Table Of Contents
8.1 Terminal Point-to-Point and Linear ADM Configurations
8.3 Path-Protected Mesh Networks
SONET Topologies and Upgrades
Note
The terms "Unidirectional Path Switched Ring" and "UPSR" may appear in Cisco literature. These terms do not refer to using Cisco ONS 15xxx products in a unidirectional path switched ring configuration. Rather, these terms, as well as "Path Protected Mesh Network" and "PPMN," refer generally to Cisco's path protection feature, which may be used in any topological network configuration. Cisco does not recommend using its path protection feature in any particular topological network configuration.
This chapter explains Cisco ONS 15310-CL SONET topologies and upgrades. To provision topologies, refer to the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide.
Chapter topics include:
•
Terminal Point-to-Point and Linear ADM Configurations
8.1 Terminal Point-to-Point and Linear ADM Configurations
You can configure ONS 15310-CLs in a terminal point-to-point network (two nodes) or as a line of add/drop multiplexers (ADMs) (3 or more nodes) by configuring the OC-3 ports as the working path and a second set as the protect path. Unlike rings, terminal and linear ADMs require that the OC-3 port at each node be in 1+1 protection to ensure that a break to the working line is automatically routed to the protect line.
Note
In a linear ADM configuration, two OC-N ports in 1+1 protection are connected to two OC-N ports in 1+1 protection on a second node. On the second node, two more OC-N ports are connected to a third node. The third node can be connected to a fourth node, and so on, depending on the number of nodes in the linear ADM. The ONS 15310-CL has only two optical ports. This restricts an ONS 15310-CL to being the end node in a linear ADM network since both ports are necessary to create the 1+1 protection group to the neighbor node.
Figure 8-1 shows two ONS 15310-CLs in a linear ADM configuration with an ONS 15454. In this example, working traffic flows from the ONS 15310 Node 1/Slot 2/Port 2-1 to the ONS 15454 Node 2/Slot 5, and from Node 2/Slot 12 to the ONS 15310 Node 3/Slot 2/Port 2-1. You create the protect path by placing Slot 2/Port 2-1 in 1+1 protection with Slot 2/Port 1-1 at Nodes 1 through 3.
Figure 8-1 Linear ADM Configuration
8.2 Interoperability
The ONS 15310-CL supports up to ten SONET SDCCs and 1 path protection per node. You can install ONS 15310-CL nodes into a network comprised entirely of ONS 15310-CL nodes or into a network that has a mix of ONS 15310-CL, ONS 15454, and ONS 15327 nodes. The ONS 15310-CL interoperates with the ONS 15454 and ONS 15327 in linear or path protection configurations. Because connection procedures for these types of nodes are the same (for example, adding or dropping nodes from a path protection or linear configuration, or creating DCCs), follow the instructions in the "Add and Remove Nodes" chapter of the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide whenever you make connections between ONS 15310-CL, ONS 15454, and ONS 15327 nodes.
8.2.1 Linear Connections
Figure 8-2 shows a basic linear or path protection connection between ONS 15310-CL and ONS 15454 nodes.
Figure 8-2 Linear or Path Protection Connection Between ONS 15454 and ONS 15310-CL Nodes
8.3 Path-Protected Mesh Networks
In addition to single path protection configurations, terminal point-to-point or linear ADMs, you can extend ONS 15310-CL traffic protection by creating path-protected mesh networks (PPMNs). PPMNs include multiple ONS 15310-CL SONET topologies and extend the protection provided by a single path protection to the meshed architecture of several interconnecting rings. In a PPMN, circuits travel diverse paths through a network of single or multiple meshed rings. When you create circuits, you can have CTC automatically route circuits across the PPMN, or you can manually route them. You can also choose levels of circuit protection. For example, if you choose full protection, CTC creates an alternate route for the circuit in addition to the main route. The second route follows a unique path through the network between the source and destination and sets up a second set of cross-connections.
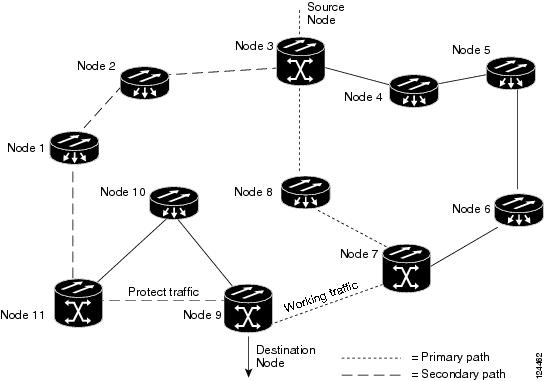
For example, in Figure 8-3, a circuit is created from Node 3 to Node 9. CTC determines that the shortest route between the two nodes passes through Node 8 and Node 7, shown by the dotted line, and automatically creates cross-connections at Nodes 3, 8, 7, and 9 to provide the primary circuit path.
If full protection is selected, CTC creates a second unique route between Nodes 3 and 9 which, in this example, passes through Nodes 2, 1, and 11. Cross-connections are automatically created at Nodes 3, 2, 1, 11, and 9, shown by the dashed line. If a failure occurs on the primary path, traffic switches to the second circuit path. In this example, Node 9 switches from the traffic coming in from Node 7 to the traffic coming in from Node 11 and service resumes. The switch occurs within 50 ms.
Figure 8-3 Path-Protected Mesh Network
8.4 Four Node Configurations
You can link multiple ONS 15310-CLs using their OC-3 ports (also known as creating a fiber-optic bus) to accommodate more access traffic than a single ONS 15310-CL can support. For example, to drop more than 21 DS-1s or 3 DS-3s (the maximum that can be aggregated in a single node), you can link the nodes but not merge multiple nodes into a single ONS 15310-CL. You can link nodes with OC-3 fiber spans as you would link any other two network nodes. The nodes can be grouped in one facility to aggregate more local traffic.
8.5 OC-N Speed Upgrades
A span is the optical fiber connection between two ONS 15310-CL nodes. In a span (optical speed) upgrade, the transmission rate of a span is upgraded from an OC-3 to OC-12 signal but all other span configuration attributes remain unchanged. With multiple nodes, a span upgrade is a coordinated series of upgrades on all nodes in the ring or protection group. The ONS 15310-CL supports the span upgrade wizard if you are upgrading two ONS 15310-CLs with 1+1 protection from OC-3 to OC-12.
To perform a span upgrade, the higher-rate pluggable port module (PPM) must replace the lower-rate PPM in the same slot. If you are using a multi-rate PPM, you do not need to physically replace the PPM. All spans in the network must be upgraded. The 1+1 protection configuration of the original lower-rate PPM is retained for the higher-rate PPM.
When performing span upgrades, Cisco recommends that you upgrade all spans in a network consecutively and in the same maintenance window. Until all spans are upgraded, mismatched PPM types will be present.
If you are upgrading two ONS 15310-CLs with 1+1 protection from OC-3 to OC-12, Cisco recommends using the Span Upgrade Wizard to perform span upgrades. Although you can also use the manual span upgrade procedures, the manual procedures are mainly provided as error recovery for the wizard. The Span Upgrade Wizard and the manual span upgrade procedures require at least two technicians (one at each end of the span) who can communicate with each other during the upgrade. Upgrading a span is non-service affecting and will cause no more than three switches, each of which is less than 50 ms in duration. To initiate the span upgrade, right-click the span and choose Span Upgrade.
Note
Span upgrades do not upgrade SONET topologies (for example, a 1+1 group to a path protection). Refer to the "Convert Network Configurations" chapter of the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide for topology upgrade procedures.
8.5.1 Span Upgrade Wizard
The Span Upgrade Wizard automates all steps in the manual 1+1 span upgrade procedure, if you are upgrading two ONS 15310-CLs from OC3 to OC12. The wizard can upgrade both lines of a 1+1 group. The Span Upgrade Wizard requires that spans have DCCs enabled.
The Span Upgrade Wizard provides no way to back out of an upgrade. In the case of an error, you must exit the wizard and initiate the manual procedure to either continue with the upgrade or back out of it. To continue with the manual procedure, examine the standing conditions and alarms to identify the stage in which the wizard failure occurred.
8.5.2 Manual Span Upgrades
Manual span upgrades are mainly provided as error recovery for the Span Upgrade Wizard, but they can be used to perform span upgrades. You can perform a manual span upgrade on a 1+1 protection group, if you are upgrading two ONS 15310-CLs from OC-3 to OC-12.
Downgrading can be performed to back out of a span upgrade. The procedure for downgrading is the same as upgrading except that you provision a lower-rate PPM (OC-3) and install a lower-rate PPM (if you are not using a multi-rate PPM). You cannot downgrade if circuits exist on the STSs that will be removed (the higher STSs).