Table Of Contents
Information About PPPoE Client
PPPoE Client Support on ATM PVCs and Ethernet Interfaces
PPPoE Client Session Initiation
Benefits of the PPPoE Client Feature
How to Configure a PPPoE Client
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T
Enabling PPPoE in a VPDN Group
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
Configuring the Dialer Interface
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
Configuring the Dialer Interface
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Configuration Examples for PPPoE Client
PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T: Examples
PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases: Example
PPP over Ethernet Client
The PPP over Ethernet Client feature provides PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client support on routers on customer premises.
History for the PPP over Ethernet Client Feature
12.2(2)T
This feature was introduced.
12.2(13)T
PPPoE client functionality was separated from VPDN functionality, resulting in changes to PPPoE client configuration.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS software image support. Access Cisco Feature Navigator at http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. You must have an account on Cisco.com. If you do not have an account or have forgotten your username or password, click Cancel at the login dialog box and follow the instructions that appear.
Contents
•
Restrictions for PPPoE Client
•
Information About PPPoE Client
•
How to Configure a PPPoE Client
•
Configuration Examples for PPPoE Client
Restrictions for PPPoE Client
For PPPoE over ATM, one PVC will support only one PPPoE client. Multiple PPPoE clients can run concurrently on different PVCs, but each PPPoE client must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
For PPPoE over Ethernet, each PPPoE client must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
Information About PPPoE Client
Before you configure a PPPoE client, you should understand the following concepts:
•
PPPoE Client Network Topology
•
PPPoE Client Support on ATM PVCs and Ethernet Interfaces
•
PPPoE Client Session Initiation
•
Benefits of the PPPoE Client Feature
PPPoE Client Network Topology
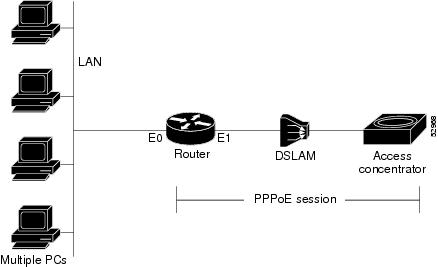
The PPP over Ethernet Client feature provides PPPoE client support on routers on customer premises. Before the introduction of this feature, Cisco IOS software supported PPPoE on the access server side only. Figure 1 shows the typical network topology for PPPoE client deployment.
Figure 1 Typical Network Topology for PPPoE Deployment
PPPoE Client Support on ATM PVCs and Ethernet Interfaces
The PPPoE Client feature provides PPPoE client support on ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs) and Ethernet interfaces. A dialer interface must be used for cloning virtual access.
One ATM PVC will support one PPPoE client. Multiple PPPoE clients can run concurrently on different PVCs, but each PPPoE client must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
Multiple PPPoE client sessions can be configured on an Ethernet interface, but each session must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
PPPoE Client Session Initiation
A PPPoE session is initiated by the PPPoE client. If the session has a timeout or is disconnected, the PPPoE client will immediately attempt to reestablish the session.
The following four steps describe the exchange of packets that occurs when a PPPoE client initiates a PPPoE session:
1.
The client broadcasts a PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation (PADI) packet.
2.
When the access concentrator receives a PADI that it can serve, it replies by sending a PPPoE Active Discovery Offer (PADO) packet to the client.
3.
Because the PADI was broadcast, the host may receive more than one PADO packet. The host looks through the PADO packets it receives and chooses one. The choice can be based on the access concentrator name or on the services offered. The host then sends a single PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) packet to the access concentrator that it has chosen.
4.
The access concentrator responds to the PADR by sending a PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation (PADS) packet. At this point a virtual access interface is created that will then negotiate PPP, and the PPPoE session will run on this virtual access.
If a client does not receive a PADO for a preceding PADI, the client sends out a PADI at predetermined intervals. That interval length is doubled for every successive PADI that does not evoke a response, until the interval reaches a configured maximum.
If PPP negotiation fails or the PPP line protocol is brought down for any reason, the PPPoE session and the virtual access will be brought down. When the PPPoE session is brought down, the client waits for a predetermined number of seconds before trying again to establish a PPPoE.
Benefits of the PPPoE Client Feature
PPPoE is a commonly used application in the deployment of digital subscriber lines (DSL). The PPP over Ethernet Client feature expands PPPoE functionality by providing support for PPPoE on the client as well as on the server.
How to Configure a PPPoE Client
This section contains the following procedures:
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T
Perform the following tasks to configure a PPPoE client in releases prior to Cisco IOS release 12.2(13)T:
•
Enabling PPPoE in a VPDN Group
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
•
Configuring the Dialer Interface
•
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
•
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Enabling PPPoE in a VPDN Group
Perform this task to enable PPPoE in a virtual private dial-up network (VPDN) group.
Restrictions
This task applies only to releases prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
vpdn enable
4.
vpdn-group name
5.
request-dialin
6.
protocol pppoe
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
Perform this task to configure a PPPoE client on an ATM PVC.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface atm number
4.
pvc [name] vpi/vci
5.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
DETAILED STEPS
Note
If commands are added to the PVC configuration after the PPPoE client session is established, the session is automatically terminated and reestablished.
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
Perform this task to configure a PPPoE client on an Ethernet interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface ethernet number
4.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Dialer Interface
Perform this task to configure the dialer interface to be used for cloning on the PVC.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface dialer number
4.
mtu bytes
5.
ip address negotiated
6.
dialer pool number
7.
dialer-group group-number
DETAILED STEPS
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
Perform this task to clear PPPoE client sessions.
Restrictions
This task applies only to releases prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
clear vpdn tunnel pppoe
DETAILED STEPS
Note
To permanently terminate a PPPoE client session, use the no pppoe-client dial-pool-number command in interface configuration mode or interface-atm-vc configuration mode.
Verifying the PPPoE Client
Perform this task to verify PPPoE client configuration.
Prerequisites
This task assumes that the PPPoE client has been configured.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show vpdn
3.
show vpdn session packet
4.
show vpdn session all
5.
show vpdn tunnel
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Perform this task to troubleshoot the PPPoE client.
Restrictions
This task applies only to releases prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
debug vpdn pppoe-data
3.
debug vpdn pppoe-errors
4.
debug vpdn pppoe-events
5.
debug vpdn pppoe-packets
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring a PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases
Perform the following tasks to configure a PPPoE client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T or later releases:
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
•
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
•
Configuring the Dialer Interface
•
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
•
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an ATM PVC
Perform this task to configure a PPPoE client on an ATM PVC.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface atm number
4.
pvc [name] vpi/vci
5.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
DETAILED STEPS
Note
If commands are added to the PVC configuration after the PPPoE client session is established, the session is automatically terminated and reestablished.
Configuring a PPPoE Client on an Ethernet Interface
Perform this task to configure a PPPoE client on an Ethernet interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface ethernet number
4.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring the Dialer Interface
Perform this task to configure the dialer interface to be used for cloning on the PVC.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
configure terminal
3.
interface dialer number
4.
mtu bytes
5.
ip address negotiated
6.
dialer pool number
7.
dialer-group group-number
DETAILED STEPS
Clearing PPPoE Client Sessions
Perform this task to clear PPPoE client sessions.
Restrictions
This task applies only to Cisco IOS release 12.2(13)T and later releases.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
clear pppoe {interface type number [vc {[vpi/]vci | vc-name}] | rmac mac-address | all}
DETAILED STEPS
Note
To permanently terminate a PPPoE client session, use the no pppoe-client dial-pool-number command in interface configuration mode or interface-atm-vc configuration mode.
Verifying the PPPoE Client
Perform this task to verify PPPoE client configuration.
Prerequisites
This task assumes that the PPPoE client has been configured.
Restrictions
This task applies only to Cisco IOS release 12.2(13)T and later releases.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
show pppoe session [all | packets]
DETAILED STEPS
Troubleshooting PPPoE Client Sessions
Perform this task to troubleshoot the PPPoE client.
Prerequisites
This task applies only to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and later releases.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.
enable
2.
debug pppoe {data | errors | events | packets}
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for PPPoE Client
This section contains the following examples:
•
PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T: Examples
•
PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases: Example
PPPoE Client in Releases Prior to Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T: Examples
In the following example, a PPPoE client is configured on a PVC on ATM interface 0. The PPPoE client will use dialer interface 1 as its virtual access interface.
vpdn enablevpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol pppoe!interface atm0pvc 1/100pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1!interface dialer 1ip address negotiateddialer pool 1dialer-group 1!In the following example, two PPPoE client sessions are configured on an Ethernet interface. Each PPPoE client will use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
vpdn enablevpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol pppoe!interface ethernet1/1pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1pppoe-client dial-pool-number 2!interface dialer 1ip address negotiateddialer pool 1dialer-group 1!interface dialer 2ip address negotiateddialer pool 2dialer-group 2PPPoE Client in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(13)T and Later Releases: Example
The following example shows how to configure a PPPoE client on an Ethernet interface. Note that in Releases 12.2(13)T and later it is not necessary to configure a global VPDN group before configuring the PPPoE client.
interface Ethernet 0pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1interface Dialer 1ip address negotiateddialer pool 1mtu 1492Additional References
The following sections provide references related to PPPoE client configuration.
Related Documents
VPDN configuration
Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
VPDN commands
Cisco IOS Dial Technologies Command Reference, Release 12.2
PPPoE configuration
Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Configuration Guide, Release 12.2
PPPoE commands
Cisco IOS Wide-Area Networking Command Reference, Release 12.2
Standards
MIBs
RFCs
Technical Assistance
Command Reference
This section documents new and modified commands only. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.2 command reference publications.
•
pppoe-client dial-pool-number
clear vpdn tunnel
To shut down a specifiedvirtual private dial-up network (VPDN) tunnel and all sessions within the tunnel, use the clear vpdn tunnel command in privileged EXEC mode.
L2TP or PPTP Tunnels
clear vpdn tunnel {pptp | l2tp} {all | hostname remote-name [local-name] | id local-id | ip local-ip-address | ip remote-ip-address}
L2F Tunnels
clear vpdn tunnel l2f {all | hostname nas-name hgw-name | id local-id | ip local-ip-address | ip remote-ip-address}
Syntax Description
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
Usage Guidelines
Manual termination of a VPDN tunnel results in the immediate shutdown of the specified VPDN tunnel and all sessions within that tunnel, resulting in a sudden disruption of VPDN services.
You can shut down VPDN tunnels more gradually by issuing the vpdn softshut command, which prevents the establishment of new VPDN sessions in all VPDN tunnels that terminate on the device. Existing VPDN sessions are not affected.
A manually terminated VPDN tunnel can be restarted immediately when a user logs in. Manually terminating and restarting a VPDN tunnel while VPDN event logging is enabled can provide useful troubleshooting information about VPDN session establishment. VPDN event logging is enabled by issuing the vpdn logging command.
Examples
The following example clears all L2TP tunnels connecting to a remote peer named NAS1:
Router# clear vpdn tunnel l2tp hostname NAS1The following example clears all PPTP tunnels connecting the devices with the hostnames NAS3 and tun1:
Router# clear vpdn tunnel pptp NAS3 hostname tun1The following example clears all L2F tunnels originating from the specified IP address:
Router# clear vpdn tunnel l2f ip 10.1.1.1Related Commands
vpdn logging
Enables the logging of generic VPDN events.
vpdn softshut
Prevents new sessions from being established on a VPDN tunnel without disturbing existing sessions.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number
To configure a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client and to specify dial-on-demand routing (DDR) functionality, use the pppoe-client dial-pool-number command in either interface configuration mode or ATM virtual circuit configuration mode. To disable any configured functionality, use the no form of this command.
pppoe-client dial-pool-number number [dial-on-demand]
no pppoe-client dial-pool-number number [dial-on-demand]
Syntax Description
number
Unique number of a dial group configured with the dialer-group dialer interface command.
dial-on-demand
(Optional) Enables DDR functionality for the PPPoE connection.
Defaults
A PPPoE client is not configured, and DDR functionality is disabled.
Command Modes
Interface configuration
ATM virtual circuit configurationCommand History
Usage Guidelines
One permanent virtual circuit (PVC) will support only one PPPoE client. Multiple PPPoE clients can run concurrently on different permanent virtual circuits (PVCs), but each PPPoE client must use a separate dialer interface and a separate dialer pool.
Use this command to configure dial-on-demand routing (DDR) interesting traffic control list functionality of the dialer interface with a PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) client. When the DDR functionality is configured for this command, the following DDR commands must also be configured: dialer-group, dialer hold-queue, dialer idle-timeout, and dialer-list.
Tips for Configuring the Dialer Interface
If you are configuring a hard-coded IP address under the dialer interface, you can configure a default IP route using the ip route command as follows:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dialer1But if you are configuring a negotiated IP address using the ip address negotiated command under the dialer interface, you must configure a default IP route using the ip route command as follows:
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 dialer1 permanentThe reason is that the dialer interface will lose its IP address when a PPPoE session is brought down (even if the dialer does not go down), and hence the route removal routine will take effect and remove all IP routes pointed at the dialer interface, even the default IP route. Although the default IP route will be added back about one minute later by IP background processes, you may risk losing incoming packets during the interval.
Examples
PPPoE Client DDR Idle-Timer on an Ethernet Interface
The following example shows how to configure the PPPoE client DDR idle-timer on an Ethernet interface and includes the required DDR commands:
!vpdn enableno vpdn logging!vpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol pppoe!interface Ethernet1pppoe enablepppoe-client dial-pool-number 1 dial-on-demand!interface Dialer1ip address negotiatedip mtu 1492encapsulation pppdialer pool 1dialer idle-timeout 180 eitherdialer hold-queue 100dialer-group 1!dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit!ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer1PPPoE client DDR Idle-Timer on an ATM PVC
The following example shows how to configure the PPPoE client DDR idle-timer on an ATM PVC interface and includes the required DDR commands:
!vpdn enableno vpdn logging!vpdn-group 1request-dialinprotocol pppoe!interface ATM2/0pvc 2/100pppoe-client dial-pool-number 1 dial-on-demand!interface Dialer1ip address negotiatedip mtu 1492encapsulation pppdialer pool 1dialer idle-timeout 180 eitherdialer hold-queue 100dialer-group 1!dialer-list 1 protocol ip permit!ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Dialer1Related Commands

 Feedback
Feedback