Contents
- Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Restrictions for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Information About Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting Network Topology
- Benefits of Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Per IP Subscriber Triggered RADIUS Accounting Behavior
- How to Configure Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Configuring Method Lists for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Configuration Examples for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Subinterface RADIUS Accounting Configuration Example
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
The Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting feature enables system administrators to track IP session activity on a per-subscriber basis and periodically extract subscriber accounting records. Transactions between the client and the RADIUS accounting server are authenticated via an Access Client module that maintains per-subscriber accounting statistics.
Per IP Subscriber RADIUS Accounting works with DHCP IP address assignment on Cisco 7600 series routers only, and it improves the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) of broadband service delivery. Subscribers are attributed a unique AAA ID in addition to the unique ID created by DHCP in order to process secure START and STOP accounting messages and allow them to abstract accounting information in a client-server environment.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Restrictions for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Information About Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- How to Configure Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Configuration Examples for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- You must configure accounting on a subset of RADIUS servers to which subscriber accounting statistics will be exported, as defined by the aaa accountingcommand.
- You must configure the number of IP address assignment leases offered to DHCP clients to only one per subscriber, as defined by the ip dhcp limit lease per interface 1 command.
Restrictions for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- The Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting feature is enabled only for subscribers operating with Access Type interfaces on a Cisco 7600 series Broadband Remote Access Server (B-RAS).
- This feature does not support the collection of IP statistics from each source IP address. The feature collects IP statistics for each subinterface rather than each subscriber, and it is triggered only if the command to allow one IP address assignment via DHCP is configured.
Information About Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
- Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting Network Topology
- Per IP Subscriber Triggered RADIUS Accounting Behavior
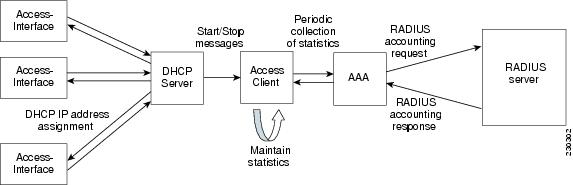
Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting Network Topology
Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting is implemented in a distributed networking environment, based on the following client-server components:
- Access Interface--Used by subscribers to operate on a Cisco 7600 router.
- DHCP Server--Grants permission to the DHCP client to use a particular IP address for a specified lease time.
- AAA Server--Transmits secure START and STOP accounting messages.
After the periodic timer is configured on the unit under test (UUT), the AAA module on the UUT sends an interim periodic update to the RADIUS server.
The figure below shows how the Access Client, referred to as the âaaa-access-clientâ module, is initialized to serve as a client of the RADIUS accounting server. The module is independent of existing DHCP RADIUS Accounting modules.
The Access Client comprises two sub-modules that enable improved IP session awareness, tracking, and reporting functionality:
- Access-Subscriber Management module (Access-Acct-Mgmt): Invoked by a successful DHCP IP assignment, this sub-module generates a unique AAA ID for each subscriber that combines with the DHCP unique ID to track an accounting session.
- Access-Subscriber Accounting Management (Access-Acct-Update): Invoked by the AAA server, this sub-module collects subscriber statistics and periodically reports on the accounting session.
Benefits of Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
IP Session Awareness and Security
RADIUS accounting provides information about subscribersâ network connections and usage in the form of accounting records.
The Access Client passes per-subscriber accounting statistics to the designated server, with a secure unique AAA ID. The periodic reporting of IP session activity gives system administrators the accounting information they need to make informed security, billing, and resource allocation decisions.
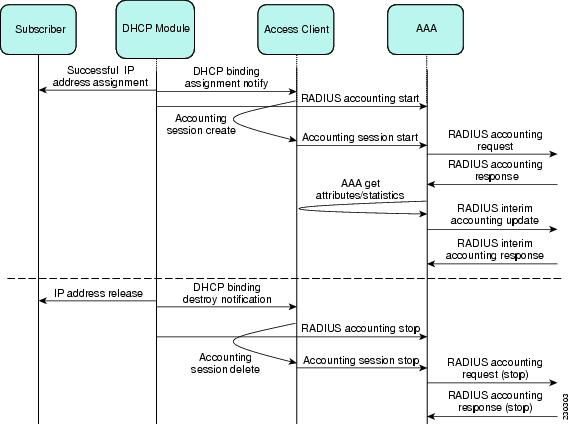
Per IP Subscriber Triggered RADIUS Accounting Behavior
When a client with an Access Type of interface is configured for Per IP Subscriber RADIUS Accounting, the statistics collection and reporting mechanism can be invoked by the DHCP module. A successful DHCP IP assignment or release triggers three types of accounting events via the Access Client module:
- RADIUS accounting start: An Accounting Start packet, ACCT_START, is sent to the accounting server to flag the start of service delivery, the type of service being delivered, and the user it is being delivered to.
- RADIUS accounting interim-update: An Accounting Interim Update packet, ACCT_UPDATE, is sent to the accounting server to flag an ongoing client association and IP session activity.
- RADIUS accounting stop: An Accounting Stop packet, ACCT_STOP, is sent to the accounting server to flag the end of service delivery, the type of service that was delivered and optional statistics such as elapsed time, and input and output packets.
Accounting requests, for any packet type, are submitted to the RADIUS accounting server via the network, and are acknowledged in these forms:
- RADIUS Accounting Response (START)
- RADIUS Interim Accounting Response
- RADIUS Accounting Response (STOP)
The figure below shows the AAA Access Client process flow and how the client interacts with the required modules.
How to Configure Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
Configuring Method Lists for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
Each subscriber is configured on a per-interface basis. To invoke the Access Client and trigger the statistics collection mechanism on a subinterface, you must specify RADIUS as the accounting method and define a backup system for accounting in case the initial method fails. A method list is a named list describing the accounting methods to be queried in sequence.
Perform this task to configure a named method list for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting.
DETAILED STEPS
Configuration Examples for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
Subinterface RADIUS Accounting Configuration Example
In the following example, the aaa accounting command for periodic RADIUS accounting is issued in the context of an IP address assignment via DHCP. A named method list is not explicitly defined, and the default method list automatically applies to the subinterface. If no method list is defined, no accounting takes place.
configure terminal aaa new-model radius-server host 75.0.1.1 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 key lab radius-server key lab ! aaa accounting network default start-stop group radius aaa accounting update periodic 1 end ! configure terminal ip dhcp pool pool1 network 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 lease 0 0 3 ! configure terminal interface Gigabitethernet 1/0/1.2 access encapsulation dot1q 102 ip address 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 accounting dhcp source-ip aaa list default end
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting feature.
MIBs
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting |
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting |
12.2(33)SRB |
The Per IP Subscriber DHCP Triggered RADIUS Accounting feature enables system administrators to track IP session activity on a per-subscriber basis and periodically extract subscriber accounting records. In 12.2(33)SRB, this feature was introduced on the Cisco 7600 router. The following command was introduced by this feature: accounting dhcp source-ip aaa list. |
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.

 Feedback
Feedback