-
Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide, Release 3.3(3)
-
Index
-
New and Changed Information
-
Preface
- Getting Started
- Installation and Switch Management
- Switch Configuration
-
Fabric Configuration
-
Configuring and Managing VSANs
-
SAN Device Virtualization
-
Creating Dynamic VSANs
-
Configuring Inter-VSAN Routing
-
Distributing Device Alias Services
-
Configuring Fibre Channel Routing Services and Protocols
-
Managing FLOGI, Name Server, FDMI, and RSCN Databases
-
Discovering SCSI Targets
-
Configuring FICON
-
Advanced Features and Concepts
-
Configuring and Managing Zones
-
-
Security
-
Configuring FIPS
-
Configuring Users and Common Roles
-
Configuring SNMP
-
Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
-
Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
-
Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
-
Configuring IPsec Network Security
-
Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
-
Configuring Port Security
-
Configuring Fabric Binding
-
- IP Services
- Intelligent Storage Services
- Network and Switch Monitoring
- Traffic Management
- Troubleshooting
-
Configuration Limits for Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.x
-
Table Of Contents
Configuring NASB
The Storage Services Module (SSM) supports Network-Accelerated Serverless Backup (NASB).
For licensing details, see Chapter 3, "Obtaining and Installing Licenses."
This chapter includes the following sections:
About NASB
Data movement in the fabric uses considerable processor cycles, which can cause client applications to slow down noticeably. Offloading data movement operations to a media server allows the client applications to run normally even during a backup operation. Media servers can further offload the data movement operation to NASB devices, which allows the media server to focus on the coordination functions needed to complete the backup.
Most backups performed today are server-free. In server-free backups, the application server is not involved in moving the data. The data can be moved by either a media server or a NASB device.
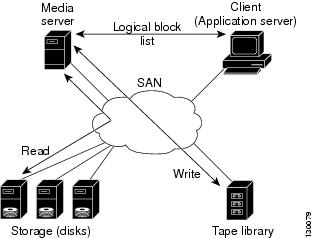
When the media server is the data mover, it moves the data between the disks and the tapes. The backup application runs on both the client device and the media server. However, the backup application in the client device performs minimal tasks for the backup operation.
The media server performs the following backup operations:
•
Manages disks as well as one or more tape backup devices.
•
Contacts the client devices to retrieve the list of logical blocks that need to be backed up.
•
Performs data movement from disk to tape media based on the logical block list provided by the client device.
The backup application in the client device maps the data to be backed up and creates the logical block list associated with the data. The movement of data from the physical disks to the backup device (tape) is not performed by the client device. This reduces substantial load on the client device.
Note
The media server, disk, and tape can be located anywhere in the fabric.
An example configuration is shown in Figure 51-1. The media server moves the data directly between the storage disks and the tape devices during backups.
Figure 51-1 Example Configuration with Media Server as Data Mover
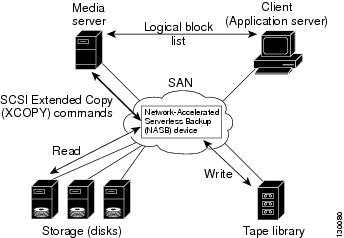
When the NASB is the data mover, it moves the data between the disks and the tapes. The NASB device is a SCSI target device capable of handling SCSI Extended Copy (XCOPY) commands as well as a SCSI initiator device capable of issuing READ/WRITE commands to disks and other backup media, such as tapes. See Figure 51-2.
Figure 51-2 Example Configuration with NASB Device as Data Mover
The task of managing and preparing the source and destination targets is performed by the media server. For example, if the destination is a tape library, the media server issues commands to load and unload the correct tape and position of the tape write head at the correct offset within the tape.
Configuring NASB
Network-Accelerated Serverless Backup (NASB) can be enabled on an entire SSM or it can be enabled on one or more groups of four ports on an SSM. Enabling NASB on interfaces has the following restrictions:
•
The fewest number of interfaces that you can enable is four. You can specify fc1 through fc4 but not fc1 through fc2.
•
The first interface in the group must be 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 25, or 29. You can specify fc5 through fc8 but not fc7 through fc10.
•
The groups of four interfaces do not need to be consecutive. You can specify fc1 through fc8 and fc17 through fc20.
To configure the NASB feature, follow these steps:
Note
You cannot simultaneously configure the intelligent services SANTap and NASB on a single SSM.
NASB Target Rediscovery
You can initiate a rediscovery of a target device (disk or tape) if the configuration on the target side has changed without generating an RSCN in the fabric, such as a change in the access list or LUN-mapping on the target. Use the following step to initiate target device rediscovery:
Step 1
switch# nasb rediscover module 2 vsan 9 target-pwwn 20:02:00:a0:b8:16:a1:5f
nasb rediscovery initiated
Initiates a rediscovery of a target device for the SSM in slot 2.
Displaying NASB Information
Use the show nasb command to display information about NASB (see Example 51-1 to Example 51-4).
Example 51-1 Displays NASB Information
switch# show nasbNASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=22f90005300036a2, pWWN=22fa0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=22fb0005300036a2, pWWN=22fc0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=22fd0005300036a2, pWWN=22fe0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=22ff0005300036a2, pWWN=26000005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26010005300036a2, pWWN=26020005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26030005300036a2, pWWN=26040005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26050005300036a2, pWWN=26060005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26070005300036a2, pWWN=26080005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=26090005300036a2, pWWN=260a0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=260b0005300036a2, pWWN=260c0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=260d0005300036a2, pWWN=260e0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=260f0005300036a2, pWWN=26100005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26110005300036a2, pWWN=26120005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26130005300036a2, pWWN=26140005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26150005300036a2, pWWN=26160005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26170005300036a2, pWWN=26180005300036a2 (provisioned)Example 51-2 Displays NASB Information for a Specific Module
switch# show nasb module 3NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=22f90005300036a2, pWWN=22fa0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=22fb0005300036a2, pWWN=22fc0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=22fd0005300036a2, pWWN=22fe0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=22ff0005300036a2, pWWN=26000005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26010005300036a2, pWWN=26020005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26030005300036a2, pWWN=26040005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26050005300036a2, pWWN=26060005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26070005300036a2, pWWN=26080005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=26090005300036a2, pWWN=260a0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=260b0005300036a2, pWWN=260c0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=260d0005300036a2, pWWN=260e0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=260f0005300036a2, pWWN=26100005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26110005300036a2, pWWN=26120005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26130005300036a2, pWWN=26140005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26150005300036a2, pWWN=26160005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26170005300036a2, pWWN=26180005300036a2 (provisioned)Example 51-3 Displays NASB Information for a Specific Module for a VSAN
switch# show nasb module 3 vsan 2NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=26090005300036a2, pWWN=260a0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=260b0005300036a2, pWWN=260c0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=260d0005300036a2, pWWN=260e0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=260f0005300036a2, pWWN=26100005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26110005300036a2, pWWN=26120005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26130005300036a2, pWWN=26140005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26150005300036a2, pWWN=26160005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 2:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26170005300036a2, pWWN=26180005300036a2 (provisioned)Example 51-4 Displays NASB Information for a Specific VSAN
switch# show nasb vsan 1NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-1, VT-nWWN=22f90005300036a2, pWWN=22fa0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-2, VT-nWWN=22fb0005300036a2, pWWN=22fc0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-3, VT-nWWN=22fd0005300036a2, pWWN=22fe0005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-4, VT-nWWN=22ff0005300036a2, pWWN=26000005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-5, VT-nWWN=26010005300036a2, pWWN=26020005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-6, VT-nWWN=26030005300036a2, pWWN=26040005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-7, VT-nWWN=26050005300036a2, pWWN=26060005300036a2 (provisioned)NASB:module 3 vsan 1:DPP-8, VT-nWWN=26070005300036a2, pWWN=26080005300036a2 (provisioned)Default Settings
Table 51-1 lists the default settings for NASB parameters.

 Feedback
Feedback