Release Notes for Cisco ASDM, 7.16(x)
This document contains release information for Cisco ASDM Version 7.16(x) for the Cisco ASA series.
Important Notes
-
ASDM signed-image support in 9.16(3.19)/7.18(1.152) and later—The ASA now validates whether the ASDM image is a Cisco digitally signed image. If you try to run an older ASDM image with an ASA version with this fix, ASDM will be blocked and the message “%ERROR: Signature not valid for file disk0:/<filename>” will be displayed at the ASA CLI. ASDM release 7.18(1.152) and later are backwards compatible with all ASA versions, even those without this fix. (CSCwb05291, CSCwb05264)
-
SNMPv3 users using MD5 hashing and DES encryption are no longer supported, and the users will be removed when you upgrade to 9.16(1)—Be sure to change any user configuration to higher security algorithms using the snmp-server user command before you upgrade.
-
SSH host key action required in 9.16(1)—In addition to RSA, we added support for the EDDSA and ECDSA host keys for SSH. The ASA tries to use keys in the following order if they exist: EDDSA, ECDSA, and then RSA. When you upgrade to 9.16(1), the ASA will fall back to using the existing RSA key. However, we recommend that you generate higher-security keys as soon as possible using the crypto key generate {eddsa | ecdsa} command. Moreover, if you explicitly configure the ASA to use the RSA key with the ssh key-exchange hostkey rsa command, you must generate a key that is 2048 bits or higher. For upgrade compatibility, the ASA will use smaller RSA host keys only when the default host key setting is used. RSA support will be removed in a later release.
-
In 9.16 and later, certificates with RSA keys are not compatible with ECDSA ciphers—When you use the ECDHE_ECDSA cipher group, configure the trustpoint with a certificate that contains an ECDSA-capable key.
-
RSA keys using that are smaller than 2048 cannot be generated in 9.16(1)—You can no longer generate RSA keys smaller than 2048 using the crypto key generate rsa command.
For SSH, existing smaller keys can continue to be used after upgrading, but we recommend that you upgrade to a larger size, or to a higher security key type.
For other features, existing certificates signed with RSA key sizes smaller than 2048 cannot be used in ASA 9.16.1 and later. You can use the crypto ca permit-weak-crypto command to allow use of existing smaller keys, but even with this command, you cannot generate new smaller RSA keys..
-
ssh version command removed in 9.16(1)—This command has been removed. Only SSH version 2 is supported.
-
SAMLv1 feature removed in 9.16(1)—Support for SAMLv1 was removed.
-
No support for DH groups 2, 5, and 24 in 9.16(1)—Support has been removed for the DH groups 2, 5, and 24 in SSL DH group configuration. The ssl dh-group command has been updated to remove the command options group2, group5, and group24.
-
Cisco announces the feature deprecation for Clientless SSL VPN effective with ASA version 9.17(1)—Limited support will continue on releases prior to 9.17(1).
-
No support in ASA 9.15(1) and later for the ASA 5525-X, ASA 5545-X, and ASA 5555-X—ASA 9.14(x) is the last supported version. For the ASA FirePOWER module, the last supported version is 6.6.
-
For the Firepower 1010, invalid VLAN IDs can cause problems—Before you upgrade to 9.15(1) or later, make sure you are not using a VLAN for switch ports in the range 3968 to 4047. These IDs are for internal use only, and 9.15(1) includes a check to make sure you are not using these IDs. For example, if these IDs are in use after upgrading a failover pair, the failover pair will go into a suspended state. See CSCvw33057 for more information.
-
Chacha-poly ciphers—AnyConnect has an updated list of supported cryptographic algorithms: AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client Features, Licenses, and OSs, Release 4.10, which are proposed to the ASA when starting TLS-based VPN traffic.
System Requirements
ASDM requires a computer with a CPU with at least 4 cores. Fewer cores can result in high memory usage.
ASDM Java Requirements
You can install ASDM using Oracle JRE 8.0 (asdm-version.bin) or OpenJRE 1.8.x (asdm-openjre-version.bin).
 Note |
ASDM is not tested on Linux. |
|
Operating System |
Browser |
Oracle JRE |
OpenJRE |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Firefox |
Safari |
Chrome |
|||||||
|
Microsoft Windows (English and Japanese):
|
Yes |
No support |
Yes |
8.0 version 8u261 or later |
1.8
|
||||
|
Apple OS X 10.4 and later |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes (64-bit version only) |
8.0 version 8u261 or later |
1.8 |
||||
ASDM Compatibility Notes
The following table lists compatibility caveats for ASDM.
|
Conditions |
Notes |
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
ASDM Launcher compatibility with ASDM version |
"Unable to Launch Device Manager" error message. If you upgrade to a new ASDM version and then get this error, you may need to re-install the latest Launcher.
|
||
|
Windows Active Directory directory access |
In some cases, Active Directory settings for Windows users may restrict access to program file locations needed to successfully launch ASDM on Windows. Access is needed to the following directories:
If your Active Directory is restricting directory access, you need to request access from your Active Directory administrator. |
||
|
Windows 10 |
"This app can't run on your PC" error message. When you install the ASDM Launcher, Windows 10 might replace the ASDM shortcut target with the Windows Scripting Host path, which causes this error. To fix the shortcut target:
|
||
|
OS X |
On OS X, you may be prompted to install Java the first time you run ASDM; follow the prompts as necessary. ASDM will launch after the installation completes. |
||
|
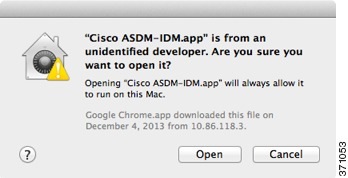
OS X 10.8 and later |
You need to allow ASDM to run because it is not signed with an Apple Developer ID. If you do not change your security preferences, you see an error screen. 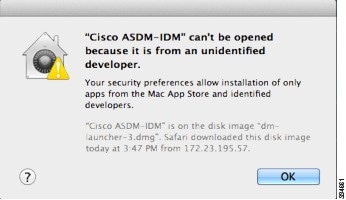
|
||
|
Requires Strong Encryption license (3DES/AES) on ASA
|
ASDM requires an SSL connection to the ASA. You can request a 3DES license from Cisco:
|
||
|
When the ASA uses a self-signed certificate or an untrusted certificate, Firefox and Safari are unable to add security exceptions when browsing using HTTPS over IPv6. See https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=633001. This caveat affects all SSL connections originating from Firefox or Safari to the ASA (including ASDM connections). To avoid this caveat, configure a proper certificate for the ASA that is issued by a trusted certificate authority. |
||
|
If you change the SSL encryption on the ASA to exclude both RC4-MD5 and RC4-SHA1 algorithms (these algorithms are enabled by default), then Chrome cannot launch ASDM due to the Chrome “SSL false start” feature. We suggest re-enabling one of these algorithms (see the pane); or you can disable SSL false start in Chrome using the --disable-ssl-false-start flag according to Run Chromium with flags. |
Install an Identity Certificate for ASDM
When using Java 7 update 51 and later, the ASDM Launcher requires a trusted certificate. An easy approach to fulfill the certificate requirements is to install a self-signed identity certificate.
See Install an Identity Certificate for ASDM to install a self-signed identity certificate on the ASA for use with ASDM, and to register the certificate with Java.
Increase the ASDM Configuration Memory
ASDM supports a maximum configuration size of 512 KB. If you exceed this amount you may experience performance issues. For example, when you load the configuration, the status dialog box shows the percentage of the configuration that is complete, yet with large configurations it stops incrementing and appears to suspend operation, even though ASDM might still be processing the configuration. If this situation occurs, we recommend that you consider increasing the ASDM system heap memory. To confirm that you are experiencing memory exhaustion, monitor the Java console for the "java.lang.OutOfMemoryError" message.
Increase the ASDM Configuration Memory in Windows
To increase the ASDM heap memory size, edit the run.bat file by performing the following procedure.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Go to the ASDM installation directory, for example C:\Program Files (x86)\Cisco Systems\ASDM. |
|
Step 2 |
Edit the run.bat file with any text editor. |
|
Step 3 |
In the line that starts with “start javaw.exe”, change the argument prefixed with “-Xmx” to specify your desired heap size. For example, change it to -Xmx768M for 768 MB or -Xmx1G for 1 GB. |
|
Step 4 |
Save the run.bat file. |
Increase the ASDM Configuration Memory in Mac OS
To increase the ASDM heap memory size, edit the Info.plist file by performing the following procedure.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
Right-click the Cisco ASDM-IDM icon, and choose Show Package Contents. |
|
Step 2 |
In the Contents folder, double-click the Info.plist file. If you have Developer tools installed, it opens in the Property List Editor. Otherwise, it opens in TextEdit. |
|
Step 3 |
Under , change the string prefixed with “-Xmx” to specify your desired heap size. For example, change it to -Xmx768M for 768 MB or -Xmx1G for 1 GB. 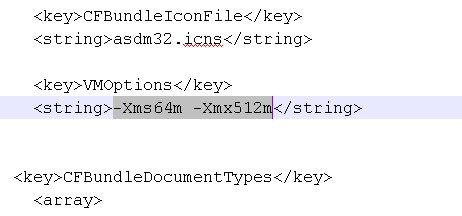 |
|
Step 4 |
If this file is locked, you see an error such as the following: 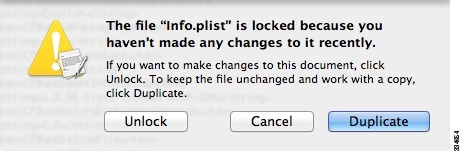 |
|
Step 5 |
Click Unlock and save the file. If you do not see the Unlock dialog box, exit the editor, right-click the Cisco ASDM-IDM icon, choose Copy Cisco ASDM-IDM, and paste it to a location where you have write permissions, such as the Desktop. Then change the heap size from this copy. |
ASA and ASDM Compatibility
For information about ASA/ASDM software and hardware requirements and compatibility, including module compatibility, see Cisco ASA Compatibility.
VPN Compatibility
For VPN compatibility, see Supported VPN Platforms, Cisco ASA 5500 Series.
New Features
This section lists new features for each release.
 Note |
New, changed, and deprecated syslog messages are listed in the syslog message guide. |
New Features in ASA 9.16(4)
Released: October 13, 2022
There are no new features in this release.
New Features in ASA 9.16(3)
Released: April 6, 2022
There are no new features in this release.
New Features in ASA 9.16(2)
Released: August 18, 2021
There are no new features in this release.
New Features in ASDM 7.16(1.150)
Released: June 15, 2021
There are no new features in this release.
New Features in ASA 9.16(1)/ASDM 7.16(1)
Released: May 26, 2021
|
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Firewall Features |
|
|
New Section 0 for system-defined NAT rules. |
A new Section 0 has been added to the NAT rule table. This section is exclusively for the use of the system. Any NAT rules that the system needs for normal functioning are added to this section, and these rules take priority over any rules you create. Previously, system-defined rules were added to Section 1, and user-defined rules could interfere with proper system functioning. You cannot add, edit, or delete Section 0 rules, but you will see them in show nat detail command output. |
|
The default SIP inspection policy map drops non-SIP traffic. |
For SIP-inspected traffic, the default is now to drop non-SIP traffic. The previous default was to allow non-SIP traffic on ports inspected for SIP. We changed the default SIP policy map to include the no traffic-non-sip command. |
|
Ability to specify the IMSI prefixes to be dropped in GTP inspection. |
GTP inspection lets you configure IMSI prefix filtering, to identify the Mobile Country Code/Mobile Network Code (MCC/MNC) combinations to allow. You can now do IMSI filtering on the MCC/MNC combinations that you want to drop. This way, you can list out the unwanted combinations, and default to allowing all other combinations. We changed the following screens: The Drop option was added to the IMSI Prefix Filtering tab for GTP inspection maps. |
|
Configure the maximum segment size (MSS) for embryonic connections |
You can configure a service policy to set the server maximum segment size (MSS) for SYN-cookie generation for embryonic connections upon reaching the embryonic connections limit. This is meaningful for service policies where you are also setting embryonic connection maximums. New/Modified screens: Connection Settings in the Add/Edit Service Policy wizard. |
|
Improved CPU usage and performance for many-to-one and one-to-many connections. |
The system no longer creates local host objects and locks them when creating connections, except for connections that involve dynamic NAT/PAT and scanning threat detection and host statistics. This improves performance and CPU usage in situations where many connections are going to the same server (such as a load balancer or web server), or one endpoint is making connections to many remote hosts. We changed the following commands: clear local-host (deprecated), show local-host |
|
Platform Features |
|
|
ASAv support for VMware ESXi 7.0 |
The ASAv virtual platform supports hosts running on VMware ESXi 7.0. New VMware hardware versions have been added to the vi.ovf and esxi.ovf files to enable optimal performance and usability of the ASAv on ESXi 7.0. No modified commands. No modified screens. |
|
Intel QuickAssist Technology (QAT) on ASAv |
The ASAv supports hardware crypto acceleration for ASAv deployments that use the Intel QuickAssist (QAT) 8970 PCI adapter. Hardware crypto acceleration for the ASAv using QAT is supported on VMware ESXi and KVM only. No modified commands. No modified screens. |
|
ASAv on OpenStack |
The ASAv virtual platform has added support for OpenStack. No modified commands. No modified screens. |
|
High Availability and Scalability Features |
|
|
Improved PAT port block allocation for clustering on the Firepower 4100/9300 |
The improved PAT port block allocation ensures that the control unit keeps ports in reserve for joining nodes, and proactively reclaims unused ports. To best optimize the allocation, you can set the maximum nodes you plan to have in the cluster using the cluster-member-limit command. The control unit can then allocate port blocks to the planned number of nodes, and it will not have to reserve ports for extra nodes you don't plan to use. The default is 16 nodes. You can also monitor syslog 747046 to ensure that there are enough ports available for a new node. New/Modified screens: field |
|
show cluster history command improvements |
We have added additional outputs for the show cluster history command. New/Modified commands: show cluster history brief , show cluster history latest , show cluster history reverse , show cluster history time |
|
Firepower 1140 maximum contexts increased from 5 to 10 |
The Firepower 1140 now supports up to 10 contexts. |
|
Certificate Features |
|
|
Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST) for certification |
ASA supports certificate enrollment using the Enrollment over Secure Transport (EST). However, you can configure to use EST enrollments only with RSA and ECDSA keys. You cannot use EdDSA keypair for a trustpoint configured for EST enrollment. New/Modified screens: . |
|
Support for new EdDSA key |
The new key option, EdDSA, was added to the existing RSA and ECDSA options. New/Modified screens: . |
|
Command to override restrictions on certificate keys |
Support to use SHA1with RSA Encryption algorithm for certification and support for certificates with RSA key sizes smaller than 2048 were removed. You can use crypto ca permit-weak-crypto command to override these restrictions. New/Modified screens: , , and |
|
Administrative and Troubleshooting Features |
|
|
SSH security improvements |
SSH now supports the following security improvements:
New/Modified screens: |
|
Monitoring Features |
|
|
SNMPv3 Authentication |
You can now use SHA-224 and SHA-384 for user authentication. You can no longer use MD5 for user authentication. You can no longer use DES for encryption. New/Modified screens: |
|
VPN Features |
|
|
Support for IPv6 on Static VTI |
ASA supports IPv6 addresses in Virtual Tunnel Interfaces (VTI) configurations. A VTI tunnel source interface can have an IPv6 address, which you can configure to use as the tunnel endpoint. If the tunnel source interface has multiple IPv6 addresses, you can specify which address to be used, else the first IPv6 global address in the list is used by default. The tunnel mode can be either IPv4 or IPv6, but it must be the same as IP address type configured on VTI for the tunnel to be active. An IPv6 address can be assigned to the tunnel source or the tunnel destination interface in a VTI. |
|
Support for 1024 VTI interfaces per device |
The number of maximum VTIs to be configured on a device has been increased from 100 to 1024. Even if a platform supports more than 1024 interfaces, the VTI count is limited to the number of VLANs configurable on that platform. For example, ASA 5510 supports 100 VLANs, the tunnel count would be 100 minus the number of physical interfaces configured. New/Modified screens: None |
|
Support for DH group 15 in SSL |
Support has been added for DH group 15 for SSL encryption. New/Modified commands: ssl dh-group group15 |
|
Support for DH group 31 for IPsec encryption |
Support has been added for DH group 31 for IPsec encryption. New/Modified commands: set pfs |
|
Support to limit the SA in IKEv2 queue |
Support has been added to limit the number of queues in SA-INIT packets. New/Modified commands: crypto ikev2 limit queue sa_init |
|
Option to clear IPsec statistics |
CLIs have been introduced to clear and reset IPsec statistics. New/Modified commands: clear crypto ipsec stats and clear ipsec stats |
Upgrade the Software
This section provides the upgrade path information and a link to complete your upgrade.
ASA Upgrade Path
To view your current version and model, use one of the following methods:
-
ASDM: Choose .
-
CLI: Use the show version command.
This table provides upgrade paths for ASA. Some older versions require an intermediate upgrade before you can upgrade to a newer version. Recommended versions are in bold.
 Note |
Be sure to check the upgrade guidelines for each release between your starting version and your ending version. You may need to change your configuration before upgrading in some cases, or else you could experience an outage. |
 Note |
For guidance on security issues on the ASA, and which releases contain fixes for each issue, see the ASA Security Advisories. |
 Note |
ASA 9.14 was the final version for the ASA 5525-X, 5545-X, and 5555-X. ASA 9.12 was the final version for the ASA 5512-X, 5515-X, 5585-X, and ASASM. ASA 9.2 was the final version for the ASA 5505. ASA 9.1 was the final version for the ASA 5510, 5520, 5540, 5550, and 5580. |
|
Current Version |
Interim Upgrade Version |
Target Version |
|---|---|---|
|
9.15 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 |
|
9.14 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 |
|
9.13 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 |
|
9.12 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 |
|
9.10 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 |
|
9.9 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 |
|
9.8 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 |
|
9.7 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.6 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.5 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.4 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.3 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.2 |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.16 → 9.15 → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 |
|
9.1(2), 9.1(3), 9.1(4), 9.1(5), 9.1(6), or 9.1(7.4) |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
9.1(1) |
→ 9.1(2) |
Any of the following: → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
9.0(2), 9.0(3), or 9.0(4) |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.6 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
9.0(1) |
→ 9.0(4) |
Any of the following: → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
8.6(1) |
→ 9.0(4) |
Any of the following: → 9.14 → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
8.5(1) |
→ 9.0(4) |
Any of the following: → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
8.4(5+) |
— |
Any of the following: → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) → 9.0(4) |
|
8.4(1) through 8.4(4) |
→ 9.0(4) |
→ 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
8.3 |
→ 9.0(4) |
Any of the following: → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
|
8.2 and earlier |
→ 9.0(4) |
Any of the following: → 9.12 → 9.8 → 9.1(7.4) |
Upgrade Link
To complete your upgrade, see the ASA upgrade guide.
Open and Resolved Bugs
The open and resolved bugs for this release are accessible through the Cisco Bug Search Tool. This web-based tool provides you with access to the Cisco bug tracking system, which maintains information about bugs and vulnerabilities in this product and other Cisco hardware and software products.
 Note |
You must have a Cisco.com account to log in and access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. If you do not have one, you can register for an account. If you do not have a Cisco support contract, you can only look up bugs by ID; you cannot run searches. |
For more information about the Cisco Bug Search Tool, see the Bug Search Tool Help & FAQ.
Open Bugs
This section lists open bugs in each version.
Open Bugs in Version 7.16(1.150)
The following table lists select open bugs at the time of this Release Note publication.
|
Caveat ID Number |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Appliance mode : checksum does not match issue while downloading asa image from CCO |
|
|
ASDM: Need support for MAC in Launcher 1.9.1 |
|
|
Check box not available for disable delete tunnel with no delay in simultaneous connection prempt |
|
|
Cipher changes require in VPN wizard according to 9161/7161 CLIs |
Open Bugs in Version 7.16(1)
The following table lists select open bugs at the time of this Release Note publication.
|
Caveat ID Number |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Appliance mode : checksum does not match issue while downloading asa image from CCO |
|
|
ASDM: Need support for MAC in Launcher 1.9.1 |
|
|
Check box not available for disable delete tunnel with no delay in simultaneous connection prempt |
|
|
Cipher changes require in VPN wizard according to 9161/7161 CLIs |
Resolved Bugs
This section lists resolved bugs per release.
Resolved Bugs in Version 7.16(1.150)
The following table lists select resolved bugs at the time of this Release Note publication.
|
Caveat ID Number |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ASDM session being abruptly terminated when switching between different admin and system contexts |
|
|
SSH cipher (aes128-gcm@openssh.com and chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com) is missing on ASDM GUI |
|
|
ssh key-exchange group options should be disabled in MC mode - User context |
Resolved Bugs in Version 7.16(1)
The following table lists select resolved bugs at the time of this Release Note publication.
|
Caveat ID Number |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ASDM 7.12.2 doesn't send client certificate during SSL handshake |
|
|
ASDM Fails to Launch with error - invalid SHA1 signature file digest for LZMA/LzmaInputStream.class |
|
|
Not able to configure Split tunneling on group policy on ASDM v7.14.1.46 |
|
|
Power over Ethernet dialog has incorrect label for checkbox |
|
|
ASDM creates wrong outside identity NAT rule during creation of connection profile for s2s vpn |
|
|
dns-class inside of DNS Class-Map gets incorrect value |
|
|
Remove the engineID field from ASDM UI - ASA Traceback |
|
|
ASDM - ACL on management can't be added even interface configured with "no management-only" |
|
|
NSF Wait Interval in ASDM OSPF Process Advanced Properties should not be mandatory |
|
|
Unable to edit AnyConnect Custom Attribute Name value |
|
|
Start-up configuration cannot be resotred when using ASDM |
|
|
When you click next to the checkbox in ASDM then the checkbox is selected anyway |
|
|
NSF wait interval warning popup is not showing when configuring wrong value |
|
|
ASDM Display "n/a" for "Peak Usage (KB)" Under Tab "Context Usage" of Memory Status |
|
|
ASA Cluster ASDM real-time log viewer showing same events on Master and Slave |
|
|
ASDM does not recognize SCTP port as per the parser Errors |
End-User License Agreement
For information on the end-user license agreement, go to http://www.cisco.com/go/warranty.
Related Documentation
For additional information on the ASA, see Navigating the Cisco ASA Series Documentation.

 Feedback
Feedback