Table Of Contents
Cisco Transport Controller Operation
4.1 CTC Software Delivery Methods
4.1.1 CTC Software Installed on the 15310-CL-CTX Card
4.1.2 CTC Software Installed on the PC or UNIX Workstation
4.3 PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
4.5.4 Print and Export CTC Data
4.7 CE-100T-8 and ML100T-8 Card Reset
4.8 15310-CL-CTX Card Database
Cisco Transport Controller Operation
This chapter describes Cisco Transport Controller (CTC), the Cisco ONS 15310-CL software interface. For CTC set up and login information, refer to the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide.
Chapter topics include:
•
CTC Software Delivery Methods
•
PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
•
CE-100T-8 and ML100T-8 Card Reset
4.1 CTC Software Delivery Methods
ONS 15310-CL provisioning and administration is performed using CTC software. CTC is a Java application that is installed in two locations; CTC is stored on the 15310-CL-CTX card, and it is downloaded to your workstation the first time you log into the ONS 15310-CL with a new software release.
4.1.1 CTC Software Installed on the 15310-CL-CTX Card
CTC software is preloaded on the 15310-CL-CTX cards; therefore, you do not need to install software.
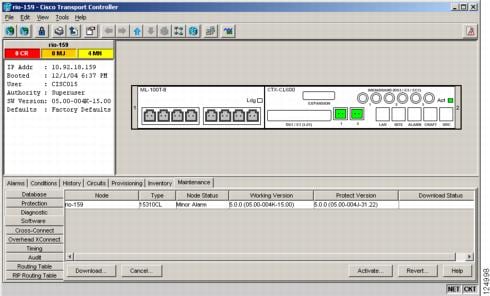
You can view the software versions that are installed on an ONS 15310-CL by selecting the Maintenance > Software tabs in node view (Figure 4-1). Select the tabs in network view to view the software versions installed on all the network nodes.
Figure 4-1 CTC Software Versions, Node View
4.1.2 CTC Software Installed on the PC or UNIX Workstation
CTC software Java Archive (JAR) files are installed on your computer using one of the following methods:
•
The JAR files are downloaded from the 15310-CL-CTX card and installed on your computer automatically the first time you connect to an ONS 15310-CL. Downloading the CTC software files at login ensures that your computer has the same CTC software version as the ONS 15310-CL you are accessing. The CTC JAR files are stored in the temporary directory designated by your computer operating system.
You can use the Delete CTC Cache button to remove files. If the files are deleted, they are downloaded the next time you connect to an ONS 15310-CL. Downloading the CTC JAR files may take 1-2 minutes, or 45-50 minutes, depending on the bandwidth of the connection between your workstation and the ONS 15310-CL. JAR files downloaded from a modem or a data communication channel (DCC) network link will require more time than JAR files downloaded over a LAN connection.
•
You can install the ONS 15310-CL JAR files on your computer using the CTC setup wizard provided on the CTC software or documentation CDs. Installing the JAR files with the setup wizard eliminates the need to wait for the files to download the first time you log into the ONS 15310-CL. In addition, you can manage ONS 15310-CL nodes that are added to networks with ONS nodes running older software releases. After you install the ONS 15310-CL JAR files, you can log into an ONS 15454 running the earlier software release and manage the ONS 15310-CL nodes. However, if you use the Delete CTC Cache function, you must reinstall the JAR files from the CD.
4.2 CTC Installation Overview
To connect to an ONS 15310-CL using CTC, enter the ONS 15310-CL IP address in the URL field of Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer. After connecting to an ONS 15310-CL, the following events occur automatically:
1.
The CTC launcher applet downloads from the 15310-CL-CTX card to your computer.
2.
The launcher determines whether your computer has a CTC release matching the release on the 15310-CL-CTX card.
3.
If the computer does not have CTC installed, or if the installed release is older than the 15310-CL-CTX card version, the launcher downloads the CTC program files from the 15310-CL-CTX card.
4.
The launcher starts CTC. The CTC session is separate from the web browser session, so the web browser is no longer needed.
5.
You should always log into nodes having the latest software release unless run the CTC setup wizard and install the ONS 15310-CL Java Archive (JAR) client software files on your computer. If the JAR files are installed on your computer, you can log into ONS 15454s running Release 4.1 or 4.6 to manage ONS 15310-CL nodes that are connected by DCCs to the ONS 15454s.
Each ONS 15310-CL can handle up to five concurrent CTC sessions. CTC performance can vary, depending upon the volume of activity in each session, network bandwidth, and 15310-CL-CTX card load.
Note
You can also use TL1 commands to communicate with the Cisco ONS 15310-CL through VT100 terminals and VT100 emulation software, or you can Telnet to an ONS 15310-CL using TL1 port 3083. Refer to the Cisco ONS SONET TL1 Command Guide for a comprehensive list of TL1 commands.
4.3 PC and UNIX Workstation Requirements
To use CTC in the ONS 15310-CL, your computer must have a web browser with the correct Java Runtime Environment (JRE) installed for the software release in use. The correct JRE for each CTC software release is included on the Cisco ONS 15310-CL software CD and the ONS 15310-CL documentation CD. Table 4-1 lists the requirements for PCs and UNIX workstations. In addition to the JRE, the Java plug-in is included on the ONS 15310-CL software CD and the ONS 15310-CL documentation CD.
Note
To avoid network performance issues, Cisco recommends managing a maximum of 50 nodes concurrently with CTC. The 50 nodes can be on a single DCC or split across multiple DCCs. Cisco does not recommend running multiple CTC sessions when managing two or more large networks.
To manage more than 50 nodes, Cisco recommends using Cisco Transport Manager (CTM). If you do use CTC to manage more than 50 nodes, you can improve performance by adjusting the heap size; see the "General Troubleshooting" chapter of the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Troubleshooting Guide. You can also create login node groups; see the "Connect the PC and Log Into the GUI" chapter of the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide.4.4 ONS 15310-CL Connection
You can connect to the ONS 15310-CL in multiple ways. You can connect your PC directly to the ONS 15310-CL (local craft connection) using the CRAFT port on the front of the ONS 15310-CL, or by connecting your PC to a hub or switch that is connected to the LAN port on the front of the ONS 15310-CL. You can connect to the ONS 15310-CL through a LAN or modem, and you can establish TL1 connections from a PC or TL1 terminal. Table 4-2 lists the ONS 15310-CL connection methods and requirements.
4.5 CTC Window
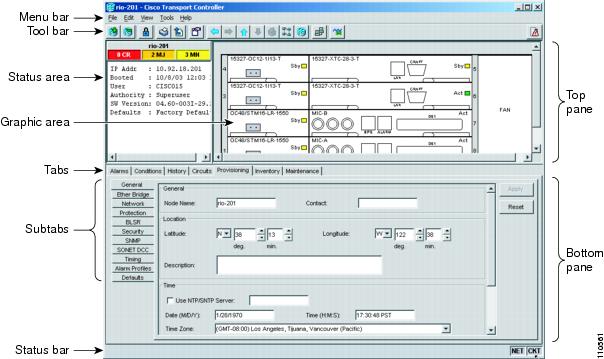
The CTC window appears after you log into an ONS 15310-CL. Figure 4-2 shows an example of the CTC window. The window includes a menu bar, toolbar, and a top and bottom pane. The top pane provides status information about the selected objects and a graphic of the current view. The bottom pane provides tabs and subtabs to view ONS 15310-CL information and perform ONS 15310-CL provisioning and maintenance. From this window you can display three ONS 15310-CL views: network, node, and card.
Figure 4-2 Node View (Default Login View) Example
4.5.1 Node View
Node view, shown in Figure 4-2, is the first view that appears after you log into an ONS 15310-CL. The login node is the first node shown, and it is the "home view" for the session. Node view allows you to view and manage one ONS 15310-CL node. The status area shows the node name; IP address; session boot date and time; number of Critical (CR), Major (MJ), and Minor (MN) alarms; the name of the current logged-in user; the security level of the user; software version; and the network element default setup.
4.5.1.1 CTC Card Colors
The graphic area of the CTC window depicts the ONS 15310-CL shelf assembly. The colors of the cards in the graphic reflect the real-time status of the physical card and slot (Table 4-3).
The port color in both card and node view indicates the port service state. Table 4-4 lists the port colors and their service states. For more information about port service states, see Appendix B, "Administrative and Service States."
Table 4-4 Node View Card Port Colors and Service States
Cyan (blue)
OOS-MA,LPBK
(Out-of-Service and Management, Loopback) Port is in a loopback state. On the card in node view, a line between ports indicates that the port is in terminal or facility loopback (see Figure 4-3 and Figure 4-4). Traffic is carried and alarm reporting is suppressed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command.
Cyan (blue)
OOS-MA,MT
(Out-of-Service and Management, Maintenance) Port is out-of-service for maintenance. Traffic is carried and loopbacks are allowed. Alarm reporting is suppressed. Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. Use OOS-MA,MT for testing or to suppress alarms temporarily. Change the state to IS-NR, OOS-MA,DSBLD, or OOS-AU,AINS when testing is complete.
Gray
OOS-MA,DSBLD
(Out-of-Service and Management, Disabled) The port is out-of-service and unable to carry traffic. Loopbacks are not allowed in this service state.
Green
IS-NR
(In-Service and Normal) The port is fully operational and performing as provisioned. The port transmits a signal and displays alarms; loopbacks are not allowed.
Violet
OOS-AU,AINS
(Out-of-Service and Autonomous, Automatic In-Service) The port is out-of-service, but traffic is carried. Alarm reporting is suppressed. The node monitors the ports for an error-free signal. After an error-free signal is detected, the port stays in OOS-AU,AINS state for the duration of the soak period. After the soak period ends, the port service state changes to IS-NR.
Raised fault conditions, whether or not their alarms are reported, can be retrieved on the CTC Conditions tab or by using the TL1 RTRV-COND command. The AINS port will automatically transition to IS-NR when a signal is received for the length of time provisioned in the soak field.
Figure 4-3 Terminal Loopback Indicator
Figure 4-4 Facility Loopback Indicator
Table 4-5 lists the card statuses.
Table 4-5 Node View Card Statuses
Stby
Card is in standby.
Act
Card is active.
NP
Card is not present.
Mis
Card is mismatched.
Ldg
Card is resetting.
4.5.1.2 Node View Card Shortcuts
If you move your mouse over cards in the graphic, popups display additional information about the card including the card type; card status (active or standby); the type of alarm, such as Critical, Major, and Minor (if any); and the alarm profile used by the card. Right-click a card to reveal a shortcut menu, which you can use to open, reset, or delete the card. Right-click a card slot to preprovision it before installing the card.
4.5.1.3 Node View Tabs
Table 4-6 lists the tabs and subtabs available in the node view.
Table 4-6 Node View Tabs and Subtabs
Alarms
Lists current alarms (CR, MJ, MN) for the node and updates them in real time.
—
Conditions
Displays a list of standing conditions on the node.
—
History
Provides a history of node alarms including date, type, and severity of each alarm. The Session subtab displays alarms and events for the current session. The Node subtab displays alarms and events retrieved from a fixed-size log on the node.
Session, Node
Circuits
Creates, deletes, edits, and maps circuits.
Circuits, Rolls
Provisioning
Provisions the ONS 15310-CL node.
General, Network, OSI, Protection, Security, SNMP, Comm Channels, Timing, Alarm Profiles, Defaults
Inventory
Provides inventory information (part number, serial number, Common Language Equipment Identification [CLEI] codes) for cards installed in the node. Allows you to delete and reset cards, and to change card service state. For more information on card service states, see Appendix B, "Administrative and Service States."
—
Maintenance
Performs maintenance tasks for the node.
Database, OSI, Protection, Software, Cross-Connect, Overhead XConnect, Diagnostic, Timing, Audit, RIP Routing Table, Routing Table,
4.5.2 Network View
Network view allows you to view and manage ONS 15310-CL nodes that have DCC connections to the node that you logged into and any login node groups you have selected. Nodes with DCC connections to the login node will not display if you selected Disable Network Discovery on the Login dialog box.
The graphic area displays a background image with colored ONS 15310-CL icons. A Superuser can set up the logical network view feature, which enables each user to see the same network view. The icon colors indicate the node status (Table 4-7).
The lines show DCC connections between the nodes. DCC connections can be green (active) or gray (fail). The lines can also be solid (circuits can be routed through this link) or dashed (circuits cannot be routed through this link).
There are four possible combinations for the appearance of DCCs: green/solid, green/dashed, gray/solid, and gray/dashed. DCC appearance corresponds to the following states: active/routable, active/nonroutable, failed/routable, or failed/nonroutable. Circuit provisioning uses active/routable links. Selecting a node or span in the graphic area displays information about the node and span in the status area.
The color of a node in network view indicates the node alarm status. Table 4-7 lists the node colors shown in network view.
Table 4-8 lists the tabs and subtabs available in the network view.
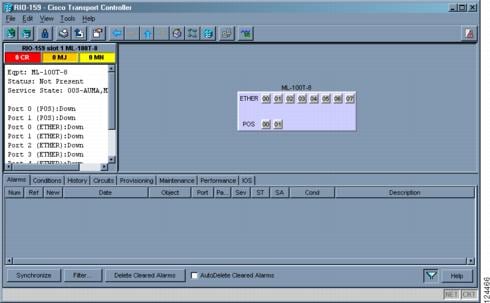
4.5.3 Card View
Card view provides information about individual ONS 15310-CL cards. Use this view to perform card-specific maintenance and provisioning (Figure 4-5). A graphic showing the ports on the card appears in the graphic area. The status area provides the node name, slot, number of alarms, card type, equipment type, and either the card status (active or standby), card service state if the card is present, or port service state (Table 4-4). The information that appears and the actions you can perform depend on the card.
Figure 4-5 CTC Card View Showing an ML100T-8 Card
Table 4-9 shows the tabs and subtabs available in card view. The subtabs, fields, and information shown under each tab depend on the card type selected.
4.5.4 Print and Export CTC Data
You can use the File > Print or File > Export options to print or export CTC provisioning information for record keeping or troubleshooting. The functions can be performed in card, node, or network views. The File > Print function sends the data to a local or network printer. File > Export exports the data to a file where it can be imported into other computer applications, such as spreadsheets and database management programs.
Whether you choose to print or export data, you can choose from the following options:
•
Entire frame—Prints or exports the entire CTC window including the graphical view of the card, node, or network. This option is available for all windows.
•
Tabbed view—Prints or exports the lower half of the CTC window containing tabs and data. The printout includes the selected tab (on top) and the data shown in the tab window. For example, if you print the History window tabbed view, you print only history items appearing in the window. This option is available for all windows.
•
Table Contents—Prints CTC data in table format without graphical representations of shelves, cards, or tabs. This option does not apply to all windows; refer to the print task in the Cisco ONS 15310-CL Procedure Guide for specifics.
•
The Table Contents option prints all the data contained in a table with the same column headings. For example, if you print the History window Table Contents view, you print all data included in the table whether or not items appear in the window.
4.6 15310-CL-CTX Card Reset
You can reset the ONS 15310-CL card by using the hard-reset or soft-reset commands in CTC. A soft reset reboots the 15310-CL-CTX card and reloads the operating system and the application software. A hard reset temporarily removes power from the 15310-CL-CTX card and clears all buffer memory. Before you hard-reset a card, the card must be put in standby mode by completing a soft-reset.
From the node view, select a card and right-click to open a menu with the hard-reset and soft-reset commands. Soft resets do not impact traffic, however hard resets are service affecting. A card must be in the Out-of-Service and Management, Maintenance (OOS-MA,MT) service state before you can perform a hard reset.
4.7 CE-100T-8 and ML100T-8 Card Reset
You can reset the CE-100T-8 and ML100T-8 cards by using the hard-reset or soft-reset commands in CTC. A soft reset reboots the card and reloads the operating system and the application software. A hard reset temporarily removes power from the card and clears all buffer memory.
From the node view, select a card and right-click to open a menu with the hard-reset and soft-reset commands. A card must be in the Out-of-Service and Management, Maintenance (OOS-MA,MT) service state before you can perform a hard reset.
4.8 15310-CL-CTX Card Database
You can store a back-up version of the database on the workstation running CTC. This operation should be part of a regular ONS 15310-CL maintenance program performed at approximately weekly intervals, and should also be completed when preparing an ONS 15310-CL for a pending natural disaster, such as a flood.
Note
The following parameters are not backed up and restored: node name, IP address, mask and gateway, and Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) port. If you change the node name and then restore a backed up database with a different node name, the circuits will map to the new node name. Cisco recommends keeping a record of the old and new node names.
4.9 Software Revert
When you click the Activate button after a software upgrade, the 15310-CL-CTX copies the current working database and saves it in a reserved location in the 15310-CL-CTX flash memory. If you later need to revert to the original working software load from the protect software load, the saved database installs automatically. You do not need to restore the database manually or recreate circuits.
The revert feature is useful if a maintenance window closes while you are upgrading CTC software. You can revert to the standby software load without losing traffic. When the next maintenance window opens, complete the upgrade and activate the new software load.
Circuits that were created and provisioning that was performed after a software load is activated (upgraded to a higher release) do not reinstate with a revert. The database configuration at the time of activation is reinstated after a revert. This does not apply to maintenance reverts (for example 6.0.1 to 6.0.0), because maintenance releases use the same database.