
•
Port tracking (Chapter 58, "Configuring Port Tracking")

 Feedback
Feedback